Abstract
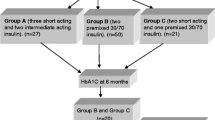
The aim of this study is to determine the proper initial dose adjustment when switching from multiple daily injections to continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for type-1 diabetic pediatric patients. Our hypothesis is that the insulin adjustment varies depending on the pubertal status and the previous long-acting insulin used. Charts of 60 patients were reviewed. Data regarding insulin dose, type of insulin administrated, HbA1c, BMI, severe hypoglycemia and DKA events were collected during the previous year and after 6 weeks of pump therapy. In the prepubertal patients the reduction was 19% (26% if the previous insulin used was detemir). Pubertal patients experienced a decrease of 26%, and the detemir group 33%. The ratio long acting-basal/short acting-bolus insulin changed from 1.26 ± 0.84 to 0.93 ± 0.46 (P < 0.05). The total daily insulin dose needs to be decreased. Basal insulin constitutes 40–45% in prepubertal and 45–50% in pubertal patients. The reduction is different depending on the previous long-acting insulin used; being greater if the insulin is detemir.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maniatis A, Klingesmith G, Slover R, Mowry C, Chase P (2001) Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for children and adolescents: an option for routine diabetes care. Pediatrics 107:351–356
Willi S, Planton J, Egede L, Schwarz S (2003) Benefits of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in children with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr 143:796–801
Litton J, Rice A, Friedman N, Oden J, Lee M, Freemerk M (2002) Insulin pump therapy in toddlers and preschool children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr 141:490–495
McMahon S, Airey L, Marangou D, McElwee K, Carne C, Clarey A et al (2005) Insulin pump therapy in children and adolescents: improvements in key parameters of diabetes management including quality of life. Diabet Med 22:92–96
Plotnick L, Clark L, Brancati F, Erlinger T (2003) Safety and effectiveness of insulin pump therapy in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 26:1142–1146
Weinzimer S, Ahern J, Doyle E, Vincent M, Dziura J, Steffen A et al (2004) Persistence of benefits of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in very young children with type 1 diabetes: a follow-up report. Pediatrics 114:1601–1605
DiMeglio L, Pottorff T, Boyd S, France L, Fineberg N, Eugster E (2004) A randomized, controlled study of insulin pump therapy in diabetic preschoolers. J Pediatr 145:380–384
Wilson D, Buckingham B, Kunselman E, Sullivan M, Paguntalan H, Gitelman S (2005) A two-center randomized controlled feasibility trial of insulin pump therapy in young children with diabetes. Diabetes Care 28:15–19
Boland E, Grey M, Oesterle A, Fredrickson L, Tamborlane W (1999) Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Care 22:1779–1784
Ahern J, Boland E, Doane R et al (2002) Insulin pump therapy in pediatrics: a therapeutic alternative to safely lower HbA1c levels across all age groups. Pediatr Diabetes 3:10–15
Conrad S, McGrath M, Gitelman S (2002) Transition from multiple daily injections to continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr 140:235–240
Liberatore R Jr, Perlman K, Buccino J, Artiles-Sisk A, Daneman D (2004) Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump treatment in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 17(2):223–226
Phillip M, Battelino T, Rodriguez H et al (2007) Use of insulin pump therapy in the pediatric age-group: consensus statement from the European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology, the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society, and the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes, endorsed by the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 30(6):1653–1662
Kaufman F, Halvorson M, Miller D, Mackenzie M, Fisher L, Pitukcheewanont P (1999) Insulin pump therapy in type 1 pediatric patients: now and into the year 2000. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 15:338–352
Hanas R (2002) Selection for and initiation of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Horm Res 57(suppl 1):101–104
Danne T, von Schutz W, Lange K, Nestoris C, Datz N, Kordonouri O (2006) Current practice of insulin pump therapy in children and adolescents—the Hanover recipe. Pediatr Diabetes 7(Suppl 4):25–31
Bulsara M, Holman C, Davis E, Jones T (2004) The impact of a decade of changing treatment on rates of severe hypoglycemia in a population-based cohort of children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27:2293–2298
Knerr I, Hofer E, Holterhust P et al (2007) Prevailing therapeutic regimes and predictive factors for prandial insulin substitution in 26687 children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes in Germany and Austria. Diabet Med 24(12):1478–1481
Hernandez M, Castellet J, Narvaiza J, Rincón J, Ruiz I, Sánchez E et al (1988) Curvas y tablas de crecimiento. Garsi, Madrid
Siverstein J, Klingensmith G, Copeland K et al (2005) Care of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1:186–212
Sulli N, Shashaj B (2006) Long-term benefits of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in children with type 1 diabetes: a 4-year follow-up. Diabet Med 23:900–906
Berhe T, Postellon D, Wilson B, Stone R (2006) Feasibility and safety of insulin pump therapy in children aged 2 to 7 years with type 1 diabetes: a retrospective study. Pediatrics 117:2132–2137
Robertson K, Schoenle E, Gucev Z, Mordhorst L, Gall M, Ludvigsson J (2007) Insulin detemir compared with NPH insulin in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med 24:27–34
Porcelatti F, Rossetti P, Ricci Busciantella N et al (2007) Comparison of pharmacokinetics and dynamics of the long-acting insulin analogs glargine and detemir at steady state in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:2447–2452
Klinkert C, Bachran R, Heidtmann B, Grabert M, Holl R (2008) Age-specific characteristics of the basal insulin rate for pediatric patients on CSII. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 116:118–122
Acknowledgments
Research fund was granted to E. Colino by Fundación Miguel Servet.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colino, E., Álvarez, M.Á., Carcavilla, A. et al. Insulin dose adjustment when changing from multiple daily injections to continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in the pediatric age group. Acta Diabetol 47 (Suppl 1), 1–6 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-009-0103-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-009-0103-x