Abstract
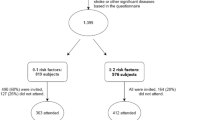
The aim of this article is to investigate the relation of the anti-inflammatory effect of pioglitazone with cardiac autonomic function and metabolic control in diabetic patients. In this prospective open label trial, 36 type 2 diabetic patients (age 60 ± 10, 20 M) without overt cardiovascular disease were randomized to add pioglitazone (30 mg) to their therapy or to continue standard therapy. C-reactive protein (CRP) serum levels, metabolic parameters and cardiac autonomic function (assessed by heart rate variability [HRV] on 24-h ECG Holter monitoring) were measured at baseline and after 3 months. Clinical and laboratory variables were similar in the two groups. No significant changes were observed after 3 months for metabolic and anthropometric parameters, except for a mild increase in HDL levels in the pioglitazone group only (P = 0.04 vs. controls). CRP levels decreased significantly at follow-up in the pioglitazone group (3.2 ± 1.97 vs. 2.37 ± 1.56 mg/l) but not in the control group (3.0 ± 1.92 vs. 3.93 ± 2.14 mg/l; P = 0.003). No differences were found in basal and follow-up HRV variables between the two groups. In type 2 diabetic patients pioglitazone exerts favourable effects on inflammation even after short-term therapy. This effect precedes those on metabolic and anthropometric parameters and is not associated with changes in cardiac autonomic function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- LF:
-
Low frequency amplitude
- HF:
-
High frequency amplitude
- PPAR:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
- SDNN:
-
Standard deviation of NN intervals
- SDNNi:
-
Mean of the standard deviations of NN intervals of all 5 min segments in the recording
- VLF:
-
Very low frequency amplitude
References
Jarvinen HY (2004) Thiazolidinediones. N Engl J Med 351:1106–1118
Dormandy JA, Charbonnel B, Eckland DJ, Erdmann E, Massi-Benedetti M, Maules IK et al (2005) Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial in macroVascular Events): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 366:1279–1289
Miyazaki Y, Mahankali A, Matsuda M, Glass L, Mahankali S, Ferrannini E et al (2001) Improved glycemic control and enhanced insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic subjects treated with pioglitazone. Diabetes Care 24:710–719
Szapary PO, Bloedon LT, Samaha FF, Duffy D, Wolfe ML, Soffer D et al (2006) Effect of pioglitazone on lipoproteins, inflammatory markers and adipokines in nondiabetic patients with metabolic syndrome. Atherioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:182–188
Miyazaki Y, Mahankali A, Matsuda M, Mahankali S, Hardies J, Cusi K et al (2002) Effect of pioglitazone on abdominal fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:2784–2791
Martens FM, Visseren FL, de Koning EJ, Rabelink TJ (2005) Short-term pioglitazone treatment improve vascular function irrespective of metabolic changes in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 46:773–778
Zhang WY, Schwartz EA, Permana PA, Reaven PD (2008) Pioglitazone inhibits the expression of inflammatory cytokines from both monocytes and lymphocytes in patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:2312–2318
Saremi A, Anderson R, Luo P, Moritz TE, Schwenke DC, Allison M et al (2009) Association between IL-6 and the extent of coronary atherosclerosis in the veterans affairs diabetes trial (VADT). Atherosclerosis 203:610–614
Maser RE, Mitchell BD, Vinik AI, Freeman R (2003) The association between cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and mortality in individuals with diabetes: a metanalysis. Diabetes Care 26:1895–1901
Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1991) Blood to brain transport of interleukin links the immune and central nervous systems. Life Sci 48:PL117–PL121
Goehler LE, Gaykema RP, Hansen MK, Anderson K, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2000) Vagal immune-to-brain communication: a visceral chemosensory pathway. Auton Neurosci 85:49–59
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR et al (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405:458–462
