Abstract
Objective
Lumbar facet joint (LFJ) syndrome is one of the common causes of low back pain (LBP). There are different views on percutaneous and endoscopic radiofrequency. The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to explore the therapeutic effect of radiofrequency ablation on LBP originating from LFJ and compare the therapeutic effect of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and endoscopic neurotomy.
Methods
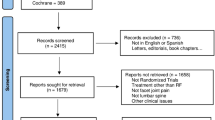
We included randomized controlled trials which compared the efficiency of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and conservative treatment (sham procedures, facet joint injection, physiotherapy, exercise, or oral medication) or compared the efficiency of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and endoscopic neurotomy for LFJ syndrome. We searched in PubMed and Web of Science from inception to March 27, 2023. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4 software.
Results
A total of 11 randomized controlled trials were included. Among them, nine studies were used for evaluating efficiency of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation, and two studies were used for evaluating efficiency of endoscopic neurotomy. Pooled data from two studies reporting outcomes at 1 year did not show a benefit from facet joint denervation by comparing the percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and conservative treatment (standardized mean difference (SMD) = −0.87, 95% confidence interval (CI) [−2.10, 0.37], P = 0.17). There was no significant difference between percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and endoscopic neurotomy at 1-month follow-up (mean difference (MD) = −0.13, 95%CI [−0.18, −0.44], P = 0.41). At 12-month follow-up the pain relief in the endoscopic neurotomy was significantly better than that in the percutaneous radiofrequency ablation group (MD = 1.98, 95%CI [1.60, 2.36], P < 0 .0001).
Conclusion
The LBP was significantly relieved shortly after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Compared with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation, endoscopic neurotomy seems to have a longer effect. A longer follow-up period is needed to confirm its effectiveness.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böning G, Hartwig T, Freyhardt P, de Bucourt M, Teichgräber U, Streitparth F (2021) MR-guided lumbar facet radiofrequency denervation for treatment of patients with chronic low back pain in an open 1.0 Tesla MRI system. Ann Transl Med 9(13):1056. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-633
Chen YS, Liu B, Gu F, Sima L (2022) Radiofrequency denervation on lumbar facet joint pain in the elderly: a randomized controlled prospective trial. Pain Phys 25(8):569–576
Civelek E, Cansever T, Kabatas S, Kircelli A, Yilmaz C, Musluman M, Ofluoglu D, Caner H (2012) Comparison of effectiveness of facet joint injection and radiofrequency denervation in chronic low back pain. Turk Neurosurg 22(2):200–206. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.5207-11.1
Conger A, Burnham T, Salazar F, Tate Q, Golish M, Petersen R, Cunningham S, Teramoto M, Kendall R, McCormick ZL (2020) The Effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation of medial branch nerves for chronic lumbar facet joint syndrome in patients selected by guideline-concordant dual comparative medial branch blocks. Pain Med 21(5):902–909. https://doi.org/10.1093/pm/pnz248
Cosman ER Jr, Dolensky JR, Hoffman RA (2014) Factors that affect radiofrequency heat lesion size. Pain Med 15(12):2020–2036. https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12566
Curtis L, Shah N, Padalia D (2023) Facet joint disease. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing
Du T, Lu G, Li J, Ni B, Shu W, Sun T, Yang D, Zhu H (2022) Pain-free survival after endoscopic rhizotomy versus radiofrequency for lumbar facet joint pain: a real-world comparison study. Pain Phys 25(1):E87–E94
Juch JNS, Maas ET, Ostelo RWJG, Groeneweg JG, Kallewaard JW, Koes BW, Verhagen AP, van Dongen JM, Huygen FJPM, van Tulder MW (2017) Effect of radiofrequency denervation on pain intensity among patients with chronic low back pain: the mint randomized clinical trials. JAMA 318(1):68–81. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.7918
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA; Cochrane Bias Methods Group; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group (2011) The Cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928
Kapetanakis S, Gkantsinikoudis N (2021) Anatomy of lumbar facet joint: a comprehensive review. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 80(4):799–805. https://doi.org/10.5603/FM.a2020.0122
Knezevic NN, Candido KD, Vlaeyen JWS, Van Zundert J, Cohen SP (2021) Low back pain. Lancet 398(10294):78–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00733-9
Lakemeier S, Lind M, Schultz W, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, Timmesfeld N, Foelsch C, Peterlein CD (2013) A comparison of intraarticular lumbar facet joint steroid injections and lumbar facet joint radiofrequency denervation in the treatment of low back pain: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Anesth Analg 117(1):228–235. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182910c4d
Leclaire R, Fortin L, Lambert R, Bergeron YM, Rossignol M (2001) Radiofrequency facet joint denervation in the treatment of low back pain: a placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess efficacy. Spine 26(13):1411–1416. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200107010-00003
Moussa WM, Khedr W (2016) Percutaneous radiofrequency facet capsule denervation as an alternative target in lumbar facet syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 150:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.09.004
Moussa WM, Khedr W, Elsawy M (2020) Percutaneous pulsed radiofrequency treatment of dorsal root ganglion for treatment of lumbar facet syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 199:106253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106253
