Abstract.
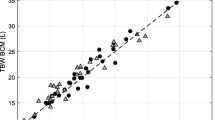
Bioelectric impedance analysis (BIA) is commonly used in clinical settings and field studies for estimating total, extracellular, and intracellular water compartments. The objective of the present study was to carry out a meta-analysis of published reports in which total body water (TBW) was estimated using BIA techniques and comparisons were made with reference values. We identified 16 reports conducted among healthy and obese adults and individuals with chronic renal failure. Based on the weighted mean difference, we found that those studies using only multi-frequency BIA did not significantly overestimate the TBW compared with the reference values. Thus, among BIA techniques, multi-frequency BIA seems to be a more accurate method for estimating the TBW compartment for healthy and obese adults and for those with chronic renal failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinoli, R., Mohamed, E.I., Maiolo, C. et al. Total body water estimation using bioelectrical impedance: a meta-analysis of the data available in the literature. Acta Diabetol 40 (Suppl 1), s203–s206 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-003-0066-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-003-0066-2