Lanza GA, Pitocco D, Navarese EP, Sestito A, Sgueglia GA, Manto A et al (2007) Association between cardiac autonomic dysfunction and inflammation in type 1 diabetic patients: effect of beta-blockade. Eur Heart J 28:814–820
Park SW, Yi JH, Miranpuri G, Satriotomo I, Bowen K, Resnick DK et al (2007) Thiazolidinedione class of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists prevent neuronal damage, motor dysfunction, myelin loss, neuropathic pain and inflammation after spinal cord injury in adult rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:1002–1012
Schutz B, Reimann J, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L, Kappes-Horn K, Landreth GE, Schumann B et al (2005) The oral antidiabetic pioglitazone protects from neurodegeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like symptoms in superoxide dismutase-G93A transgenic mice. J Neurosci 25:7805–7812
American Diabetes Association (2008) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes. Diabetes Care 31:S55–S60
Karagiannis E, Pfützner A, Forst T, Lubben G, Roth W, Grabellus M et al (2008) The IRIS V study: pioglitazone improves systemic chronic inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes under daily routine conditions. Diabetes Technol Ther 10:206–212
Mannucci E, Monami M, Lamanna C, Gensini GF, Marchionni N (2008) Pioglitazone and cardiovascular risk. A comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab 10:1221–1238
Casis O, Echevarria E (2004) Diabetic cardiomyopathy: electromechanical cellular alterations. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2:237–248
Perciaccante A, Fiorentini A, Paris A, Serra P, Tubani L (2006) Circadian rhythm of the autonomic nervous system in insulin resistant subjects with normoglycemia, impaired fasting glycemia, impaired glucose tolerance, type 2 diabetes. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 6:19–28
Lanza GA, Sgueglia GA, Angeloni G, Valsecchi S, Sestito A, Rebuzzi AG et al (2009) Prognostic value of heart rate turbulence and its relation to inflammation in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 103:1066–1072
Tracey KJ (2002) The inflammatory reflex. Nature 420:853–859
Manzella D, Grella R, Esposito K, Giugliano D, Barbagallo M, Paolisso G (2004) Blood pressure and cardiac autonomic nervous system in obese type 2 diabetic patients: effect of metformin administration. Am J Hypertens 17:223–227
Carter AM, Bennett CE, Bostock JA, Grant PJ (2005) Metformin reduces C-reactive protein but not complement factor C3 in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 22:1282–1284
Barter PJ, Nicholls S, Rye KA, Anantharamaiah GM, Navab M, Fogelman AM (2004) Antiinflammatory properties of HDL. Circ Res 95:764–772
Wadham C, Albanese N, Roberts J, Wang L, Bagley CJ, Gamble JR et al (2004) High-density lipoproteins neutralize C-reactive protein inflammatory activity. Circulation 109:2116–2122
Goldberg RB, Kendall DM, Deeg MA, Buse JB, Zagar AJ, Pinaire JA et al (2005) A comparison of lipid and glycemic effect of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia. Diabetes Care 28:1547–1554
Satoh N, Ogawa Y, Usui T, Tagami T, Kono S, Uesugi H et al (2003) Antiatherogenic effect of pioglitazone in type 2 diabetic patients irrespective of the responsiveness to its antidiabetic effect. Diabetes Care 26:2493–2499
Kawai T, Funae O, Shimada A, Tabata M, Hirata T, Atsumi Y et al (2008) Effect of pretreatment with low-dose metformin on metabolic parameters and weight gain by pioglitazone in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Intern Med 47:1181–1188
Nissen SE, Nicholls SJ, Wolski K, Nesto R, Kupfer S, Perez A et al (2008) Comparison of pioglitazone vs glimepiride on progression of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: the PERISCOPE Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 299:1561–1573
Competing interest
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
R. Nerla and D. Pitocco contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nerla, R., Pitocco, D., Zaccardi, F. et al. Effect of pioglitazone on systemic inflammation is independent of metabolic control and cardiac autonomic function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 47 (Suppl 1), 117–122 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-009-0150-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-009-0150-3