Abstract
Background
Only a little is known about whether type of surgical intervention has an effect on mortality of these patients. Our primary objective was to assess whether different type of surgical procedures has an effect on mortality among elderly patients with hip fracture. A secondary objective was to examine factors that are related to mortality in our patient population. Our hypothesis is that type of surgical procedure, especially external fixation, should have an influence on mortality outcomes.
Methods
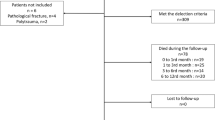
We included 785 patients age 65 years or older, with hip fractures. Operative treatment consisted of external fixation, internal fixation, total hip arthroplasty and hip hemiarthroplasty. Age, gender, type of fracture, type of surgery performed, American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) grade, clinical comorbidities, anesthesia type, blood transfusion requirement, time to surgery, intensive care unit requirement, operation length and length of hospital stay and number of comorbidities were documented.
Results
During the study period, 785 patients (262 male, 523 female) were included to study, Overall mortality rate was 37.2 % (292/785). Their age ranged between 65 and 100 years (mean 81). Surgery type Kaplan–Meier cumulative mortality curves suggested no significant difference between four different types of surgery groups (p = 0.064). Transfusion requirement was significantly lower in external fixation group comparing to other groups (p = 0.014). Cox regression analysis showed the number of comorbidities 2 and ≥ 3 (p = 0.0027, p = 0.015), transfusion requirement (p = 0.0001), ASA 4 (p = 0.016) to be significant predictors of mortality.
Conclusions
Transfusion requirement, ASA grade 4 and having more than two comorbidities are risk factors for mortality in geriatric hip fractures. Type of surgical intervention and fracture type had similar mortality rates in our patient population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnell O, Kanis JA (2006) An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int J Establ Result Coop Between Eur Found Osteoporos Natl Osteoporos Found USA 17:1726–1733
Melton LJ (1993) Hip fractures: a worldwide problem today and tomorrow. Bone 114(Suppl 1):S1–S8
Negrete-Corona J, Alvarado-Soriano JC, Reyes-Santiago LA (2014) Hip fracture as risk factor for mortality in patients over 65 years of age. Case-control study. Acta Ortop Mex 28:352–362
Norring-Agerskov D, Laulund AS, Lauritzen JB, Duus BR, Van der Mark S, Mosfeldt M et al (2013) Metaanalysis of risk factors for mortality in patients with hip fracture. Dan Med J 60(8):A4675
Daugaard CL, Jørgensen HL, Riis T, Lauritzen JB, Duus BR, Van der Mark S (2012) Is mortality after hip fracture associated with surgical delay or admission during weekends and public holidays? A retrospective study of 38,020 patients. Acta Orthop 83:609–613
Eschbach D-A, Oberkircher L, Bliemel C, Mohr J, Ruchholtz S, Buecking B (2013) Increased age is not associated with higher incidence of complications, longer stay in acute care hospital and in hospital mortality in geriatric hip fracture patients. Maturitas 74:185–189
González-Zabaleta J, Pita-Fernandez S, Seoane-Pillado T, López-Calviño B, Gonzalez-Zabaleta JL (2015) Comorbidity as a predictor of mortality and mobility after hip fracture. Geriatr Gerontol Int 16(5):561–569
Gregersen M, Zintchouk D, Hougaard K, Krogshede A, Almasi F, Holm-Petersen IØ et al (2010) Interdisciplinary geriatric intervention among nursing home residents with hip fracture reduces mortality. Ugeskr Laeger 172:1902–1907
Ireland AW, Kelly PJ, Cumming RG (2015) Risk factor profiles for early and delayed mortality after hip fracture: analyses of linked Australian Department of Veterans’ Affairs databases. Injury 46:1028–1035
Owens WD, Felts JA, Spitznagel EL (1978) ASA physical status classifications: a study of consistency of ratings. Anesthesiology 49:239–243
Kazemian GH, Manafi AR, Najafi F, Najafi MA (2014) Treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly highrisk patients: dynamic hip screw vs. external fixation. Injury 45:568–572
Kenzora JE, McCarthy RE, Lowell JD, Sledge CB (1984) Hip fracture mortality. Relation to age, treatment, preoperative illness, time of surgery, and complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res 186:45–56
Geiger F, Zimmermann-Stezel M, Heisel C, Lehner B, Daecke W (2007) Trochanteric fractures in the elderly: the influence of primary hip arthroplasty on 1-year mortality. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127(10):959–966
Bilsel K, Erdil M, Gulabi D, Elmadag M, Cengiz O, Sen C (2013) Factors affecting mortality after hip fracture surgery: a retrospective analysis of 578 patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 23(8):895–900
Vestergaard P, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L (2007) Has mortality after a hip fracture increased? J Am Geriatr Soc 55:1720–1726
Karademir G, Bilgin Y, Erşen A, Polat G, Buget MI, Demirel M, Balcı HI (2015) Hip fractures in patients older than 75 years old: Retrospective analysis for prognostic factors. Int J Surg. 24(Pt A):101–104
Karn NK, Singh GK, Kumar P, Singh MP, Shrestha BP, Chaudhary P (2009) Management of trochanteric fractures of the femur with external fixation in high-risk patients. Int Orthop 33:785–788
