Abstract
Background
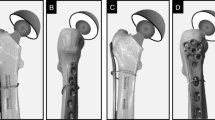
Establishing fracture consolidation and avoiding postoperative complications of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures of the femur are technically challenging. The authors delineated a technical description of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) by using a reverse distal femur locking compression plate (LCP-DF) and retrospectively reviewed the outcomes of these particular fractures.
Methods
Fifty patients with 51 type C subtrochanteric fractures of the femur were operated on by MIPO and reverse LCP-DF fixation. The collected data included postoperative complications, union times, and clinical outcomes.
Results
All fractures were united with a mean union time of 19.4 weeks (range 16–22). Regarding postoperative complications, asymptomatic valgus angulation occurred in five patients and trochanteric pain in six. According to Harris hip score, nine patients were determined to be excellent, 36 to be good and five to be fair.
Conclusion
MIPO by reverse LCP-DF is reliable and effective for type C subtrochanteric fractures of the femur particularly in situations where intramedullary nailing is not feasible.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang J, Li H, Jia H, Ma X (2020) Intramedullary versus extramedullary fixation in the treatment of subtrochanteric femur fractures: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 54(6):639–646
Kokkalis ZT, Mavrogenis AF, Ntourantonis DI, Igoumenou VG, Antoniadou T, Karamanis R et al (2019) Reduction techniques for difficult subtrochanteric fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 29(1):197–204
Amin NH, Katsman A, Chakravarty R, Harding S, Cerynik DL (2012) Use of blocking screws in intramedullary fixation of subtrochanteric fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 22(8):703–707
Guyver PM, McCarthy MJH, Jain NPM, Keenan J (2011) The short-term functional and radiological outcome of patients treated with the synthes proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) for unstable proximal femoral fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 21(7):493–501
Mirbolook A, Siavashi B, Jafarinezhad AE, Khajeh Jahromi S, Farahmand M, Roohi Rad M et al (2015) Subtrochanteric fractures: comparison of proximal femur locking plate and intramedullary locking nail fixation outcome. Indian J Surg 77:795–798
Şahin EK, İmerci A, Kınık H, Karapınar L, Canbek U, Savran A (2014) Comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) with AO dynamic condylar screws (DCS) for the treatment for unstable peritrochanteric femoral fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24(3):347–352
Han N, Sun GX, Li ZC, Li GF, Lu QY, Han QH et al (2011) Comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation blade and reverse less invasive stabilization system-distal femur systems in the treatment of proximal femoral fractures. Orthop Surg. 3(1):7–13
Kim JW, Oh CW, Byun YS, Oh JK, Kim HJ, Min WK et al (2011) A biomechanical analysis of locking plate fixation with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in a subtrochanteric fracture model. J Trauma 70(1):E19-23
Sims SH (2002) Subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Orthop Clin N Am 33:113–126
Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Nliclau T, Tscherne H (2004) Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using the DCS in proximal and distal femoral fractures. Injury 28(1):A20-30
Mehrpour SR, Aghamirsalim MR, Tavvafi M, Sorbi R (2012) Biological plate osteosynthesis of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures: a clinical study. HIP Int 22(3):324–328
Rohilla R, Singh R, Magu NK, Sangwan SS, Devgun A, Siwach R (2009) Technical aspects of the use of dynamic condylar screw in biological fixation of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 19(1):33–37
Saini P, Kumar R, Shekhawat V, Joshi N, Bansal M, Kumar S (2013) Biological fixation of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures with proximal femur locking compression plate. Injury 44(2):226–231
Lee PC, Hsieh PH, Yu SW, Shiao CW, Kao HK, Wu CC (2007) Biologic plating versus intramedullary nailing for comminuted subtrochanteric fractures in young adults: a prospective, randomized study of 66 cases. J Trauma 63(6):1283–1291
Saarenpää I, Heikkinen T, Jalovaara P (2007) Treatment of subtrochanteric fractures. A comparison of the gamma nail and the dynamic hip screw: short-term outcome in 58 patients. Int Orthop 31(1):65–70
