Abstract
Background
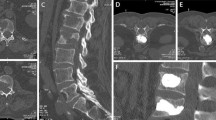
The life span of cancer patients has improved due to advancements in cancer management. With long survival periods, more patients show metastatic disease. Osteolytic tumours of spine are generated by metastatic deposits or primary tumours of the spine. A prospective study was performed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of percutaneous kyphoplasty in patients with osteolytic tumours of the thoracic and lumbar spine.
Materials and methods
Eleven patients (age range 52–77/average 65 years; 7 female, 4 male) with osteolytic tumours of the spine were treated with kyphoplasty. The main Tokuhashi score was registered preoperatively. Outcome was assessed prospectively by visual analogue scale (VAS) for pain, ECOG performance status, walking distance, standing and sitting time.
Results
Preoperative VAS (average 7.5; range 2.6–10) dropped to 3.0, 5 days postoperatively and remained below 5 for follow-up. Main Tokuhashi score was 6.3, ranging from 3 to 9. Survival time ranged from 2 to 293 (average 74.4) weeks. Average walking distance, standing and sitting time and ECOG performance score showed improvement. All patients returned home and no patient required re-operation or readmission due to local disease progression or recurrence.
Conclusion
Kyphoplasty is a suitable palliative treatment option for patients with advanced metastatic disease of the spine even with low Tokuhashi scores allowing rapid pain relief and mobilisation to increase the quality of life.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shindle MK, Shindle L, Gardner MJ, Lane JM (2006) Supportive care aspects of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in patients with cancer. Support Cancer Ther 3:214–219
Sciubba DM, Nguyen T, Gokaslan ZL (2009) Solitary vertebral metastasis. Orthop Clin North Am 40:145–154
McLain R, Weinstein JN (1999) Tumours of spine. In: Herkowitz H, Garfin S, Balderston R (eds) The spine. WB Saunders Co, Philadelphia, pp 1171–1206
Chen KY, Ma HI, Chiang YH (2009) Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty with polymethyl methacrylate for pathological fracture of the spine. J Clin Neurosci 16:1300–1304
Gofeld M, Bhatia A, Burton AW (2009) Vertebroplasty in the management of painful bony metastases. Curr Pain Headache Rep 13:288–294
Hee HT (2005) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: current concepts and local experience. Neurol India 53:475–482
Gertzbein SD (2004) Metastatic spine tumours. In: Herkowitz HN, Dvorak J, Bell G (eds) The lumbar spine, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilikns, Philadelphia, pp 792–795
Lemke DM, Hacein-Bey L (2003) Metastatic compression fractures-vertebroplasty for pain control. J Neurosci Nurs 35:50–55
Tokuhashi Y, Matsuzaki H, Toriyama S, Kawano H, Ohsaka S (1990) Scoring system for the preoperative evaluation of metastatic spine tumour prognosis. Spine 15:1110–1113
Wu AS, Fourney DR (2005) Supportive care aspects of vertebroplasty in patients with cancer. Support Cancer Ther 2:98–104
Wenger M (2003) Vertebroplasty for metastasis. Med Oncol 20:203–209
Niv D, Gofeld M, Devor M (2003) Causes of pain in degenerative bone and joint disease: a lesson from vertebroplasty. Pain 105:387–392
Trumm CG, Jakobs TF, Zech CJ et al (2008) CT fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteolytic breast cancer metastases: results in 62 sessions with 86 vertebrae treated. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19:1596–1606
Lieberman I, Reinhardt MK (2003) Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for osteolytic vertebral collapse. Clin Orthop Relat Res (415 Suppl):S176–S186
Ofluoglu O (2009) Minimally invasive management of spinal metastases. Orthop Clin North Am 40:155–168
Fourney DR, Shomer DF, Nader R et al (2003) Percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for painful vertebral body fractures in cancer patients. J Neurosurg 98(Suppl 1):21–30
Dudeney S, Lieberman IH, Reinhardt MK, Hussein M (2002) Kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteolytic vertebral compression fractures as a result of multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 20:2382–2387
Cotten A, Boutry N, Cortet B et al (1998) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: state of the art. Radiographics 18:311–323
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC et al (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5:649–655
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
König, M.A., Jehan, S., Balamurali, G. et al. Kyphoplasty for lytic tumour lesions of the spine: prospective follow-up of 11 cases from procedure to death. Eur Spine J 21, 1873–1879 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2264-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2264-5