Abstract
Introduction
Mutilating-type rheumatoid arthritis, the most aggressive type of rheumatoid arthritis, is frequently associated with destructive cervical involvement, both at the high-cervical and subaxial levels, causing significant neurological deficit, and their natural course of the disease and the survival are discouraging. For such cases, we have been actively performing occipito-thoracic fusion since 1991. Although medical treatment for rheumatoid patients has represented a marked improvement, it could not treat all of these patients because of several reasons. Therefore, it is still important to evaluate the past treatment results.
Methods
We investigated the neurological improvement and prognosis in 51 mutilating-type rheumatoid arthritis patients who underwent occipito-thoracic fusion between 1991 and 2010. The neurological status was evaluated using modified Ranawat classification; class IIIB was subdivided into IIIBa (able to sit upright) and IIIBb (bedridden).
Results
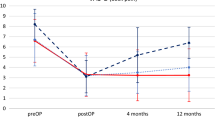
The preoperative neurologic status was IIIBa in 19 patients and IIIBb in 17 patients. 15 of the 19 patients with class IIIBa improved to being able to walk (79 %), whereas only 3 of the 17 patients with class IIIBb improved to being able to walk (18 %) after surgery. Of the 51 patients, 28 died during follow-up; the mean age at death was 67.2 years. The postoperative 5- and 10-year survival rates were 60.3 and 26.4 %, respectively.
Conclusion
The neurological improvement and prognosis after surgery was poorer in class IIIBb patients than in the other patient groups. Occipito-thoracic fusion can improve the neurological symptoms and prognosis. However, early surgical intervention is recommended, before a patient becomes bedridden (class IIIBb).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ochi T, Iwase R, Yonemasu K et al (1988) Natural course of joint destruction and fluctuation of serum C1q levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(1):37–43
Omura K, Hukuda S, Katsuura A et al (2002) Evaluation of posterior long fusion versus conservative treatment for the progressive rheumatoid cervical spine. Spine 27(12):1336–1345
Matsuyama Y, Kawakami N, Yoshihara H et al (2005) Long-term results of occipitothoracic fusion surgery in RA patients with destruction of the cervical spine. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(suppl):S101–S106
Casey AT, Crockard HA, Bland JM et al (1996) Surgery on the rheumatoid cervical spine for the non-ambulant myelopathic patient-too much, too late? Lancet 347(9007):1004–1007
Ranawat CS, O’Leary P, Pellicci P et al (1979) Cervical spine fusion in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 61(7):1003–1010
Shimizu T, Edakuni H, Iizuka H et al. (2000) Occipito-thoracic stabilization and fusion for myelopathic patients with destructive cervical disorders due to sever rheumatoid arthritis. In: 28th annual meeting of Cervical Spine Research Society Abstract book, pp 79–80
Marks JS, Sharp J (1981) Rheumatoid cervical myelopathy. Q J Med 50(199):307–319
Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Onishi T et al. (2003) Prognosis of patients with upper cervical lesions caused by rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of occipitocervical fusion between c1 laminectomy and nonsurgical management. Spine 28 (14):1581–7 (discussion 1587)
Mori K, Imai S, Omura K et al (2010) Clinical output of the rheumatoid cervical spine in patients with mutilating-type joint involvement: for better activities of daily living and longer survival. Spine 35(13):1279–1284
Sunahara N, Matsunaga S, Mori T et al. (1997) Clinical course of conservatively managed rheumatoid arthritis patients with myelopathy. Spine 22 (22):2603–7 (discussion 2608)
Grob D, Schütz U, Plötz G (1999) Occipitocervical fusion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 366:46–53
Hirano K, Matsuyama Y, Sakai Y et al (2010) Surgical complications and management of occipitothoracic fusion for cervical destructive lesions in RA patients. J Spinal Disord Tech 23(2):121–126
Ronkainen A, Niskanen M, Auvinen A et al (2006) Cervical spine surgery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: longterm mortality and its determinants. J Rheumatol 33(3):517–522
Gonzalez A, Maradit Kremers H, Crowson CS et al (2007) The widening mortality gap between rheumatoid arthritis patients and the general population. Arthritis Rheum 56(11):3583–3587
Nakajima A, Inoue E, Tanaka E et al (2010) Mortality and cause of death in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis based on a large observational cohort, IORRA. Scand J Rheumatol 39(5):360–367
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanouchi, T., Shimizu, T., Fueki, K. et al. Neurological improvement and prognosis after occipito-thoracic fusion in patients with mutilating-type rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Spine J 21, 2506–2511 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2448-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2448-z