Ozkaya U, Parmaksizoğlu AS, Gül M, Kabukçuoğlu Y, Ozkazanli G, Basilgan S (2008) Management of osteoporotic pertrochanteric fractures with external fixation in elderly patients. Acta Orthop Et Traumatol Turc 42:246–251
Karagiannis A, Papakitsou E, Dretakis K, Galanos A, Megas P, Lambiris E et al (2006) Mortality rates of patients with a hip fracture in a southwestern district of Greece: ten-year follow-up with reference to the type of fracture. Calcif Tissue Int 78:72–77
Kearns RJ, Moss L, Kinsella J (2013) A comparison of clinical practice guidelines for proximal femoral fracture. Anaesthesia 68:159–166
Alffram PA (1964) An epidemiologic study of cervical and trochanteric fractures of the femur in an urban population. Analysis of 1,664 cases with special reference to etiologic factors. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 65(suppl 65):1–109
Lu-Yao GL, Baron JA, Barrett JA, Fisher ES (1994) Treatment and survival among elderly Americans with hip fractures: a population-based study. Am J Public Health 84:1287–1291
Pioli G, Barone A, Giusti A, Oliveri M, Pizzonia M, Razzano M et al (2006) Predictors of mortality after hip fracture: results from 1-year follow-up. Aging Clin Exp Res 18:381–387
Nettleman MD, Alsip J, Schrader M, Schulte M (1996) Predictors of mortality after acute hip fracture. J Gen Intern Med 11:765–767
Dirksen A, Kjøller E (1988) Cardiac predictors of death after non-cardiac surgery evaluated by intention to treat. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 297:1011–1013
Roche JJW, Wenn RT, Sahota O, Moran CG (2005) Effect of comorbidities and postoperative complications on mortality after hip fracture in elderly people: prospective observational cohort study. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 331:1374
Shabani F, Farrier AJ, Smith R, Venkatesan M, Thomas C, Uzoigwe CE et al (2015) Hip fractures sustained in hospital: comorbidities and outcome. Postgrad Med J 91:61–64
Liu Y, Peng M, Lin L, Liu X, Qin Y, Hou X (2015) Relationship between American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) grade and 1-year mortality in nonagenarians undergoing hip fracture surgery. Osteoporos Int J Establ Result Coop Between Eur Found Osteoporos Natl Osteoporos Found USA 26:1029–1033
Holt G, Smith R, Duncan K, Hutchison JD, Gregori A (2008) Outcome after surgery for the treatment of hip fracture in the extremely elderly. J Bone Jt Surg Am 90:1899–1905
Grimes JP, Gregory PM, Noveck H, Butler MS, Carson JL (2002) The effects of time-to-surgery on mortality and morbidity in patients following hip fracture. Am J Med 112:702–709
Parker MJ, Pryor GA (1992) The timing of surgery for proximal femoral fractures. J Bone Jt Surg Br 74:203–205
Weller I, Wai EK, Jaglal S, Kreder HJ (2005) The effect of hospital type and surgical delay on mortality after surgery for hip fracture. J Bone Jt Surg Br 87:361–366
Bredahl C, Nyholm B, Hindsholm KB, Mortensen JS, Olesen AS (1992) Mortality after hip fracture: results of operation within 12 h of admission. Injury 23:83–86
Halm EA, Wang JJ, Boockvar K, Penrod J, Silberzweig SB, Magaziner J et al (2003) Effects of blood transfusion on clinical and functional outcomes in patients with hip fracture. Transfusion 43:1358–1365
Morrison RS, Magaziner J, Gilbert M et al (2000) Pain and delirium in elderly hip fracture patients. J Gen Intern Med 15(suppl):84
Hébert PC, Wells G, Tweeddale M, Martin C, Marshall J, Pham B et al (1997) Does transfusion practice affect mortality in critically ill patients? transfusion requirements in critical care (TRICC) Investigators and the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 155:1618–1623
Wu WC, Rathore SS, Wang Y, Radford MJ, Krumholz HM (2001) Blood transfusion in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 345:1230–1236
Hébert PC, Wells G, Blajchman MA, Marshall J, Martin C, Pagliarello G et al (1999) A multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial of transfusion requirements in critical care. Transfusion requirements in Critical Care Investigators, Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. N Engl J Med 340:409–417
Dunne JR, Malone D, Tracy JK, Gannon C, Napolitano LM (2002) Perioperative anemia: an independent risk factor for infection, mortality, and resource utilization in surgery. J Surg Res 102:237–244
Acknowledgments
This study presented in part as an oral presentation of free paper at the 17th European Federation of National Associations of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Congress, Geneva, Switzerland, June 1–3, 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. The authors; Ersin Ercin, Mustafa Gokhan Bilgili, Cihangir Sari, Serdar Hakan Basaran, Bulent Tanriverdi, Erdem Edipoglu, Kurmay Mumtaz Celen, Halil Cetingok and Cemal Kural, declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethics committee approval was received for this study from the local ethics committee of BEAH Clinical Studies. This study did not require informed consent. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ercin, E., Bilgili, M.G., Sari, C. et al. Risk factors for mortality in geriatric hip fractures: a compressional study of different surgical procedures in 785 consecutive patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 27, 101–106 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-016-1843-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-016-1843-2