Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed at deriving a lordosis predictive equation using the pelvic incidence and to establish a simple prediction method of lumbar lordosis for planning lumbar corrective surgery in Asians.
Methods
Eighty-six asymptomatic volunteers were enrolled in the study. The maximal lumbar lordosis (MLL), lower lumbar lordosis (LLL), pelvic incidence (PI), and sacral slope (SS) were measured. The correlations between the parameters were analyzed using Pearson correlation analysis. Predictive equations of lumbar lordosis through simple regression analysis of the parameters and simple predictive values of lumbar lordosis using PI were derived.
Results
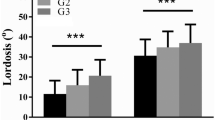
The PI strongly correlated with the SS (r = 0.78), and a strong correlation was found between the SS and LLL (r = 0.89), and between the SS and MLL (r = 0.83). Based on these correlations, the predictive equations of lumbar lordosis were found (SS = 0.80 + 0.74 PI (r = 0.78, R 2 = 0.61), LLL = 5.20 + 0.87 SS (r = 0.89, R 2 = 0.80), MLL = 17.41 + 0.96 SS (r = 0.83, R 2 = 0.68). When PI was between 30° to 35°, 40° to 50° and 55° to 60°, the equations predicted that MLL would be PI + 10°, PI + 5° and PI, and LLL would be PI – 5°, PI – 10° and PI – 15°, respectively.
Conclusion
This simple calculation method can provide a more appropriate and simpler prediction of lumbar lordosis for Asian populations. The prediction of lumbar lordosis should be used as a reference for surgeons planning to restore the lumbar lordosis in lumbar corrective surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernhardt M, Bridwell KH (1989) Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of the normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 14:717–721
Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J, Roussouly P, Labelle H (2005) Analysis of the sagittal balance of the spine and pelvis using shape and orientation parameters. J Spinal Disord Tech 18:40–47
Boulay C, Tardieu C, Hecquet J, Benaim C, Mouilleseaux B, Marty C, Prat-Pradal D, Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Pelissier J (2006) Sagittal alignment of spine and pelvis regulated by pelvic incidence: standard values and prediction of lordosis. Eur Spine J 15:415–422
Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, Kim JH, Kang SB, Kim HS, Oh SJ (2010) Risk factors of sagittal decompensation after long posterior instrumentation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:1595–1601
During J, Goudfrooij H, Keessen W, Beeker TW, Crowe A (1985) Toward standards for posture. Postural characteristics of the lower back system in normal and pathologic conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 10:83–87
Duval-Beaupere G, Schmidt C, Cosson P (1992) A Barycentremetric study of the sagittal shape of spine and pelvis: the conditions required for an economic standing position. Ann Biomed Eng 20:451–462
Farcy JP, Schwab FJ (1997) Management of flatback and related kyphotic decompensation syndromes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22:2452–2457
Gangnet N, Dumas R, Pomero V, Mitulescu A, Skalli W, Vital JM (2006) Three-dimensional spinal and pelvic alignment in an asymptomatic population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:E507–E512
Gelb DE, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Blanke K, McEnery KW (1995) An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in 100 asymptomatic middle and older aged volunteers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20:1351–1358
Hong JY, Suh SW, Modi HN, Hur CY, Song HR, Park JH (2010) Reliability analysis for radiographic measures of lumbar lordosis in adult scoliosis: a case-control study comparing 6 methods. Eur Spine J 19:1551–1557
Itoi E (1991) Roentgenographic analysis of posture in spinal osteoporotics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 16:750–756
Jackson RP, Hales C (2000) Congruent spinopelvic alignment on standing lateral radiographs of adult volunteers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25:2808–2815
Jackson RP, McManus AC (1994) Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size. A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 19:1611–1618
Janssen MM, Drevelle X, Humbert L, Skalli W, Castelein RM (2009) Differences in male and female spino-pelvic alignment in asymptomatic young adults: a three-dimensional analysis using upright low-dose digital biplanar X-rays. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:E826–E832
Kim WJ, Kang JW, Yeom JS, Kim KH, Jung YH, Lee SH, Choy WS (2003) A comparative analysis of sagittal spinal balance in 100 asymptomatic young and older aged volunteers. J Kor Soc Spine Surg 10:327–334
