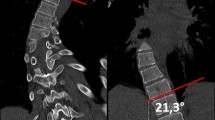
Abstract
Purpose
Preoperative curve assessment is important in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). Our objective is to clarify the role of side-bending radiographs (SBR) and fulcrum-bending radiographs (FBR) in predicting postoperative Cobb angle in nonstructural and structural curves.
Methods
Twenty-five consecutive patients with AIS who underwent correction surgery were included. The Cobb angles of structural and nonstructural curves were determined. Cobb angles were measured based on pre- and postoperative standing anteroposterior radiographs of the whole spine. The Cobb angles of SBR and FBR were measured preoperatively. The difference between the Cobb angle at each bending and the preoperative Cobb angle was defined as the predicted correction angle, whereas the difference between the preoperative Cobb angle and postoperative Cobb angle was defined as the surgical correction angle. The correction index was calculated by dividing the surgical correction angle by the predicted correction angle. The difference between the predicted correction angle and surgical correction angle was defined as the prediction error. We compared SBR and FBR for both structural and nonstructural curves in these terms.
Results
For both curves, the predicted correction angle of FBR was significantly higher than that of SBR, and the correction index of FBR was significantly lower than that of SBR. Patients with a correction index close to 1 and small prediction error had undergone FBR in the structural curve and SBR in the nonstructural curve.
Conclusion
FBR is predictive of postoperative correction angle of the structural curve, whereas SBR is predictive of postoperative correction angle of the nonstructural curve.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AIS:
-
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
- FBR:
-
Fulcrum-bending radiographs
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficients
- PT:
-
Proximal thoracic
- SBR:
-
Side-bending radiographs
References
King HA, Moe JH, Bradford DS, Winter RB (1983) The selection of fusion levels in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65:1302–1313. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-198365090-00012
Lenke LG, Betz RR, Harms J, Bridwell KH, Clements DH, Lowe TG, Blanke K (2001) Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:1169–1181. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200108000-00006
Cheung KM, Luk KD (1997) Prediction of correction of scoliosis with use of the fulcrum bending radiograph. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79:1144–1150. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-199708000-00005
Cheung KM, Lam JW, Samartzis D, Lu WW, Luk KD (2014) The use of a modified fulcrum for fulcrum bending radiographs: a technical note. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 22:248–251. https://doi.org/10.1177/230949901402200229
Li J, Dumonski ML, Samartzis D, Hong J, He S, Zhu X, Wang C, Vaccaro AR, Albert TJ, Li M (2011) Coronal deformity correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients using the fulcrum-bending radiograph: a prospective comparative analysis of the proximal thoracic, main thoracic, and thoracolumbar/lumbar curves. Eur Spine J 20:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1495-6
Schwab F, Blondel B, Chay E, Demakakos J, Lenke L, Tropiano P, Ames C, Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Glassman S, Farcy JP, Lafage V (2014) The comprehensive anatomical spinal osteotomy classification. Neurosurgery 74:112–120; discussion 120. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000182o
Luk KD, Don AS, Chong CS, Wong YW, Cheung KM (2008) Selection of fusion levels in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using fulcrum bending prediction: a prospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:2192–2198. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31817bd86a
Luk KD, Cheung KM, Lu DS, Leong JC (1998) Assessment of scoliosis correction in relation to flexibility using the fulcrum bending correction index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23:2303–2307. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-199811010-00011
Luk KD, Lu DS, Cheung KM, Wong YW (2004) A prospective comparison of the coronal deformity correction in thoracic scoliosis using four different instrumentations and the fulcrum-bending radiograph. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29:560–563. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000106494.14707.b2
Chan CY, Kwan MK, Saravanan S, Saw LB, Deepak AS (2007) The assessment of immediate post-operative scoliosis correction using pedicle screw system by utilising the fulcrum bending technique. Med J Malaysia 62:33–35
Aronsson DD, Stokes IA, Ronchetti PJ, Richards BS (1996) Surgical correction of vertebral axial rotation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: prediction by lateral bending films. J Spinal Disord 9:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002517-199606000-00006
