Abstract
Backgrounds
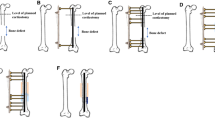
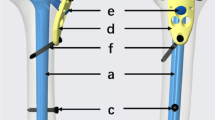
Treatment for bone defect remains a challenge for orthopedists. Bone transport gives an effective alternative, which can be performed with an external fixator alone or combined with an intramedullary nail. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. We present a retrospective study to find out the optimal choice by evaluating the outcomes of treatment for femoral bone defect with two methods.
Methods
Two groups of patients, the monolateral external fixator alone (group A, n = 13) and the monolateral external fixator combined with intramedullary nail (group B, n = 15), were compared. Duration of the external fixator, external fixator index, radiographic consolidation index, complication, and total cost for treatment was also recorded. A modified classification of the Association for the Study and Application of the Method of Ilizarov (ASAMI) was used to assess results in two groups of patients; another SF-36 health survey questionnaire was used to assess the life qualities patients of two groups.
Results
Healing was achieved in 13/13 and 13/15 of the two groups, respectively. The rates of complications were significantly higher in the group A. Two patients performed amputations because of persistent deep infections in group B. Statistically significant difference was found when comparing ASAMI scores and categories of the SF-36 health survey.
Conclusions
Bone transport by monolateral external fixator with the use of intramedullary nail reduces the incidence of complication and the duration of external fixator time that give patients a better life quality in both physical and emotional. However, if chronic osteitis exists, bone transport should be treated with monolateral external fixator alone due to a lower rate of amputations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sangkaew C (2005) Distraction osteogenesis for the treatment of post traumatic complications using a conventional external fixator: a novel technique. Injury 36:185–193
Mekhail AO, Abraham E, Gruber B, Gonzalez M (2004) Bone transport in the management of posttraumatic bone defects in the lower extremity. J Trauma 56(2):368–378
Caja V, Kim W, Larsson S, E YC (1995) Comparison of the mechanical performance of three types of external fixators: linear, circular and hybrid. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 10(8):401–406
Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Paremain G et al (1997) Femoral lengthening over an intramedullary nail: a matched-case comparison with Ilizarov femoral lengthening. J Bone Jt Surg Am 79(10):1464–1480
Paley D (1990) Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop 250:81–104
Paley D, Catagni MA, Argnani F et al (1989) Ilizarov treatment of tibial non-unions with bone loss. Clin Orthop 241:146–165
Zhang X, Liu T, Li Z, Peng W (2007) Reconstruction with callus distraction for nonunion with bone loss and leg shortening caused by suppurative osteomyelitis of the femur. J Bone Jt Surg Br 89B:1509–1514
Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Paremain G, Bhave A (1997) Femoral lengthening over an intramedullary nail: a matched-case comparison with Ilizarov femoral lengthening. J Bone Jt Surg Am 79A:1464–1480
Capanna J, Campanacci R, Belot DA et al (2007) A new reconstructive technique for intercalary defects of long bones: the association of massive allograft with vascularized fibular autograft. Long-term results and comparison with alternative techniques. Orthop Clin N Am 38:5–60
Lawal YZ, Garba ES, Ogirima MO et al (2011) Use of non-vascularized autologous fibula strut graft in the treatment of segmental bone loss. Ann Afr Med 10(1):25–28
Attias N, Lindsey RW (2006) Case reports: management of large segmental tibial defects using a cylindrical mesh cage. Clin Orthop Relat Res 450:259–266
Ilizarov GA (1990) Clinical application of the tension–stress effect for limb lengthening. Clin Orthop 250:8–26
Innocenti M, Delcroix L, Manfrini M et al (2004) Vascularized proximal fibular epiphyseal transfer for distal radial reconstruction. J Bone Jt Surg Am 86A(7):1504–1511
Tsuchiya H, Tomita K (2003) Distraction osteogenesis for treatment of bone loss in the lower extremity. J Orthop Sci 8:116–124
Green SA (1994) A comparison of bone grafting and bone transport for segmental skeletal defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res 301:111–117
Zhang X, Duan L, Li Z, Chen X (2007) Callus distraction for the treatment of acquired radial club-hand deformity after osteomyelitis. J Bone Jt Surg Br 89B:1515–1518
Liu T, Zhang X, Li Z et al (2008) Callus distraction for humeral nonunion with bone loss and limb shortening due to osteomyelitis. J Bone Jt Surg Br 90(6):795–800
Li Z, Zhang X, Duan L, Chen X (2009) Reconstruction with distraction osteogenesis technique over intramedullary nail combined with monolateral external fixator for massive postosteomyelitis skeletal defects of femur. Can J Surg 52(2):103–111
Raschke MJ, Mann JW, Oedekoven G, Claudi BF (1992) Segmental transport after unreamed intramedullary nailing. Preliminary report of a monorail system. Clin Orthop 282:233–240
Kristiansen LP, Steen H (1999) Lengthening of the tibia over an intramedullary nail, using the Ilizarov external fixator. Major complications and slow consolidation in nine lengthening. Acta Orthop Scand 70:271–274
Sun XT, Easwar TR, Stephen M et al (2011) Comparative study of callus progression in limb lengthening with or without intramedullary nail with reference to the pixel value ratio and the Ru Li’s classification. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131(10):1333–1340
Ilizarov G (1989) The tension–stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues. Part II. The influence of the rate and frequency of distraction. Clin Orthop 239:263–285
Kessler P, Neukam FW, Wiltfang J (2005) Effects of distraction forces and frequency of distraction on bony regeneration. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43:392–398
Isaksson H, Comas O, van Donkelaar CC et al (2007) Bone regeneration during distraction osteogenesis: mechano-regulation by shear strain and fluid velocity. J Biomech 40(9):2002–2011
Oh CW, Song HR, Roh JY et al (2008) Bone transport over an intramedullary nail for reconstruction of long bone defects in tibia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128(8):801–808
Acknowledgments
We thank Miss Jing Wan for her editorial and secretarial assistance to this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest with this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jun Wan and Lin Ling contribute equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, J., Ling, L., Zhang, Xs. et al. Femoral bone transport by a monolateral external fixator with or without the use of intramedullary nail: a single-department retrospective study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 23, 457–464 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-012-1008-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-012-1008-x