Abstract
Purpose
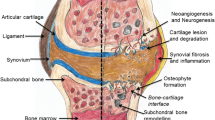
Intervertebral disc degeneration is a common disease that usually starts from the third decade of life and it represents a significant cause of socio-economic problems. The accepted surgical treatment for disc degeneration is disc removal and vertebral fusion or, in selected cases, intervertebral disc arthroplasty. Several studies have demonstrated the ability of platelet rich plasma (PRP) to stimulate cell proliferation and extracellular matrix regeneration. However, literature results are still limited and more studies are required to clarify the role of PRP in the prevention or in the treatment of degenerative disc disease. The aim of this review is to summarize and critically analyze the current preclinical evidence about the use of PRP in intervertebral disc degeneration.
Methods
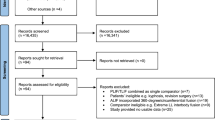
Literature search was performed through various combinations of the following keywords: Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, Platelet Rich Plasma, PRP, Intervertebral disc regeneration. Papers included in our review cover the period between 2006 and 2014. The PRISMA 2009 checklist was followed.
Results
At the end of the review process, 12 articles were included in our final manuscript, including 6 “in vitro” and 6 “in vivo” studies. All the included studies lead to positive preclinical results. No standardization of methodological analysis was observed.
Conclusion
It is not possible to draw definitive evidence about the use of PRP in IVD regeneration. We advise a proper standardization of the methodological analysis in order to compare the available data and achieve definitive results. This should be the cornerstone for future clinical applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Habibi Z, Maleki F, Meybodi AT, Mahdavi A, Saberi H (2014) Lumbosacral sagittal alignment in association to intervertebral disc diseases. Asian Spine J. 8(6):813–819
Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J, Menage J (2006) Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(Suppl 2):10–14
Shankar H, JA, Scarlett, SE. Abram (2009) Anatomy and pathophysiology of intervertebral disc disease. Tech Reg Anesth Pain Manag 13:67–75
Neroni M, Gazzeri R, Conforti G, Visocchi M (2014) State of art of recurrent lumbar disk herniation, interspinous and interlumbar fusions. J Neurosurg Sci 58(2 Suppl 1):45–48
Migacz K, Chłopek J, Morawska-Chochół A, Ambroziak M (2014) Gradient composite materials for artificial intervertebral discs. Acta Bioeng Biomech 16(3):3–12
Wang SZ, Rui YF, Lu J, Wang C (2014) Cell and molecular biology of intervertebral disc degeneration: current understanding and implications for potential therapeutic strategies. Cell Prolif 47(5):381–390
Sivan SS, Wachtel E, Roughley P (2014) Structure, function, aging and turnover of aggrecan in the intervertebral disc. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840(10):3181–3189
Freemont AJ (2009) The cellular pathobiology of the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48(1):5–10
Phillips KL, Jordan-Mahy N, Nicklin MJ, Le Maitre CL (2013) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist deficient mice provide insights into pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis 72(11):1860–1867
Ellman MB, Kim JS, An HS, Chen D, KC R, An J, Dittakavi T, van Wijnen AJ, Cs-Szabo G, Li X, Xiao G, An S, Kim SG, Im HJ (2012) Toll-like receptor adaptor signaling molecule MyD88 on intervertebral disk homeostasis: in vitro, ex vivo studies. Gene 505(2):283–290
Wang M, Tang D, Shu B, Wang B, Jin H, Hao S, Dresser KA, Shen J, Im HJ, Sampson ER, Rubery PT, Zuscik MJ, Schwarz EM, O’Keefe RJ, Wang Y, Chen D (2012) Conditional activation of β-catenin signaling in mice leads to severe defects in intervertebral disc tissue. Arthritis Rheum 64(8):2611–2623
Di Martino A, Vaccaro AR, Yung Lee J, Denaro V, Lim MR (2005) Nucleus pulposus replacement: basic science and indications for clinical use. Spine 30(16 Suppl):S16–S22