Hay D, Izatt MT, Adam CJ, Labrom RD, Askin GN (2008) The use of fulcrum bending radiographs in anterior thoracic scoliosis correction: a consecutive series of 90 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:999–1005. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31816c8343
Cheung KM, Natarajan D, Samartzis D, Wong YW, Cheung WY, Luk KD (2010) Predictability of the fulcrum bending radiograph in scoliosis correction with alternate-level pedicle screw fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92:169–176. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.H.01831
Li J, Hwang S, Wang F, Chen Z, Wu H, Li B, Wei X, Zhu X, Li M (2013) An innovative fulcrum-bending radiographical technique to assess curve flexibility in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:E1527–E1532. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182a58e89
Klepps SJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bassett GS, Whorton J (2001) Prospective comparison of flexibility radiographs in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:E74–E79. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200103010-00002
Ohrt-Nissen S, Hallager DW, Karbo T, Gehrchen M, Dahl B (2017) Radiographic and functional outcome in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis operated with hook/hybrid versus all-pedicle screw instrumentation-A retrospective study in 149 patients. Spine Deform 5:401–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2017.05.002
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Kim J, Bridwell KH, Cho SK, Cheh G, Sides B (2006) Comparative analysis of pedicle screw versus hybrid instrumentation in posterior spinal fusion of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:291–298. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000197865.20803.d4
Yilmaz G, Borkhuu B, Dhawale AA, Oto M, Littleton AG, Mason DE, Gabos PG, Shah SA (2012) Comparative analysis of hook, hybrid, and pedicle screw instrumentation in the posterior treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop 32:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318250c629
McCall RE, Bronson W (1992) Criteria for selective fusion in idiopathic scoliosis using Cotrel–Dubousset instrumentation. J Pediatr Orthop 12:475–479. https://doi.org/10.1097/01241398-199207000-00011
Winter RB, Lonstein JE, Denis F (2007) How much correction is enough? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32:2641–2643. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31815a5207
Lenke LG, Kuklo TR, Ondra S, Polly DW, Jr. (2008) Rationale behind the current state-of-the-art treatment of scoliosis (in the pedicle screw era). Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:1051–1054. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31816f2865
Shigematsu H, Cheung JP, Bruzzone M, Matsumori H, Mak KC, Samartzis D, Luk KD (2017) Preventing fusion mass shift avoids postoperative distal curve adding-on in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 475:1448–1460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-016-5216-2
Kuklo TR, Lenke LG, Won DS, Graham EJ, Sweet FA, Betz RR, Bridwell KH, Blanke KM (2001) Spontaneous proximal thoracic curve correction after isolated fusion of the main thoracic curve in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:1966–1975. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200109150-00006
Kuklo TR, Potter BK, Polly DW, Jr., Lenke LG (2005) Monaxial versus multiaxial thoracic pedicle screws in the correction of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:2113–2120. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000179260.73267.f4
Menon KV, Tahasildar N, Pillay HM, Anbuselvam M, Jayachandran RK (2014) Patterns of shoulder imbalance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a retrospective observational study. J Spinal Disord Tech 27:401–408. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0000000000000166
Namikawa T, Matsumura A, Kato M, Hayashi K, Nakamura H (2015) Radiological assessment of shoulder balance following posterior spinal fusion for thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis 10 S 18:S18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-7161-10-S2-S18
Acknowledgements
We thank to Shoji Murai, Yu Ymamoto, and Ayaka Inaba for taking appropriate fulcrum bending and side bending radiographs.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KM was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. HS conceived the report and helped to draft the manuscript. MT, AO, SK, YS, YY, MI, and TM collected and organized the patient’s data. HS and YT supervised and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by ethics committee of Nara Medical University (approval code: 3258). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for publication of this study and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Masuda, K., Shigematsu, H., Tanaka, M. et al. The clinical role of preoperative fulcrum-bending and supine side-bending radiographs on the prediction of curve correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 32, 1140–1145 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07603-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07603-w