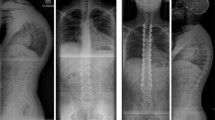
Abstract
Introduction
There is sparse literature on how best to correct Scheuermann’s kyphosis (SK). The efficacy of a combined strategy with anterior release and posterior fusion (AR/PSF) with regard to correction rate and outcome is yet to be determined.
Materials and methods
A review of a consecutive series of SK patients treated with AR/PSF using pedicle screw–rod systems was performed. Assessment of demographics, complications, surgical parameters and radiographs including flexibility and correction measures, proximal junctional kyphosis angle (JKA + 1) and spino-pelvic parameters was performed, focusing on the impact of curve flexibility on correction and clinical outcomes.
Results
111 patients were eligible with a mean age of 23 years, follow-up of 24 months and an average of eight levels fused. Cobb angle at fusion level was 68° preoperatively and 37° postoperatively. Flexibility on traction films was 34 % and correction rate 47 %. Postoperative and follow-up Cobb angles were highly correlated with preoperative bending films (r = 0.7, p < 0.05). Screw density rate was 87 %, with increased correction with higher screw density (p < 0.001, r = 0.4). Patients with an increased junctional kyphosis angle (JKA + 1) were at higher risk of revision surgery (p = 0.049). 22 patients sustained complication, and 21 patients had revision surgery. 42 patients with ≥24 months follow-up were assessed for clinical outcomes (follow-up rate for clinical measures was 38 %). This subgroup showed no significant differences regarding baseline parameters as compared to the whole group. Median approach-related morbidity (ArM) was 8.0 %, SRS-sum score was 4.0, and ODI was 4 %. There was a significant negative correlation between the SRS-24 self-image scores and the number of segments fused (r = −0.5, p < 0.05). Patients with additional surgery had decreased clinical outcomes (SRS-24 scores, p = 0.004, ArM, p = 0.0008, and ODI, p = 0.0004).
Conclusion
The study highlighted that AR/PSF is an efficient strategy providing reliable results in a large single-center series. Results confirmed that flexibility was the decisive measure when comparing surgical outcomes with different treatment strategies. Findings indicated that changes at the proximal junctional level were impacted by individual spino-pelvic morphology and determined by the individually predetermined thoracolumbar curvature and sagittal balance. Results stressed that in SK correction, reconstruction of a physiologic alignment is decisive to achieving good clinical outcomes and avoiding complications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford DS, Moe JH, Montalvo FJ, Winter RB (1975) Scheuermann’s kyphosis. Results of surgical treatment by posterior spine arthrodesis in twenty-two patients. JBJS-A 57:439–448
Ascani E, Rosa G (1994) Scheuermann kyphosis. Raven Press, New York
Denis F, Sun EC, Winter RB (2009) Incidence and risk factors for proximal and distal junctional kyphosis following surgical treatment for Scheuermann kyphosis: minimum five-year follow-up. Spine 34:E729–E734
Griss P, von Andrian-Werburg HF (1978) Results of corrective surgery in juvenile kyphosis (Scheuermann’s disease) using Harrington’s compressive rods. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 91:113–119
Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy J-P, Lafage V (2010) Adult spinal deformity—postoperative standing imbalance. Spine 35:2224–2231
Taylor TC, Wenger DR, Stephen J, Gillespie R, Bobechko WP (1979) Surgical management of thoracic kyphosis in adolescents. JBJS-A 61:496–503
Denis F (1983) Spinal instability as defined by the three-column spine concept in acute spinal trauma. Clin Orthop Rel Res 189:65–76
Hosman AJ, Langeloo DD, de Kleuver M, Anderson PG, Veth RP, Slot GH (2002) Analysis of the sagittal plane after surgical management for Scheuermann’s disease: a view on overcorrection and the use of an anterior release. Spine 27:167–175