Di Martino A, Merlini L, Faldini C (2013) Autoimmunity in intervertebral disc herniation: from bench to bedside. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17(12):1461–1470
Hegewald AA, Ringe J, Sittinger M et al (2008) Regenerative treatment strategies in spinal surgery. Front Biosci 13:1507–1525
Gou S, Oxentenko SC, Eldrige JS, Xiao L, Pingree MJ, Wang Z, Perez-Terzic C, Qu W (2014) Stem cell therapy for intervertebral disk regeneration. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 93(11 Suppl 3):S122–S131
Sun Z, Luo B, Liu ZH, Samartzis D, Liu Z, Gao B, Huang L, Luo ZJ (2015) Adipose-derived stromal cells protect intervertebral disc cells in compression: implications for stem cell regenerative disc therapy. Int J Biol Sci 11(2):133–143
Gantenbein B, Calandriello E, Wuertz-Kozak K, Benneker LM, Keel MJ, Chan SC (2014) Activation of intervertebral disc cells by co-culture with notochordal cells, conditioned medium and hypoxia. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15:422
Masuda K (2008) Biological repair of the degenerated intervertebral disc by the injection of growth factors. Eur Spine J 17(Suppl 4):441–451
Tolonen J, Grönblad M, Vanharanta H et al (2006) Growth factor expression in degenerated intervertebral disc tissue. An immunohistochemical analysis of transforming growth factor beta, fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor. Eur Spine J 15:588–596
Thompson JP, Oegema TR Jr, Bradford DS (1991) Stimulation of mature canine intervertebral disc by growth factors. Spine 16:253–260
Risbud MV, Di Martino A, Guttapalli A, Seghatoleslami R, Denaro V, Vaccaro AR, Albert TJ, Shapiro IM (2006) Towards an optimum system for intervertebral disc organ culture: TGF-b3 enhances nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus survival and function through modulation of TGFb-R expression and ERK signaling. Spine 31(8):884–890
Chujo T, An HS, Akeda K et al (2006) Effects of growth differentiation factor-5 on the intervertebral disc–in vitro bovine study and in vivo rabbit disc degeneration model study. Spine 31:2909–2917
Tolonen J, Grönblad M, Vanharanta H et al (2006) Growth factor expression in degenerated intervertebral disc tissue. An immunohistochemical analysis of transforming growth factor beta, fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor. Eur Spine J 15:588–596
Vadalà G, Russo F, Di Martino A, Denaro V (2015) Intervertebral disc regeneration: from the degenerative cascade to molecular therapy and tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 9(6):679–690
Lucarelli E, Beccheroni A, Donati D, Sangiorgi L, Cenacchi A, Del Vento AM, Meotti C, Bertoja AZ, Giardino R, Fornasari PM, Mercuri M, Picci P (2003) Platelet-derived growth factors enhance proliferation of human stromal stem cells. Biomaterials 24(18):3095–3100
Sánchez AR, Sheridan PJ, Kupp LI (2003) Is platelet-rich plasma the perfect enhancement factor? A current review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 18:93–103
Kon E, Filardo G, Di Martino A et al (2011) Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to treat sports injuries: evidence to support its use. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:516–527
Andia I, Sánchez M, Maffulli N (2011) Platelet rich plasma therapies for sports muscle injuries: any evidence behind clinical practice? Expert Opin Biol Ther 11:509–518
Kon E, Mandelbaum B, Buda R et al (2011) Platelet-rich plasma intraarticular injection versus hyaluronicacid viscosupplementation as treatments for cartilage pathology: from early degeneration to osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy 27(11):1490–1501
Sánchez M, Guadilla J, Fiz N, Andia I (2012). Ultrasound-guided platelet rich plasma injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51(1):144
Bernuzzi G, Petraglia F, Pedrini MF et al (2014) Use of platelet-rich plasma in the care of sports injuries: our experience with ultrasound-guided injection. Blood Transfus 12(Suppl 1):s229–s234
