Abstract
Purpose
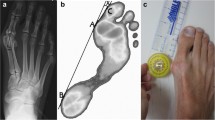
Radiographic measurements are the gold standard in the management for preoperative surgical planning of hallux valgus deformity. Plantar pressure technology is a tool that is not commonly used to evaluate and manage hallux valgus patients, and few studies have reported the correlation of plantar pressure measurements and radiography.
Methods
A prospective cohort study was designed to analyze plantar pressure measurements and radiographic variables. The inclusion criteria were age over 18 years old, and diagnosis of hallux valgus requesting surgical correction because of discomfort, pain or difficulty with shoe wear. Plantar pressure measurements were performed using a platform. Radiographic data were obtained according to the guidelines of the AOFAS Committee on Angular Measurements.
Results
A total of 114 patients met the inclusion criteria. Mean age of the patients was 50 years, and 94 patients (82.5%) were women. We found significant correlations between dynamic plantar pressure measurements and HVA, DMAA, and MDA. Mean pressure under third metatarsal head was the most associated plantar pressure measurement with hallux valgus angle and metatarsal declination angle. However, this association showed signs of weakness.
Conclusion
Hallux valgus angle and metatarsal declination angle had a minimal influence on plantar-loading parameters. Pressure values did not discriminate the magnitude of HV deformity. Others factors responsible for the observed plantar pressures pattern should be addressed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fraissler L, Konrads C, Hoberg M, Rudert M, Walcher M (2016) Treatment of hallux valgus deformity. EFORT Open Rev 1:295–302
Coughlin MJ, Jones CP (2007) Hallux valgus: demographics, etiology, and radiographic assessment. Foot Ankle Int 28:759–77
Coughlin MJ, Saltzman CL, Anderson RB (2014) HV. In: Coughlin M (ed) Mann’s surgery of the foot and ankle, 9th edn. WB Sanders, Philadelphia, pp 155–321
Welck MJ, Al-Khudairi N (2018) Imaging of hallux valgus: how to approach the deformity. Foot Ankle Clin 23:183–92
Dayton P, Feilmeier M, Hirschi J, Kauwe M, Kauwe JS (2014) Observed changes in radiographic measurements of the first ray after frontal plane rotation of the first metatarsal in a cadaveric foot model. J Foot Ankle Surg 53:274–78
Zambelli R, Baumfeld D (2020) Intraoperative and postoperative evaluation of hallux valgus correction: what is important? Foot Ankle Clin 25:127–39
Janssen DM, Sanders AP, Guldemond NA, Hermus J, Walenkamp GH, van Rhijn LW (2014) A comparison of hallux valgus angles assessed with computerized plantar pressure measurements, clinical examination and radiography in patients with diabetes. J Foot Ankle Res 7:33
Kaipel M, Krapf D, Wyss C (2011) Metatarsal length does not correlate with maximal peak pressure and maximal force. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:1161–66
Menz HB, Fotoohabadi MR, Munteanu SE, Zammit GV, Gilheany MF (2013) Plantar pressures and relative lesser metatarsal lengths in older people with and without forefoot pain. J Orthop Res 3:427–33
Lee DN (1980) Visuo-motor coordination in space-time. Adv in Psychol 1:281–95
Van der Leeden M, Dekker JH, Siemonsma PC, Lek-Westerhof SS, Steultjens MP (2004) Reproducibility of plantar pressure measurements in patients with chronic arthritis: a comparison of one-step, two-step, and three-step protocols and an estimate of the number of measurements required. Foot Ankle Int 25:739–44
Gurney JK, Kersting UG, Rosenbaum D (2008) Between-day reliability of repeated plantar pressure distribution measurements in a normal population. Gait Posture 27:706–9
Smith RW, Chairman P, Reynolds C, Stewart MJ (1984) Hallux valgus assessment: report of research committee of american orthopaedic foot and ankle society. Foot Ankle 5:92–103
Coughlin M, Saltzman C, Nunley J II (2002) Angular measurements in the evaluation of hallux valgus: a report of the ad hoc committee of the american orthopedic foot and ankle society on angular measurements. Foot Ankle Int 23:68–74
Horton GA, Park YW, Myerson MS (1999) Role of metatarsus primus elevates in the pathogenesis of hallux rigidus. Foot Ankle Int 20:777–8
Bryant A, Tinley P, Singer K (2000) A comparison of radiographic measurements in normal, hallux valgus, and hallux limitus feet. J Foot Ankle Surg 39:39–43
Hardy RH, Clapham JC (1951) Observations on hallux valgus. J Bone Joint Surg Br 33(3):376–91
Mancuso JE, Abramow SP, Landsman MJ, ldman M, Carioscia M, (2003) The zero-plus first metatarsal and its relationship with bunion deformity. J Foot Ankle Surg 42:319–26
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143:29–36
Fagan TJ (1975) Letter: nomogram for bayes theorem. N Engl J Med 293:253
Kernozek TW, Sterriker SA (2002) Chevron (Austin) distal metatarsal osteotomy for hallux valgus: comparison of pre- and post-surgical characteristics. Foot Ankle Int 23:503–08
Koller U, Willegger M, Windhager R, Wanivenhaus A, Trnka H-J, Schuh R (2014) Plantar pressure characteristics in hallux valgus feet. J Orthop Res 32:1688–93
Martinez-Nova A, Sanchez-Rodriguez R, Perez-Soriano P, Llana-Belloch S, Leal-Muro A, Pedera-Zamorano JD (2010) Plantar pressures determinants in mild hallux valgus. Gait Posture 32:425–7
Shibuya N, Roukis TS, Jupiter DC (2017) Mobility of the first ray in patients with or without hallux valgus deformity: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Foot Ankle Surg 56:1070–5
Koury K, Staggers JR, Pinto MC, Godoy-Santos AL, Smyth NA, Shah AB, Netto CC (2019) Radiographic assessment of first tarsometatarsal joint shape and orientation. Foot Ankle Int 40:1438–46
Min BC, Chung CY, Park MS, Choi Y, Koo S, Jang S, Lee KM (2019) Dynamic first tarsometatarsal instability during gait evaluated by pedobarographic examination in patients with hallux valgus. Foot Ankle Int 40:1104–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
IRB approval and informed consent were obtained.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verdu Roman, C., Martinez Gimenez, E., Bustamante Suarez de Puga, D. et al. Radiographic measurements have limited effect in dynamic plantar pressures in hallux valgus patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 32, 19–26 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-02906-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-02906-4