Abstract
Purpose of study
To describe a simple and reliable method of intra-operative localisation of thoracic spine in a single surgical setting.
Summary of background
Intra-operative localisation of thoracic spine levels can be difficult due to anatomical constraints, such as scapular shadow, patient’s size and poor bone quality. This is particularly true in cases of thoracic discectomies in which the vertebral bodies appear normal. There are several methods described in recent literature to address this. Many of them require a separate procedure which was performed often the previous day. We report a technique which addresses the issue of localising thoracic level intra-operatively.
Materials and methods
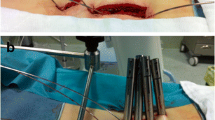
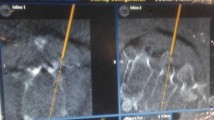
After induction of general anaesthesia, the patient was placed prone and the pedicle of interest was identified using fluoroscopy. A K-wire was then inserted percutaneously into this pedicle under image guidance [confirmed in the antero-posterior (AP) and lateral views]. The wire was then cut close to the skin after bending it. The patient was now positioned laterally and the intended procedure performed through an anterior trans-thoracic approach. The ‘K’ wire was removed at the end of the procedure.
Results and conclusion
We routinely used this technique in all our thoracic discectomies (four cases in 2 years). There were no intra-operative complications. This method is simple, avoids the patient undergoing two procedures and requires no more ability than placing an implant in the pedicle under fluoroscopy. Placing the ‘K’ wire into a fixed point like the pedicle facilitates rapid intra-operative viewing of the level of interest and is removed easily at the conclusion of surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mody MG, Nourbaksh A, Stahl DL, Gibbs M, Alfawareh M, Garges KJ (2008) The prevalence of wrong level surgery among spine surgeons. Spine 33(2):194–198
Hsu W, Sciubba DM, Sasson AD, Khavkin Y, Wolinsky JP, Gailloud P, Gokaslan ZL, Kieran Murphy K (2008) Intraoperative localization of thoracic spine level with preoperative percutaneous placement of intravertebral polymethylmethacrylate. J Spinal Disord Tech 21:72–75
Binning MJ, Schmidt MH (2010) Percutaneous placement of radiopaque markers at the pedicle of interest for preoperative localization of thoracic spine level. Spine 35(19):1821–1825
Jhawar BS, Mitsis D, Duggal N (2007) Wrong-sided and wrong-level neurosurgery: a national survey. J Neurosurg Spine 7:467–472
DeVine J, Chutkan N, Norvell DC, Dettori JR (2010) Avoiding wrong site surgery: a systematic review. Spine 35(Suppl 9):S28–S36
Paolini S, Ciapetta P, Missori P, Raco A, Delfini R (2005) Spinous process marking: a reliable method for preoperative surface localization of intradural lesions of the high thoracic spine. Br J Neurosurg 19(1):74–76
Redfern RM, Smith ETS (1986) A method for identification of vertebral level. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 68:293
Irace C, Corona C (2010) How to avoid wrong-level and wrong-side errors in lumbar microdiscectomy. J Neurosurg Spine 12:660–665
Singh H, Meyer SA, Hecht AC, Jenkins AL (2009) Novel fluoroscopic technique for localization at cervicothoracic levels. J Spinal Disord Tech 22:615–618
Marquardt G, Berkefeld J, Seifert V, Gerlach R (2009) Preoperative coil marking to facilitate intraoperative localization of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. Eur Spine J 18:1117–1120
Malanga GA, Cooke PM (2004) Segmental anatomy leading to wrong level surgery pain physician 7:107–110, ISSN 1533–3159
Rosahl SK, Gharabaghi A, Liebig T, Feste CD, Tatagiba M, Samii M (2002) Skin markers for surgical planning for intradural lesions of the thoracic spine-technical note. Surg Neurol 58:346–348
Ammerman JM, Ammerman MD, Dambrosia J, Ammerman BJ (2006) A prospective evaluation of the role for intraoperative x-ray in lumbar discectomy. Predictors of incorrect level exposure. Surg Neurol 66:470–474
Nussbaum DA, Gailloud P, Murphy K (2004) A review of complications associated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty as reported to the Food & Drug Administration medical device related web site. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15(11):1185–1192
Lee BJ, Lee SR, Yoo TY (2002) Paraplegia as a complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. Spine 27:E419–E422
Padavoni B, Kasriel O, Brunner P, Peretti-Viton P (1999) Pulmonary embolism caused by acrylic cement: a rare complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty. Am J Neuroradiol 20:375–377
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thambiraj, S., Quraishi, N.A. Intra-operative localisation of thoracic spine level: a simple “‘K’-wire in pedicle” technique. Eur Spine J 21 (Suppl 2), 221–224 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2193-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2193-3