Kepler CK, Anderson DG, Tannoury C, Ponnappan RK (2011) Intervertebral disk degeneration and emerging biologic treatments. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 19(9):543–553
Akeda K, An HS, Pichika R, Attawia M, Thonar EJ, Lenz ME, Uchida A, Masuda K (2006) Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) stimulates the extracellular matrix metabolism of porcine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus cells cultured in alginate beads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31(9):959–66
Mietsch A, Neidlinger-Wilke C, Schrezenmeier H, Mauer UM, Friemert B, Wilke HJ, Ignatius A (2013) Evaluation of platelet-rich plasma and hydrostatic pressure regarding cell differentiation in nucleus pulposus tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 7(3):244–252
Liu MC, Chen WH, Wu LC, Hsu WC, Lo WC, Yeh SD, Wang MF, Zeng R, Deng WP (2014) Establishment of a promising human nucleus pulposus cell line for intervertebral disc tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 20(1):1–10
Pirvu TN, Schroeder JE, Peroglio M, Verrier S, Kaplan L, Richards RG, Alini M, Grad S (2014) Platelet-rich plasma induces annulus fibrosus cell proliferation and matrix production. Eur Spine J 23(4):745–753
Chen WH, Lo WC, Lee JJ, Su CH, Lin CT, Liu HY, Lin TW, Lin WC, Huang TY, Deng WP (2006) Tissue-engineered intervertebral disc and chondrogenesis using human nucleus pulposus regulated through TGF-beta1 in platelet-rich plasma. J Cell Physiol 3:744–754
Kim HJ, Yeom JS, Koh YG, Yeo JE, Kang KT, Kang YM, Chang BS, Lee CK (2014) Anti-inflammatory effect of platelet-rich plasma on nucleus pulposus cells with response of TNF-α and IL-1J Orthop Res 32(4): 551–556
Nagae M, Ikeda T, Mikami Y, Hase H, Ozawa H, Matsuda K, Sakamoto H, Tabata Y, Kawata M, Kubo T (2007) Intervertebral disc regeneration using platelet-rich plasma and biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres. Tissue Eng 13(1):147–158
Sawamura K, Ikeda T, Nagae M, Okamoto S, Mikami Y, Hase H, Ikoma K, Yamada T, Sakamoto H, Matsuda K, Tabata Y, Kawata M, Kubo T (2009) Characterization of in vivo effects of platelet-rich plasma and biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres on degenerated intervertebral discs. Tissue Eng Part A 15(12):3719–3727
Obata S, Akeda K, Imanishi T, Masuda K, Bae W, Morimoto R, Asanuma Y, Kasai Y, Uchida A, Sudo A (2012) Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma-releasate on intervertebral disc degeneration in the rabbit anular puncture model: a preclinical study. Arthritis Res Ther. 14(6):R241
Hu X, Wang C, Rui Y, Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi (2012) An experimental study on effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on treatment of early intervertebral disc degeneration 26(8):977–983 (Chinese)
Gullung GB, Woodall JW, Tucci MA, James J, Black DA, McGuire RA (2011) Platelet-rich plasma effects on degenerative disc disease: analysis of histology and imaging in an animal model. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2(4):13–18
Chen WH, Liu HY, Lo WC, Wu SC, Chi CH, Chang HY, Hsiao SH, Wu CH, Chiu WT, Chen BJ, Deng WP (2009) Intervertebral disc regeneration in an ex vivo culture system using mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials 30(29):5523–5533
Johnson WE, Eisenstein SM, Roberts S (2001) Cell cluster formation in degenerate lumbar intervertebral discs is associated with increased disc cell proliferation. Connect Tissue Res 42:197–207
Roberts S, Caterson B, Menage J, Evans EH, Jaffray DC, Eisenstein SM (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanase: their role in disorders of the human intervertebral disc. Spine 25:3005–3013
Oegema TR Jr, Johnson SL, Aguiar DJ, Ogilvie JW (2000) Fibronectin and its fragments increase with degeneration in the human intervertebral disc. Spine 25:2742–2747