Ochiai N, Tasto JP, Ohtori S, Takahashi N, Moriya H, Amiel D (2007) Nerve regeneration after radiofrequency application. Am J Sports Med 35(11):1940–1944. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546507304175
Paulsen RT, Carreon L, Busch F, Isenberg-Jørgensen A (2019) A pilot cohort study of lumbar facet joint denervation in patients with chronic low-back pain. Dan Med J 66(3):A5533
Perolat R, Kastler A, Nicot B, Pellat JM, Tahon F, Attye A, Heck O, Boubagra K, Grand S, Krainik A (2018) Facet joint syndrome: from diagnosis to interventional management. Insights Imaging 9(5):773–789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-018-0638-x
Provenzano DA, Buvanendran A, de León-Casasola OA, Narouze S, Cohen SP (2018) Interpreting the MINT randomized trials evaluating radiofrequency ablation for lumbar facet and sacroiliac joint pain: a call from ASRA for better education, study design, and performance. Reg Anesth Pain Med 43(1):68–71. https://doi.org/10.1097/AAP.0000000000000699
Provenzano DA, Watson TW, Somers DL (2015) The interaction between the composition of preinjected fluids and duration of radiofrequency on lesion size. Reg Anesth Pain Med 40(2):112–124. https://doi.org/10.1097/AAP.0000000000000207
Sakuma Y, Ohtori S, Miyagi M, Ishikawa T, Inoue G, Doya H, Koshi T, Ito T, Yamashita M, Yamauchi K, Suzuki M, Moriya H, Takahashi K (2007) Up-regulation of p55 TNF alpha-receptor in dorsal root ganglia neurons following lumbar facet joint injury in rats. Eur Spine J 16(8):1273–1278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0365-3
Shuang F, Hou SX, Zhu JL, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Zhang CL, Tang JG (2015) Clinical anatomy and measurement of the medial branch of the spinal dorsal ramus. Medicine 94(52):e2367. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000002367
Song K, Li Z, Shuang F, Yin X, Cao Z, Zhao H, Qin J, Li Z (2019) Comparison of the effectiveness of radiofrequency neurotomy and endoscopic neurotomy of lumbar medial branch for facetogenic chronic low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. World Neurosurg 126:e109–e115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.251
Starr JB, Gold L, McCormick Z, Suri P, Friedly J (2019) Trends in lumbar radiofrequency ablation utilization from 2007 to 2016. Spine J 19(6):1019–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2019.01.001
Suer M, Wahezi SE, Abd-Elsayed A, Sehgal N (2022) Cervical facet joint pain and cervicogenic headache treated with radiofrequency ablation: a systematic review. Pain Phys 25(3):251–263
Thanos L, Mylona S, Kalioras V, Pomoni M, Batakis N (2004) Percutaneous CT-guided interventional procedures in musculoskeletal system (our experience). Eur J Radiol 50(3):273–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.01.024
van Kleef M, Barendse GA, Kessels A, Voets HM, Weber WE, de Lange S (1999) Randomized trial of radiofrequency lumbar facet denervation for chronic low back pain. Spine 24(18):1937–1942. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-199909150-00013
van Tilburg CW, Stronks DL, Groeneweg JG, Huygen FJ (2016) Randomised sham-controlled double-blind multicentre clinical trial to ascertain the effect of percutaneous radiofrequency treatment for lumbar facet joint pain. Bone Joint J 98-B(11):1526–1533. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.98B11.BJJ-2016-0379.R2
van Wijk RM, Geurts JW, Wynne HJ, Hammink E, Buskens E, Lousberg R, Knape JT, Groen GJ (2005) Radiofrequency denervation of lumbar facet joints in the treatment of chronic low back pain: a randomized, double-blind, sham lesion-controlled trial. Clin J Pain 21(4):335–344. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ajp.0000120792.69705.c9
Walter SG, Schildberg FA, Rommelspacher Y (2018) Endoscopic sacrolumbar facet joint denervation in osteoarthritic and degenerated zygapophyseal joints. Arthrosc Tech 7(12):e1275–e1279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eats.2018.08.014
Woiciechowsky C (2022) Comparison of endoscopic facet joint denervation to the percutaneous technique regarding efficacy in patients with low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Spine 47(17):1187–1193. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000004392
Woiciechowsky C, Richter LM (2020) Endoscopic 4 MHz radiofrequency treatment of facet joint syndrome is more than just denervation: one incision for three facets. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 81(3):238–242. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1698397
Xue Y, Ding T, Wang D, Zhao J, Yang H, Gu X, Feng D, Zhang Y, Liu H, Tang F, Wang W, Lu M, Wu C (2020) Endoscopic rhizotomy for chronic lumbar zygapophysial joint pain. J Orthop Surg Res 15(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1533-y
Zhou Q, Zhou F, Wang L, Liu K (2016) An investigation on the effect of improved X-rays-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation denervation on lumbar facet joint syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 148:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.07.018
Funding
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Foundation of Dalian (2022JJ12SN045) and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2022-MS-322). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DRH and GJ were responsible for the conception and design; DRH, GJ, WB, and LZH were responsible for manuscript writing and revision; DRH, ZJ, MM, WJZ, QWT, and LZH participated in the data analysis; and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper. No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, R., Gao, J., Wang, B. et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and endoscopic neurotomy for lumbar facet joint syndrome: are they good enough?. Eur Spine J 33, 463–473 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-08078-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-08078-5