Abstract
Purpose
To determine the reliability of pedicle screws placed in children younger than 7 years of age, and to evaluate the effect of pedicle screw insertion on further growth of the vertebra and spinal canal.
Methods
A retrospective study of 35 consecutive patients through Jan 2003–Dec 2010 for congenital scoliosis in <7 years children was performed at one spine center. Patients undergoing pedicle screw instrumentation of at least two levels, which had been followed-up for at least 24 months were included. Measurements were performed in instrumented and adjacent non-instrumented levels. The effect of pedicle screw insertion on further growth was evaluated.
Results
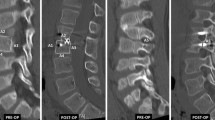
The average age at surgery was 4.4 year (53 months, range, 23–84 months). 190 segments in 35 patients met the inclusion criteria. 77 segments had no screws and 113 had at least one screw. There was a significant difference between the pre-operative and final follow-up values of the measurement of spinal canal and vertebral body parameters (P < 0.001). No significant difference existed between growth rates of vertebral bodies and the sagittal diameters of spinal canal with or without screws. The growth rates of vertebral bodies in lumbar spine were higher than in thoracic spine in both instrumented and adjacent groups.
Conclusion
Pedicle screw instrumentation does not cause a retardation effect on the development of vertebral bodies and the spinal canal in children at an early age. It is a safe and reliable procedure to achieve a stable fixation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liljenqvist U, Hackenberg L, Link T, Halm H (2001) Pullout strength of pedicle screws versus pedicle and laminar hooks in the thoracic spine. Acta Orthop Belg 67:157–163
Lehman RA Jr, Polly DW Jr, Kuklo TR, Cunningham B, Kirk KL, Belmont PJ Jr (2003) Straight-forward versus anatomic trajectory technique of thoracic pedicle screw fixation: a biomechanical analysis. Spine 28:2058–2065
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Cho YS, Riew KD (2004) Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine 29:333–342
Liljenqvist U, Lepsien U, Hackenberg L, Niemeyer T, Halm H (2002) Comparative analysis of pedicle screw and hook instrumentation in posterior correction and fusion of idiopathic thoracic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 11:336–343
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Kim J, Bridwell KH, Cho SK, Cheh G, Sides B (2006) Comparative analysis of pedicle screw versus hybrid instrumentation in posterior spinal fusion of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 31:291–298
Dobbs MB, Lenke LG, Kim YJ, Kamath G, Peelle MW, Bridwell KH (2006) Selective posterior thoracic fusions for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: comparison of hooks versus pedicle screws. Spine 31:2400–2404
Baghdadi YM, Larson AN, McIntosh AL, Shaughnessy WJ, Dekutoski MB, Stans AA (2013) Complications of pedicle screws in children 10 years or younger: a case control study. Spine 38:E386–E393
Vital JM, Beguiristain JL, Algara C, Villas C, Lavignolle B, Grenier N, Sénégas J (1989) The neurocentral vertebral cartilage: anatomy, physiology and physiopathology. Surg Radiol Anat 11:323–328
Maat GJ, Matricali B, van Persijn van Meerten EL (1996) Postnatal development and structure of the neurocentral junction. Its relevance for spinal surgery. Spine 21: 661–666
Yamazaki A, Mason DE, Caro PA (1998) Age of closure of the neurocentral cartilage in the thoracic spine. J Pediatr Orthop 18:168–172
Rajwani T, Bhargava R, Moreau M, Mahood J, Raso VJ, Jiang H, Bagnall KM (2002) MRI characteristics of the neurocentral synchondrosis. Pediatr Radiol 32:811–816
Rajwani T, Hilang EM, Secretan C, Bhargava R, Lambert R, Moreau M, Mahood J, Raso VJ, Bagnall KM (2002) The components of the magnetic resonance image of the neurocentral junction. Stud Health Technol Inform 91:235–240
Cil A, Yazici M, Daglioglu K, Aydingoz U, Alanay A, Acaroglu RE, Gulsen M, Surat A (2005) The effect of pedicle screw placement with or without application of compression across the neurocentral cartilage on the morphology of the spinal canal and pedicle in immature pigs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30(11):1287–1293
Fekete TF, Kleinstück FS, Mannion AF, Kendik ZS, Jeszenszky DJ (2011) Prospective study of the effect of pedicle screw placement on development of the immature vertebra in an in vivo porcine model. Eur Spine J 20(11):1892–1898
Yilmaz G, Demirkiran G, Ozkan C, Daglioglu K, Pekmezci M, Alanay A, Yazici M (2009) The effect of dilation of immature pedicles on pullout strength of the screws: part 2: In vivo study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34(22):2378–2383
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Allardyce TJ et al (1995) Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part I: morphometric analysis of the thoracic vertebrae. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:1193–1199
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Balderston RA et al (1995) Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part II: an anatomical and radiographic assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:1200–1206
Suk SI, Kim W, Lee S et al (2001) Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformity: are they really safe? Spine 26:2049–2057
Belmont PJ Jr, Klemme WR, Robinson M et al (2002) Accuracy of thoracic pedicle screws in patients with and without coronal plane spinal deformities. Spine 27:1558–1566
Ruf M, Harms J (2002) Pedicle screws in 1- and 2-year-old children: technique, complications, and effect on further growth. Spine 27:E460–E466
Li J, Lü GH, Wang B, Wang XB, Lu C, Kang YJ (2013) Pedicle screw implantation in the thoracic and lumbar spine of 1-4-year-old children: evaluating the safety and accuracy by a computer tomography follow-up. J Spinal Disord Tech 26(2):E46–E52
Olgun ZD, Demirkiran G, Ayvaz M, Karadeniz E, Yazici M (2012) The effect of pedicle screw insertion at a young age on pedicle and canal development. Spine 37:1778–1784
Zhang H, Sucato DJ, Nurenberg P, McClung A (2010) Morphometric analysis of neurocentral synchondrosis using magnetic resonance imaging in the normal skeletally immature spine. Spine 35:76–82
Ginsburg G, Schwend R (2010) Neurocentral synchondrosis behavior in cadaveric vertebrae in skeletally immature spines. In: Paper presented at: fourth international congress on early onset scoliosis and growing spine; Toronto, Canada
Zindrick MR, Knight GW, Sartori MJ, Carnevale TJ, Patwardhan AG, Lorenz MA (2000) Pedicle morphology of the immature thoracolumbar spine. Spine 25:2726–2735
Porter RW, Pavitt D (1987) The vertebral canal: I. Nutrition and development, an archaeological study. Spine 12:901–906
Dimeglio A (2001) Growth in pediatric orthopaedics. J Pediatr Orthop 21:549–555
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272053).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests related to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, X., Shen, J., Zhang, J. et al. X-Ray assessment of the effect of pedicle screw on vertebra and spinal canal growth in children before the age of 7 years. Eur Spine J 23, 520–529 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3035-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3035-7