Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the impact of pelvic balance, physical activity, and fear-avoidance in a cohort of patients undergoing decompression and instrumented fusion for degenerative lumbar stenosis.
Materials and methods
This study includes consecutive patients undergoing decompression and instrumented fusion for degenerative lumbar stenosis by one main surgeon from January 2014 to January 2015. Patients were interviewed by a psychologist and underwent standing whole spine X-ray. Lumbar and pelvic parameters (PI, SS, PT, iPT, LL) were measured by an independent spinal surgeon. Physical activity was measured with the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). The “fear-avoidance” was measured with the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia (TSK). Back pain was assessed by the Graphic Rating Scale (GRS). The disability was assessed by the Roland–Morris Low Back Pain and Disability Questionnaire. Statistical interpretation of the data was performed using SPSS v19 software (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Illinois).
Results
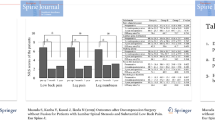
The sample included 51 patients underwent standard posterior laminectomy and instrumented fusion. Surgery has a positive global impact on the perceived low back pain. No significant (Spearman) correlations emerged among pelvic parameters and the pre- and post-surgical GSR. Patients were divided into three groups according to the IPAQ scores after the operation: “inactive” (I), “minimally inactive” (m-I), and “HEPA”. Significant differences emerged between IPAQ and Roland–Morris scores (F(2, 48) = 5.48, p = 0.007): the “inactive” (M(R-M) = 11.3) or “minimally active” (M(R-M) = 9.8) groups scored significantly higher than the “HEPA” group (M(R-M) = 4.7). Tampa scores correlated with gender (rho = −0.408, p = 0.003) and with BMI (rho = −0.369, p = 0.008). Females and obese patients reported higher levels of Tampa scores. Significant relationship was found between Tampa scores and pre-GSR (rho(pre) = 0.250, p = 0.08) and significant with post-surgical GSR (rho(post) = 0.275, p = 0.05) and with post-Roland–Morris score (rho(post) = 0.599, p < 0.01).
Conclusion
The fear-avoidance and the physical inactivity are related to the highest levels of low back pain, more than pelvic imbalance. “Inactive” and “fear-avoidant” patients have also the worst outcome after surgery and the worst level of disability.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinstein JN, Tosteson TD, Lurie JD, Tosteson AN, Blood E, Hanscom B, Herkowitz H, Cammisa F, Albert T, Boden SD, Hilibrand A, Goldberg H, Berven S, An H, SPORT Investigators (2008) Surgical versus nonsurgical therapy for lumbar spinal stenosis. N Engl J Med 358(8):794–810. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0707136
Amundsen T, Weber H, Nordal HJ, Magnaes B, Abdelnoor M, Lilleâs F (2000) Lumbar spinal stenosis: conservative or surgical management? A prospective 10-year study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25(11):1424–1435 (Discussion 1435–1436)
Strömqvist B, Fritzell P, Hägg O, Jönsson B, Sandén B, Swedish Society of Spinal Surgeons (2013) Swespine: the Swedish spine register: the 2012 report. Eur Spine J 22(4):953–974. doi:10.1007/s00586-013-2758-9
Le Huec JC, Faundez A, Dominguez D, Hoffmeyer P, Aunoble S (2015) Evidence showing the relationship between sagittal balance and clinical outcomes in surgical treatment of degenerative spinal diseases: a literature review. Int Orthop 39(1):87–95. doi:10.1007/s00264-014-2516-6 (Epub 2014 Sep 6)
Bayerl SH, Pöhlmann F, Finger T, Onken J, Franke J, Czabanka M, Woitzik J, Vajkoczy P (2015) The sagittal balance does not influence the one year clinical outcome of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis without obvious instability after microsurgical decompression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) (Epub ahead of print)
Van Wilgen CP, Dijkstra PU, Versteegen GJ, Fleuren MJ, Stewart R, van Wijhe M (2009) Chronic pain and severe disuse syndrome: long-term outcome of an inpatient multidisciplinary cognitive behavioural programme. J Rehabil Med 41(3):122–128. doi:10.2340/16501977-0292
Leeuw M, Goossens ME, Linton SJ, Crombez G, Boersma K, Vlaeyen JW (2007) The fear-avoidance model of musculoskeletal pain: current state of scientific evidence. J Behav Med 30(1):77–94 (Epub 20 Dec 2006)
Vlaeyen JWS, Linton SJ (2000) Fear avoidance and its consequences in chronic musculoskeletal pain: a state of the art. Pain 85:317–332