Burnei C, Popescu G, Barbu D, Capraru F (2011) Intramedullary osteosynthesis versus plate osteosynthesis in subtrochanteric fractures. J Med Life 4(4):324–329
Pakuts AJ (2004) Unstable subtrochanteric fractures–gamma nail versus dynamic condylar screw. Int Orthop 28(1):21–24
Vaidya SV, Dholakia DB, Chatterjee A (2003) The use of a dynamic condylar screw and biological reduction techniques for subtrochanteric femur fracture. Injury 34(2):123–128
Yadav S, Sinha S, Luther E, Arora NC, Prasad M, Varma R (2014) Comparison of extramedullary and intramedullary devices for treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fractures at tertiary level center. Chin J Traumatol 17(3):141–145
Rahme DM, Harris IA (2007) Intramedullary nailing versus fixed angle blade plating for subtrochanteric femoral fractures: a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 15(3):278–281
Li G, Li Z, Han N, Lu QY (2014) A retrospective analysis of reversed femoral less invasive stable system (LISS) for treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fracture. Int J Surg 12(5):432–436
Imerci A, Canbek U, Karatosun V, Karapınar L, Yeşil M (2015) Nailing or plating for subtrochanteric femoral fractures: a non-randomized comparative study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 25(5):889–894
Pryce Lewis JR, Ashcroft GP (2007) Reverse LISS plating for proximal segmental femoral fractures in the polytrauma patient: a case report. Injury 38(2):235–239
Crist BD, Khalafi A, Hazelwood SJ, Lee MA (2009) A biomechanical comparison of locked plate fixation with percutaneous insertion capability versus the angled blade plate in a subtrochanteric fracture gap model. J Orthop Trauma 23(9):622–627
Ehlinger M, Brinkert D, Besse J, Adam P, Arlettaz Y, Bonnomet F (2011) Reversed anatomic distal femur locking plate for periprosthetic hip fracture fixation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97(5):560–564
Gogna P, Mukhopadhyay R, Singh A, Devgan A, Arora S, Batra A et al (2015) Contralateral reversed distal femoral locking plate for fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Chinese J Traumatol 18(5):279–283
Oh CW, Kim JJ, Byun YS, Oh JK, Kim JW, Kim SY et al (2009) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of subtrochanteric femur fractures with a locking plate: a prospective series of 20 fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129(12):1659–1665
Lill M, Attal R, Rudisch A, Wick MC, Blauth M, Lutz M (2016) Does MIPO of fractures of the distal femur result in more rotational malalignment than ORIF? A retrospective study. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 42(6):733–740
Schneider K, Oh JK, Zderic I, Stoffel K, Richards RG, Wolf S et al (2015) What is the underlying mechanism for the failure mode observed in the proximal femoral locking compression plate? A biomechanical study. Injury 46(8):1483–1490
Wirtz C, Abbassi F, Evangelopoulos DS, Kohl S, Siebenrock KA, Krüger A (2013) High failure rate of trochanteric fracture osteosynthesis with proximal femoral locking compression plate. Injury 44(6):751–756
Apivatthakakul V, Apivatthakakul T (2021) Reverse distal femoral locking compression plate (DF-LCP), does it fit and how to fit on Asian’s proximal femurs? A cadaveric study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03072-3
Funding
There was no source of funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SJ were involved in drafting and revising the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content, study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, as well as acquisition of the data. AG, KS, CP and AK were involved in revising the manuscript for content and analysis and interpretation of data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
S. Jitprapaikulsarn, A. Gromprasit, K Sukha, C Patamamongkonchai and A. Kritsaneephaiboon declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study has been approved by the ethical committees of Buddhachinaraj Hospital in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jitprapaikulsarn, S., Gromprasit, A., Sukha, K. et al. The utility of reverse distal femur locking compression plate in minimally invasive osteosynthesis for type C subtrochanteric fractures of the femur: technical description and a clinical series of 50 cases. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 32, 1423–1433 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03116-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03116-8