Abstract
Background
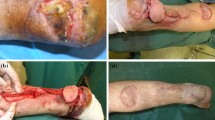
The soft tissue defects of lower third leg, ankle, and foot present a challenging problem because of the paucity of local tissue and poor circulation of skin in that region. Various forms of coverage including muscle flaps, fascial flaps, and free flaps are used for reconstruction. Each have their specific indications and inherent disadvantages. Distally based fasciocutaneous flap supplied by vascular axis around sural nerve is intensively researched and constitutes another important alternative to lower third and foot reconstruction.
Patients and method
In our department, we have treated 166 patients from January 2004 to December 2008 with reverse sural flap. Majority of patients were due to road traffic accident (RTA). Distal pivot point was kept approximately 5 cm from lateral malleolus, thus preserving the distal most perforator, and the flap was turned and insetted into the defect. Donor site was covered with a split thickness graft. Postoperative follow-up period was 15 days to 1 year at regular intervals.
Results
The procedure was uneventful in 142 cases. Infection/discharge occurred in 12 cases. Partial flap necrosis occurred in 10 cases, with resulting need for minor surgery (debridement and split thickness graft). Total flap necrosis occurred in 2 cases.
Conclusion
Distally based sural flap offers reconstruction of foot, ankle, and lower third leg with a reliable blood supply, easy elevation, and long vascular pedicle with large arc of rotation. Also, there is no sacrifice of major arteries. However, main disadvantages are sacrifice of sural nerve and unsightly scarring of upper calf.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masquelet AC, Ramana MC, Wolf G (1992) Skin island flaps supplied by the vascular axis of the sensitive superficial nerves: anatomic study and clinical experience in the leg. Plast Reconstr Surg 89:1115
Nakajima H, Imanishi N, Fukuzumi S (1999) Accompanying arteries of the lesser saphenous vein and sural nerve: anatomic study and its clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:104–120
Le Fourn B, Caye N, Pannier M (2001) Distally based sural fasciomuscular flap: anatomic study and application for filling leg or foot defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:67–72
Mustafa Y, Ozlem K, Ali B (1998) The distally based superficial sural artery island flap: clinical experiences and modifications. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:2358–2367
Hasegawa M, Torii S, Katoh H, Esaki S (1994) The distally based superficial sural artery flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 93:1012–1020
Bhandari PS, Bath AS, Sadhotra LP (2005) Management of soft tissue defects of the ankle and foot. MJAFI 61:253–255
Ponten B (1981) The fasciocutaneous flap. Its use in soft tissue defects of the lower leg. Br J Plast Surg 34:215
Jeng SF, Wei FC (1997) Distally based sural island flap for foot and ankle reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 99:744–750
Huisinga RL, Houpt P, Dijkstra R, van Storm L JB (1998) The distally based sural artery flap. Ann Plast Surg 41:58–65
Jeng SF, Wei FC, Kuo YR (1999) Salvage of the distal foot using the distally based sural island flap. Ann Plast Surg 43:499–505
Hollier L, Sharma S, Babigumira E, Klebuc M (2002) Versatility of the sural fascocutaneous flap in the coverage of lower extremity wounds. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:1673
Coskunfirat OK, Velidedeoglu HV, Sahin U, Demir Z (1999) Reverse neurofasciocutaneous flaps for soft- tissue coverage of the lower leg. Ann Plast Surg 43:14–20
Bocchi A, Merelli S, Morellini A, Baldassarre S, Caleffi E, Papadia F (2000) Reverse fasciosubcutaneous flap versus distally pedicled sural island flap- two elective methods for distal-third leg reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 45:284–291
Ferreira AC, Reis J, Pinho C, Martins A, Amarante J (2001) The distally based island superficial sural artery flap: clinical experience with 36 flaps. Ann Plast Surg 46:308–313
Almeida MF, Robero da Costa P, Okawa RY (2002) Reverse flow island sural flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:583–591
Fraccalvieri M, Verna G, Dolcet M (2000) The distally based superficial sural flap: our experience in reconstructing the lower leg and foot. Ann Plast Surg 45:32–39
Singh S, Naasan A (2001) Use of distally based superficial sural island artery flaps in acute open fractures of the lower leg. Ann Plast Surg 47:505–510
Conflict of interest
Nil. No funds received in support of this study. No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party in any form related directly or indirectly to th subject of this manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.






Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kansal, S., Goil, P. & Singh, J. Surgical review: the versatile reverse flow sural artery flap for lower 1/3 leg and foot defects: clinical series. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 21, 553–556 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-011-0768-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-011-0768-z