Lafage V, Schwab F, Skalli W, Hawkinson N, Gagey PM, Ondra S, Farcy JP (2008) Standing balance and sagittal plane spinal deformity: analysis of spinopelvic and gravity line parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:1572–1578
Lafage V, Smith JS, Bess S, Schwab FJ, Ames CP, Klineberg E, Arlet V, Hostin R, Burton DC, Shaffrey CI, International Spine Study G (2012) Sagittal spino-pelvic alignment failures following three column thoracic osteotomy for adult spinal deformity. Eur Spine J 21:698–704
Lamartina C, Berjano P, Petruzzi M, Sinigaglia A, Casero G, Cecchinato R, Damilano M, Bassani R (2012) Criteria to restore the sagittal balance in deformity and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 21(Suppl 1):S27–S31
Lazennec JY, Ramare S, Arafati N, Laudet CG, Gorin M, Roger B, Hansen S, Saillant G, Maurs L, Trabelsi R (2000) Sagittal alignment in lumbosacral fusion: relations between radiological parameters and pain. Eur Spine J 9:47–55
Le Huec JC, Leijssen P, Duarte M, Aunoble S (2011) Thoracolumbar imbalance analysis for osteotomy planification using a new method: FBI technique. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):669–680
Lee CS, Lee CK, Kim YT, Hong YM, Yoo JH (2001) Dynamic sagittal imbalance of the spine in degenerative flat back: significance of pelvic tilt in surgical treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:2029–2035
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G (2005) Sagittal plane alignment of the spine and gravity: a radiological and clinical evaluation. Acta Orthop Belg 71:213–220
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Hecquet J, Marty C (1998) Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J 7:99–103
Mac-Thiong JM, Labelle H, Berthonnaud E, Betz RR, Roussouly P (2007) Sagittal spinopelvic balance in normal children and adolescents. Eur Spine J 16:227–234
Mac-Thiong JM, Wang Z, de Guise JA, Labelle H (2008) Postural model of sagittal spino-pelvic alignment and its relevance for lumbosacral developmental spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:2316–2325
Mendoza-Lattes S, Ries Z, Gao Y, Weinstein SL (2010) Natural history of spinopelvic alignment differs from symptomatic deformity of the spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:E792–E798
Obeid I, Hauger O, Aunoble S, Bourghli A, Pellet N, Vital JM (2011) Global analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in major deformities: correlation between lack of lumbar lordosis and flexion of the knee. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):681–685
Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, Hoff JT, McGillicuddy JE (2004) Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29:1938–1944
Rose PS, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Cronen GA, Mulconrey DS, Buchowski JM, Kim YJ (2009) Role of pelvic incidence, thoracic kyphosis, and patient factors on sagittal plane correction following pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:785–791
Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J (2005) Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:346–353
Schwab F, Lafage V, Patel A, Farcy JP (2009) Sagittal plane considerations and the pelvis in the adult patient. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:1828–1833
Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP, Lafage V (2010) Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:2224–2231
Sergides IG, McCombe PF, White G, Mokhtar S, Sears WR (2011) Lumbo-pelvic lordosis and the pelvic radius technique in the assessment of spinal sagittal balance: strengths and caveats. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):591–601
Stagnara P, De Mauroy JC, Dran G, Gonon GP, Costanzo G, Dimnet J, Pasquet A (1982) Reciprocal angulation of vertebral bodies in a sagittal plane: approach to references for the evaluation of kyphosis and lordosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 7:335–342
Vedantam R, Lenke LG, Keeney JA, Bridwell KH (1998) Comparison of standing sagittal spinal alignment in asymptomatic adolescents and adults. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23:211–215
Vialle R, Levassor N, Rillardon L, Templier A, Skalli W, Guigui P (2005) Radiographic analysis of the sagittal alignment and balance of the spine in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87:260–267
Acknowledgments
No funds were received in support of this work. No benefits in any form have been or will be received of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.S., Chung, S.S., Park, S.J. et al. Simple prediction method of lumbar lordosis for planning of lumbar corrective surgery: radiological analysis in a Korean population. Eur Spine J 23, 192–197 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2895-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2895-1