Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the feasibility and clinical improvement of a total posterior arthroplasty system in the surgical management of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis and or spinal stenosis.
Methods
During a 1-year period (June 2006 to July 2007), ten patients were enrolled in a non-randomized prospective clinical study. The primary indication was neurogenic claudication due to spinal stenosis with single-level degenerative spondylolisthesis. Patients were evaluated with X-rays and MRI scans, visual analog scale (VAS) for back and leg pain, the Oswestry disability questionnaire, and the SF-36 health survey preoperatively, at 6 weeks, 3 months and 6 months and at 1, 2, 3 and 7 years postoperatively.
Results
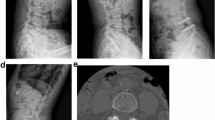
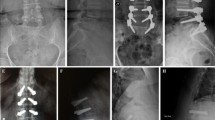
The VAS score for back pain dropped from 56.2 preoperatively to 12.5 at 6 weeks and 19 at 7 years follow-up. The VAS score for worse leg pain dropped from 83.5 before surgery to 13 at 6 weeks and 8.8 at 7 years follow-up. The ODI dropped from 49.1 preoperatively to 13.5 at 6 weeks and 7.8 at 7 years follow-up. MRI examination at 7 years after surgery did not demonstrate stenosis adjacent to the stabilized segment. Spondylolisthesis did not progress in any of the cases. One patient had a symptomatic L3–L4 far lateral disc herniation 5 years after surgery whose symptoms resolved with non-operative treatment. In one patient, conversion to posterolateral fusion was performed due to an early device malfunction.
Conclusion
In patients with spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis, decompression and posterior arthroplasty with the TOPS System can maintain clinical improvement and radiologic stability over time.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen T, Christensen FB, Laursen M, Høy K, Hansen ES, Bünger C (2001) Smoking as a predictor of negative outcome in lumbar spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:2623–2628
Aota Y, Kumano K, Hirabayashi S (1995) Postfusion instability at the adjacent segments after rigid pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. J Spinal Disord 8:464–473
Atlas SJ, Delitto A (2006) Spinal stenosis: surgical versus nonsurgical treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 443:198
Bassewitz H, Herkowitz H (2001) Lumbar stenosis with spondylolisthesis: current concepts of surgical treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 384:54–60
Bridwell KH, Sedgewick TA, O’Brien MF et al (1993) The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 6:461–472
Eck JC, Humphreys SC, Hodges SD (1999) Adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion: a review of clinical, biomechanical, and radiologic studies. Am J Orthop 28:336–340
Glassman SD, Rose SM, Dimar JR, Puno RM, Campbell MJ, Johnson JR (1998) The effect of postoperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug administration on spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23:834–838
Hambly MF, Wiltse LL, Raghavan N et al (1998) The transition zone above a lumbosacral fusion. Spine 23:1785–1792
Harrop J, Youssef J, Maltenfort M et al (2008) Lumbar adjacent segment degeneration and disease after arthrodesis and total disc arthroplasty. Spine 33:1701–1707
Herkowitz HN (1995) Spine update. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine 20:1084–1090
Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT (1991) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:802–808
Jacobsen S, Sonne-Holm S, Rovsing H et al (2007) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: an epidemiological perspective: the Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study. Spine 32:120–125
Johnsson KE, Willner S, Johnsson K (1986) Postoperative instability after decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 11:107–110
Katz JN, Lipson SJ, Larson MG et al (1991) The outcome of decompressive laminectomy for degenerative lumbar stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:809–816
Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Wedge JH, Yong Hing K, Reilly J (1978) Pathology and pathogenesis of lumbar spondylosis and stenosis. Spine 3:319–328
Kornblum MB, Fischgrund JS, Herkowitz HN, Abraham DA, Berkower DL, Ditkoff JS (2004) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29:726–733
Lee CK (1998) Accelerated degeneration of the segment adjacent to a lumbar fusion. Spine 13:375–377
Lombardi JS, Wiltse LL, Reynolds J et al (1985) Treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 10:821–827
Matsunaga S, Ijiri K, Hayashi K (2000) Nonsurgically managed patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis: a 10- to 18-year follow-up study. J Neurosurg 93:194–198
Meyers K, Tauber M, Sudin Y, Fleischer S, Arnin U, Girardi F, Wright T (2008) Use of instrumented pedicle screws to evaluate load sharing in posterior dynamic stabilization systems. Spine J 8:926–932
Rahm MD, Hall BB (1996) Adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion with instrumentation: a retrospective study. J Spinal Disord 9:392–400
Schlegel JD, Smith JA, Schleusener RL (1996) Lumbar motion segment pathology adjacent to thoracolumbar, lumbar, and lumbosacral fusions. Spine 21:970–981
Sears WR, Sergides IG, Kazemi N, Smith M, White GJ, Osburg B (2011) Incidence and prevalence of surgery at segments adjacent to a previous posterior lumbar arthrodesis. Spine J 11:11–20
Stoll TM, Dubois G, Schwarzenbach O (2002) The dynamic neutralization system for the spine: a multi-center study of a novel non-fusion system. Eur Spine J 11:S170–S178
Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Zhao W, Blood EA, Tosteson AN, Birkmeyer N, Herkowitz H, Longley M, Lenke L, Emery S, Hu SS (2009) Surgical compared with nonoperative treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. Four-year results in the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) randomized and observational cohorts. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:1295–1304
Wild A, Jaeger M, Bushe C, Raab P, Krauspe R (2001) Biomechanical analysis of Graf’s dynamic spine stabilisation system ex vivo. Biomed Tech (Berl) 46:290–294
Wilke JH, Schmidt H, Werner K, Schmoltz W, Drumm J (2006) Biomechanical evaluation of a new total posterior-element replacement system. Spine 24:2790–2796
Wright T, Tauber M, Meyers K, Sudin Y, Fleischer S, Arnin U, Girardi F (2005) The biomechanics of posterior motion preservation systems. Spine J 7:S143–S144
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Assaf Harofeh Medical Center.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anekstein, Y., Floman, Y., Smorgick, Y. et al. Seven years follow-up for total lumbar facet joint replacement (TOPS) in the management of lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 24, 2306–2314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3850-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3850-0