Bortz WM 2nd (1984) The disuse syndrome. West J Med 141(5):691–694
Verbunt JA, Seelen HA, Vleayen JW, van de Heijden GJ, Heuts PH, Pons K, Knottnerus JA (2003) Disuse and deconditioning in chronic low back pain: concepts and hypotheses on contributing mechanisms. Eur J Pain 7:9–21
Kreiner DS, Shaffer WO, Baisden JL, Gilbert TJ, Summers JT, Toton JF, Hwang SW, Mendel RC, Reitman CA, North American Spine Society (2013) An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis (update). Spine J 13(7):734–743. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2012.11.059 (Review)
Boulay C, Tardieu C, Hecquet J, Benaim C, Mouilleseaux B, Marty C, Prat-Pradal D, Legaye J, Duval-Beaupère G, Pélissier J (2006) Sagittal alignment of spine and pelvis regulated by pelvic incidence: standard values and prediction of lordosis. Eur Spine J 15(4):415–422 (Epub 23 Sep 2005)
Vialle R, Levassor N, Rillardon L, Templier A, Skalli W, Guigui P (2005) Radiographic analysis of the sagittal alignment and balance of the spine in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87(2):260–267
Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, Pratt M, Ekelund U, Yngve A, Sallis JF, Oja P (2003) International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(8):1381–1395
Kamada M, Kitayuguchi J, Lee IM, Hamano T, Imamura F, Inoue S, Miyachi M, Shiwaku K (2014) Relationship between physical activity and chronic musculoskeletal pain among community-dwelling Japanese adults. J Epidemiol 24(6):474–483 (Epub 26 Jul 2014)
Miller RP, Kori S, Todd D (1991) The Tampa Scale: a measure of kinesiophobia. Clin J Pain 7(1):51–52
Freyd M (1923) The graphic rating scale. J Educ Psychol 14:83–102
Roland M, Morris R (1983) A study of the natural history of low-back pain. Part II: Development of guidelines for trials of treatment in primary care. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 8(2):145–150
Bener A, Alwash R, Gaber T, Lovasz G (2003) Obesity and low back pain. Coll Antropol. 27(1):95–104
Webb R, Brammah T, Lunt M, Urwin M, Allison T, Symmons D (2003) Prevalence and predictors of intense, chronic, and disabling neck and back pain in the UK general population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28(11):1195–1202
Youdas JW, Garrett TR, Egan KS, Therneau TM (2000) Lumbar lordosis and pelvic inclination in adults with chronic low back pain. Phys Ther 80(3):261–275
Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F (2005) The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30(18):2024–2029
Sigmundsson FG, Jönsson B, Strömqvist B (2014) Preoperative pain pattern predicts surgical outcome more than type of surgery in patients with central spinal stenosis without concomitant spondylolisthesis: a register study of 9051 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 39(3):E199–E210. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000101
Donnarumma P, Tarantino R, Nigro L, Rullo M, Messina D, Diacinti D, Delfini R (2016) Decompression versus decompression and fusion for degenerative lumbar stenosis: analysis of the factors influencing the outcome of back pain and disability. J Spine Surg 2(1):52–58. doi:10.21037/jss.2016.03.07
Perruchoud C, Buchser E, Johanek LM, Aminian K, Paraschiv-Ionescu A, Taylor RS (2014) Assessment of physical activity of patients with chronic pain. Neuromodulation 17:42–47
Bize R, Johnson JA, Plotnikoff RC (2007) Physical activity level and health-related quality of life in the general adult population: a systematic review. Prev Med 45:401–415
Kottke FJ (1966) The effects of limitation of activity upon the human body. JAMA 196(10):825–830
Urban-Baeza A, Zárate-Kalfópulos B, Romero-Vargas S, Obil-Chavarría C, Brenes-Rojas L, Reyes-Sánchez A (2015) Influence of depression symptoms on patient expectations and clinical outcomes in the surgical management of spinal stenosis. J Neurosurg Spine 22(1):75–79. doi:10.3171/2014.10.SPINE131106
Zale EL, Ditre JW (2015) Pain-related fear, disability, and the fear-avoidance model of chronic pain. Curr Opin Psychol 5:24–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donnarumma, P., Presaghi, F., Tarantino, R. et al. The impact of pelvic balance, physical activity, and fear-avoidance on the outcome after decompression and instrumented fusion for degenerative lumbar stenosis. Eur Spine J 26, 428–433 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4644-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4644-8