Lonner BS, Murthy SK, Boachie-adjei O (2005) Single-staged double anterior and posterior spinal reconstruction for rigid adult spinal deformity: a report of four cases. The Spine J 5:104–108
Jansen RC, van Rhijn LW, van Ooij A (2006) Predictable correction of the unfused lumbar lordosis after thoracic correction and fusion in Scheuermann kyphosis. Spine 31:1227–1231
Coe JD, Smith JS, Berven S, Arlet V, Donaldson W, Hanson D, Mudiyam R, Perra J, Owen J, Marks MC, Shaffrey CI (2009) Complications of spinal fusion for Scheuermann kyphosis—a report of the scoliosis research society morbidity and mortality committee. Spine 35:99–103
Lowe G, Breton G (2007) Evidence based medicine. Anal Scheuermann Kyphosis 32:S115–S119
Lowe TG (1987) Double L-rod instrumentation in the treatment of severe kyphosis secondary to Scheuermann’s disease. Spine 12:336–341
Lowe TG, Kasten T (1994) An analysis of sagittal curves and balance after Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation for kyphosis secondary to Scheuermann’s disease. A review of 32 patients. Spine 19:1680–1685
Lowe TG (1999) Scheuermann’s disease. Orthop Clin North Am 30:475–487
Tribus CB (1998) Scheuermann’s kyphosis in adolescents and adults: diagnosis and management. J Acad Orthop Surg 6:36–43
Bradford DS, Ahmed KB, Moe JH, Winter RB, Lonstein JE (1980) The surgical management of patients with Scheuermann’s disease: a review of twenty-four cases managed by combined anterior and posterior spine fusion. JBJS-A 62:705–712
Speck GR, Chopin DC (1986) The surgical treatment of Scheuermann’s kyphosis. JBJS-Br 68:189–193
Tsirikos AI, Jain AK (2011) Scheuermann’s kyphosis; current controversies. JBJS-Br 93:857–864
Sturm PF, Dobson JC, Armstrong GW (1993) The surgical management of Scheuermann’s disease. Spine 18:685–691
Hamzaoglu A, Talu U, Tezer M, Mirzanli C, Domanic U, Goksan SB (2005) Assessment of curve flexibility in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 30:1637–1642
Ferreira-Alves A, Resina J, Palma-Rodrigues R (1995) Scheuermann’s kyphosis. The Portuguese technique of surgical treatment. JBJS-Br 77:943–950
Koptan WM, Elmiligui YH, Elsebaie HB (2009) All pedicle screw instrumentation for Scheuermann’s kyphosis correction: is it worth it? Spine J 9:296–302
Papagelopoulos PJ, Klassen RA, Peterson HA, Dekutoski MB (2001) Surgical treatment of Scheuermann’s disease with segmental compression instrumentation. CORR 386:139–149
Glassmann SD, Hamill CL, Bridwell KH, Schwab FJ, Dimar JR, Lowe TG (2007) The impact of perioperative complications on clinical outcome in adult deformity surgery. Spine 32:2764–2770
Poolman RW, Been HD, Ubags LH (2002) Clinical outcome and radiographic results after operative treatment of Scheuermann’s disease. Eur Spine J 11:561–569
Lim M, Green DW, Billinghurst JE, Huang RC, Rawlins BA, Widmann RF, Burke SW, Boachie-Adjei O (2004) Scheuermann kyphosis: safe and effective surgical treatment using multisegmental instrumentation. Spine 29:1789–1794
Herrera-Soto JA, Parikh SN, Al-Sayyad MJ, Crawford AH (2005) Experience with combined video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) anterior spinal release and posterior spinal fusion in Scheuermann’s kyphosis. Spine 30:2176–2181
Lee SS, Lenke LG, Kuklo TR, Valente L, Bridwell KH, Sides B, Blanke K (2006) Comparison of Scheuermann kyphosis correction by posterior-only thoracic pedicle screw fixation versus combined anterior/posterior fusion. Spine 31:2316–2321
Lonner BS, Newton P, Betz R, Schaf C, O’Brien M, Sponseller P, Lenke L, Crawford A, Lowe T, Letko L, Harms J, Shufflebarger H (2007) Operative management of Scheuermann’s kyphosis in 78 patients: radiographic outcomes, complications, and technique. Spine 2007:2644–2652
de Jonge T, Illes T, Bellyei G (2001) Surgical correction of Scheuermann’s kyphosis. Int Orthop 25:70–73