Formica M, Berjano P, Cavagnaro L, Zanirato A, Piazzolla A, Formica C (2014) Extreme lateral approach to the spine in degenerative and post traumatic lumbar diseases: selection process, results and complications. Eur Spine J 23(Suppl 6):684–692
Allain J, Delecrin J, Beaurain J, Poignard A, Vila T, Flouzat-Lachaniette CH (2014) Stand-alone ALIF with integrated intracorporeal anchoring plates in the treatment of degenerative lumbar disc disease: a prospective study on 65 cases. Eur Spine J 23(10):2136–2143
Høy K, Bünger C, Niederman B, Helmig P, Hansen ES, Li H, Andersen T (2013) Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus posterolateral instrumented fusion (PLF) in degenerative lumbar disorders: a randomized clinical trial with 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J 22(9):2022–2029
Cavagnaro L, Basso M, Alessio Mazzola M, Formica M (2014) Lumbar traction in the management of low back pain: a survey of latest results. J Nov Physiother 4:5
Wegner I, Widyahening IS, van Tulder MW, Blomberg SE, de Vet HC (2013) Traction for low-back pain with or without sciatica. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 8:CD003010
Anderson DG, Albert TJ, Fraser JK, Risbud M, Wuisman P, Meisel HJ, Tannoury C, Shapiro I, Vaccaro AR (2005) Cellular therapy for disc degeneration. Spine 30:S14–S19
Alini M, Roughley PJ, Antoniou J, Stoll T, Aebi M (2002) A biological approach to treating disc degeneration: not for today, but may be for tomorrow. Eur Spine J 11:S215–S220
Crevensten G, Walsh AJ, Ananthakrishnan D, Page P, Wahba GM, Lotz JC, Berven S (2004) Intervertebral disc cell therapy for regeneration: mesenchymal stem cell implantation in rat intervertebral discs. Ann Biomed Eng 32:430–434
Fontana G, See E, Pandit A (2015) Current trends in biologics delivery to restore intervertebral disc anabolism. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 84:146–158
Carter CA, Jolly DG, Worden CE Sr, Hendren DG, Kane CJ (2003) Platelet-rich plasma gel promotes differentiation and regeneration during equine wound healing. Exp Mol Pathol 74(3):244–255
Weibrich G, Hansen T, Kleis W et al (2004) Effect of platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma on peri-implant bone regeneration. Bone 34:665–671
Marx RE (2001) Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): what is PRP and what is not PRP? Implant Dent 10:225–228
Castillo TN, Pouliot MA, Kim HJ et al (2011) Comparison of growth factor and platelet concentration from commercial platelet-rich plasma separation systems. Am J Sports Med 39:266–271
Orozco L, Soler R, Morera C, Alberca M, Sánchez A, García-Sancho J (2011) Intervertebral disc repair by autologous mesenchymal bone marrow cells: a pilot study. Transplantation 92(7):822–828
Akeda K, Imanishi T, Ohishi K, Masuda K, Uchida A, Sakakibara T, Kasai Y, Sudo A (2012) intradiscal injection of autologous platelet-rich-plasma for the treatment of lumbar disc degeneration preliminary prospective clinical trial for discogenic low back pain patients. Poster No. 2194. ORS 2012 Annual Meeting
Wang SZ, Rui YF, Tan Q et al (2013) Enhancing intervertebral disc repair and regeneration through biology: platelet-rich plasma as an alternative strategy. Arthritis Res Ther 15:220
Wang SZ, Chang Q, Lu J, Wang C (2015) Growth factors and platelet-rich plasma: promising biological strategies for early intervertebral disc degeneration. Int Orthop
Landis SC et al (2012) A call for transparent reporting to optimize the predictive value of preclinical research. Nature 490(7419):187–191
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Prof. Roberta Aronica for English revision of the current manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Formica, M., Cavagnaro, L., Formica, C. et al. What is the preclinical evidence on platelet rich plasma and intervertebral disc degeneration?. Eur Spine J 24, 2377–2386 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-4189-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-4189-2