Abstract
Purpose
The optimal means of local antibiotic delivery for fracture related infection is unknown. Until now, intramedullary application of calcium sulphate based local antibiotics has been challenging. We report on the use of a newly available mode of preparation and delivery: the Stimulan Bullet Mat and Introducer (Biocomposites Ltd, Staffordshire, England).
Methods
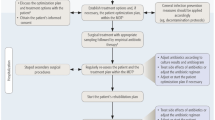
A retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data for infection cases at two separate tertiary referral institutions was performed. We included cases of long bone FRI with a retained intramedullary nail, treated with a single stage protocol of metalwork removal, debridement, local antibiotic application using the novel mould and applicator, with additional bony stabilisation and soft tissue reconstruction where required.
Results
All 13 patients achieved infection remission rate with an average follow-up of 19.7 months (range 12–28). All 6 patients with infection around an unhealed fracture achieved union at an average 8 months (range 4–12) from debridement. No patients developed aseptic wound leak.
Conclusions
Antibiotic impregnated calcium sulphate can be used safely as part of a single stage treatment protocol for the treatment of long bone fracture related infection following intramedullary nailing. We have demonstrated high rates of infection remission and union, using a newly available intramedullary applicator.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Court-Brown CM, Keating JF, McQueen MM (1992) Infection after intramedullary nailing of the tibia Incidence and protocol for management. The J Bone Joint Surg 74(5):770–774
Makridis KG, Tosounidis T, Giannoudis PV (2013) Management of infection after intramedullary nailing of long bone fractures: treatment protocols and outcomes. The Open Orthop J 7:219–226. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874325001307010219
Iliadis AD, Shivji F, Debuka E, Trompeter A, Narayan B, Heidari N (2021) Current concepts in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of fracture-related infection (FRI). Eur J Orthop SurgTraumatol Orthop Traumatol 31(5):957–966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-02956-8
Metsemakers WJ, Smeets B, Nijs S, Hoekstra H (2017) Infection after fracture fixation of the tibia: analysis of healthcare utilization and related costs. Injury 48(6):1204–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2017.03.030
Simpson AH, Tsang J (2017) Current treatment of infected non-union after intramedullary nailing. Injury 48(Suppl 1):S82–S90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2017.04.026
Beuerlein MJ, McKee MD (2010) Calcium sulfates: what is the evidence? J Orthop Trauma 24(Suppl 1):S46–S51. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181cec48e
Mauffrey C, Hak DJ, Giannoudis P, Alt V, Nau C, Marzi I, Augat P, Oh JK, Frank J, Mavrogenis A, Flecher X, Argenson JN, Gavaskar A, Rojas D, Bedeir YH, From the ORS, ISFR expert group on Tibial bone defects, (2019) Treatment of infection following intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures-results of the ORS/ISFR expert group survey. Int Orthop 43(2):417–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3964-1
Ene R, Nica M, Ene D, Cursaru A, Cirstoiu C (2021) Review of calcium-sulphate-based ceramics and synthetic bone substitutes used for antibiotic delivery in PJI and osteomyelitis treatment. EFORT Open Rev 6(5):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.6.200083
Masrouha KZ, Raad ME, Saghieh SS (2018) A novel treatment approach to infected nonunion of long bones without systemic antibiotics. Strat Trauma Limb Reconstr 13(1):13–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-018-0303-4
Zhang HA, Zhou CH, Meng XQ, Fang J, Qin CH (2020) Intramedullary reaming and irrigation and antibiotic-loaded calcium sulfate implantation for the treatment of infection after intramedullary nailing: a retrospective study of 19 cases. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 21(1):710. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-03734-z
Pincher B, Fenton C, Jeyapalan R, Barlow G, Sharma HK (2019) A systematic review of the single-stage treatment of chronic osteomyelitis. J Orthop Surg Res 14(1):393. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1388-2
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception, design and material preparation. Operations were performed by the senior authors AI, AV, NH and AT. Data collection, analysis and first draft were done by PP. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript and have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, P., Iliadis, AD., Vris, A. et al. Intramedullary application of local antibiotic bullets for the treatment of long bone fracture related infection. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 33, 385–391 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03205-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03205-2