Abstract
Purpose
Acute paraplegia due to thoracic intervertebral disc protrusion and calcification is rare. The purpose of this study was to report two cases with acute paraplegia due to a calcified thoracic disc prolapse, and discuss its clinical diagnosis and surgical treatment with literature reviews.
Methods
These two cases were verified by patient history, physical examination, laboratory examination, CT and MRI studies, and pathological findings.
Results
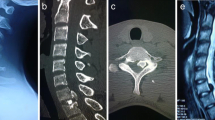
CT scan revealed disc calcification and protrusion at the T11–12 level in case 1 and at the T10–11 level in case 2, respectively. MRI images revealed severe spinal cord compression with a hyperintense central core and surrounding hypointense area in two cases, which were directly connected to the calcified intervertebral nucleus pulposus. Pathological examination revealed calcium deposition. Patients underwent discectomy followed by interbody fusion, and satisfactory therapeutic outcomes were obtained.
Conclusions
We suggest that decompression surgery should be carried out as early as possible for patients with early spinal myelopathy or paraplegia caused by a calcified protruded disc.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinberger A, Myers AR (1978) Intervertebral disc calcification in adults: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 8:69–75. doi:10.1016/0049-0172(78)90035-5
Nogueira-Barbosa MH, da Silva Herrero CFP, Pasqualini W, Defino HLA (2013) Calcific discitis in an adult patient with intravertebral migration and spontaneous remission. Skelet Radiol 42:1161–1164
Okada Y, Shimizu K, Ido K, Kotani S (1997) Multiple thoracic disc herniations: case report and review of the literature. Spinal Cord 35:183–186
Coscia MF, Strate RW (1993) Calcified thoracic disc herniation with paraparesis. A case report. Acta Orthop Scand 64:489–490
Major NM, Helms CA, Genant HK (1993) Calcification demonstrated as high signal intensity on T1-weighted MR images of the disks of the lumbar spine. Radiology 189:494–496. doi:10.1148/radiology.189.2.8210379
Bangert BA, Modic MT, Ross JS, Obuchowski NA, Perl J, Ruggieri PM, Masaryk TJ (1995) Hyperintense disks on T1-weighted MR images: correlation with calcification. Radiology 195:437–443. doi:10.1148/radiology.195.2.7724763
Henkelman RM, Watts JF, Kucharczyk W (1991) High signal intensity in MR images of calcified brain tissue. Radiology 179:199–206. doi:10.1148/radiology.179.1.1848714
Dell LA, Brown MS, Orrison WW, Eckel CG, Matwiyoff NA (1988) Physiologic intracranial calcification with hyperintensity on MR imaging: case report and experimental model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 9:1145–1148
Park SM, Kim ES, Sung DH (2005) Cervical radiculopathy caused by neural foraminal migration of a herniated calcified intervertebral disk in childhood: a case report. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:2214–2217. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2005.06.009
Peck FC Jr (1957) A calcified thoracic intervertebral disk with herniation and spinal cord compression in a child; case report. J Neurosurg 14:105–109. doi:10.3171/jns.1957.14.1.0105
McAllister VL, Sage MR (1976) The radiology of thoracic disc protrusion. Clin Radiol 27:291–299
Paolini S, Ciappetta P, Guiducci A, Principi M, Missori P, Delfini R (2005) Foraminal deposition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in the thoracic spine: possible relationship with disc herniation and implications for surgical planning. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg Spine 2:75–78. doi:10.3171/spi.2005.2.1.0075
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest with this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, B., Chen, B., Zou, Yw. et al. Thoracic intervertebral disc calcification and herniation in adults: a report of two cases. Eur Spine J 25 (Suppl 1), 118–123 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-4214-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-4214-5