Abstract
Introduction
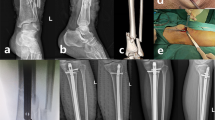
Intramedullary nailing is the most frequent procedure used for the treatment of tibial fractures that do not involve the articular surfaces. The goal of this study is to analyse the clinical outcomes, time of surgery and use of fluoroscopy in patients with midshaft and distal tibial fractures treated with suprapatellar and infrapatellar nailing and compare the results between these different groups.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted, and patients were selected between the period of March 2018 and October 2019. The following variables were studied: age, gender, AO classification, time of surgery (minutes), time of fluoroscopy (seconds), quality of reduction in postoperative controls and 1 year follow-up (using the angles MPTA, LDTA, PPTA, ADTA). Functional outcomes were studied at 1 month and 1 year follow-up. The visual analogue scale was used to study and compare the postoperative pain of the patients. The Lysholm Knee Score was used to evaluate the functional outcomes of the patients.
Results
A total of 80 patients meeting the inclusion criteria were included in this study. The suprapatellar approach was used in 44 patients and the infrapatellar in 36 patients. The time of surgery (p=0.008) and the mean time of use of fluoroscopy (p <0.001) difference were significant in favour of the suprapatellar approach. In the quality of reduction analysis, we have statistically significant results in the LDTA and ADTA angles. Also, in the evaluation of postoperative pain, significant difference was found in favour of the suprapatellar approach.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our study compared the suprapatellar approach and the infrapatellar approach for the treatment of midshaft and distal tibia fractures with intramedullary nailing. The results showed lesser time of surgery and use of fluoroscopy, lower knee pain, and lower rate of malalignment with the suprapatellar approach than with the infrapatellar approach.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson JH, Jahangir A (2020) Tibia fractures overview. In: StatPearls. treasure island. StatPearls Publishing
Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM (2011) Randomized, prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibia shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 25(12):736–41. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e318213f709
Cui Y, Hua X, Schmidutz F, Zhou J, Yin Z, Yan SG (2019) Suprapatellar versus infrapatellar approaches in the treatment of tibia intramedullary nailing: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 20(1):573. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2961-x
Williamson M, Iliopoulos E, Williams R, Trompeter A (2018) Intra-operative fluoroscopy time and radiation dose during suprapatellar tibial nailing versus infrapatellar tibial nailing. Injury 49(10):1891–1894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2018.07.004
Lu Y, Wang G, Hu B, Ren C, Sun L, Wang Z, He C, Xue H, Li Z, Zhang K, Ma T, Wang Q (2020) Comparison of suprapatellar versus infrapatellar approaches of intramedullary nailing for distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 15(1):422. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01960-8
MacDonald DRW, Caba-Doussoux P, Carnegie CA, Escriba I, Forward DP, Graf M, Johnstone AJ (2019) Tibial nailing using a suprapatellar rather than an infrapatellar approach significantly reduces anterior knee pain postoperatively a multicentre clinical trial. Bone Joint J. 101(9):1138–1143. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.101B9.BJJ-2018-1115.R2
Paley D (2005) “Principles of deformity correction Corr 3rd printing. Springer, Switzerland
Horn J, Linke B, Höntzsch D et al (2009) Angle stable interlocking screws improve construct stability of intramedullary nailing of distal tibia fractures: a biomechanical study. Injury. 40(7):76771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2009.01.117
Bleeker NJ, Reininga IHF, van de Wall BJM, Hendrickx LAM, Beeres FJP, Duis KT, Doornberg JN, Jaarsma RL, Kerkhoffs GMMJ (2021) Difference in pain, complication rates, and clinical outcomes after suprapatellar versus infrapatellar nailing for tibia fractures? a systematic review of 1447 patients. J Orthop Trauma. 35(8):391–400. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000002043
Bible JE, Choxi AA, Dhulipala S et al (2013) Quantification of anterior cortical bone removal and intermeniscal ligament damage at the tibial nail entry zone using parapatellar and retropatellar approaches. J Orthop Trauma. 27:437–441
Avilucea FR, Triantafillou K, Whiting PS et al (2016) Suprapatellar intramedullary nail technique lowers rate of malalignment of distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 30:557–560
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they ave no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llano, L., Soruco, M.L., Taype Zamboni, D. et al. Comparison between functionality and quality of reduction between suprapatellar vs infrapatellar approaches in the treatment of diaphyseal and distal tibial fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 33, 889–892 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03230-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03230-1