Wilk B, Karol LA, Johnston CE, Colby S, Haideri N (2006) The effect of scoliosis fusion on spinal motion: a comparison of fused and nonfused patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 31:309–314
Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Baldus C, Blanke K, Schonecker PL (1993) Ability of Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation to preserve distal lumbar motion segments in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord 6:339–350
Betz RR, Harms J, Clements D, Lenke L, Low T, Jeszensky D, Shufflebarger HL, Beele B (1999) Comparison of anterior and posterior instrumentation for correction of adolescent thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 24:225–239
Marks M, Newton PO, Petcharaporn M, Bastrom TP, Shah S, Betz R, Lonner B, Miyanji F (2011) Postoperative segmental motion of the unfused spine distal to the fusion in 100 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. Spine e-pub 2011
Johnston CE, Elerson E, Dagher G (2005) Correction of adolescent hyperkyphosis with posterior-only threaded rod compression instrumentation: is anterior spinal fusion still necessary? Spine 30:1528–1534
Cho K-J, Lenke L, Bridwell KH, Kamiya M, Sides B (2009) Selection of the optimal distal fusion level in posterior instrumentation and fusion for thoracic hyperkyphosis. Spine 34:765–770
Hamzaoglu A, Ozturk C, Korkmaz FM, Karatoprak O, Enercan M, Zezer M (2009) A new technique to prevent proximal junctional kyphosis in the surgical treatment of Scheuermann disease. IMAST, Vienna
Otsuka NY, Hall JE, Mah JY (1990) Posterior fusion for Scheuermann’s kyphosis. CORR 251:134–139
Arlet V, Schlenzka D (2005) Scheuermann’s kyphosis: surgical treatment. Eur Spine J 14:817–827
Ning Y, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Koester L (2011) How to determine optimal fusion levels of Scheuermann’s kyphosis. SRS annual meeting, Louisville
Clements DH, Betz RR, Newton PO, Rohmiller M, Marks MC, Bastrom T (2009) Correlation of scoliosis curve correction with the number and type of fixation anchors. Spine 34:2147–2150
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Kim J, Cho SK, Cheh G, Yoon J (2007) Proximal junctional kyphosis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis after 3 different types of posterior segmental spinal instrumentation and fusions—incidence and risk factor analysis of 410 cases. Spine 32:2731–2738
Winter RB, Lonstein JE, Denis F (2009) Sagittal spinal alignment: the true measurement, norms, and description of correction for thoracic kyphosis. J Spinal Disord 22:311–314
Lafage V, Bharucha NJ, Schwab F, Hart RA, Burton D, Boachie-Adjei O, Smith JS, Hostin R, Shaffrey C, Gupta M, Akbarnia BA, Bess S (2012) Multicenter validation of a formula predicting postoperative spinopelvic alignment. JNS 16:15–21
Abel MF, Herndon SK, Sauer LD, Novicoff WM, Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Spinal Deformity Study Group (2011) Selective versus nonselective fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: does lumbosacral takeoff angle change? Spine 36:1103–1112
Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB (2000) The Oswestry Disability Index. Spine 25:2940–2953
Zenner J, Koller H, Hempfing A, Hutter J, Hitzl W, Resch H, Tauber M, Meier O, Ferraris L (2010) Approach-related morbidity in transthoracic anterior spine surgery: a clinical study and review of literature. Coluna Columna 9:72–84
Arlet V (2000) Anterior thoracoscopic spine release in deformity surgery: a meta-analysis and review. Eur Spine J 9(Suppl 1):S17–S23
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koller, H., Juliane, Z., Umstaetter, M. et al. Surgical treatment of Scheuermann’s kyphosis using a combined antero-posterior strategy and pedicle screw constructs: efficacy, radiographic and clinical outcomes in 111 cases. Eur Spine J 23, 180–191 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2894-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2894-2