Abstract
Study design
Technical report on the surgical technique of asymmetric osteotomy of the spine for coronal imbalance.
Objective
To describe a successful method of performing asymmetrical pedicle subtraction osteotomy (APSO) through a posterior only approach.
Summary of background
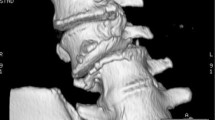
Rigid coronal deformity of the spine can be sharply angulated and can create significant coronal imbalance. Surgical correction is the only definitive treatment of restoring the balance as bracing is unhelpful. Corrective surgery can be anterior or posterior. The literature on the methods of surgical correction of rigid coronal deformities of the spine is limited. Unlike osteotomies for sagittal imbalance, blunt dissection of the anterior cortex is necessary in asymmetrical osteotomy to allow resection of the anterior cortex for closure of the wedge. We describe a method by which we performed this in the thoracic and lumbar spine with case examples.
Method
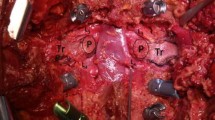
After insertion of pedicle screws, laminectomy and unilateral facetectomy of the proposed level of osteotomy is performed. Next, dissection lateral to the pedicle and vertebral body is performed bluntly with mastoids to reach the front of the anterior cortex and confirmed with fluoroscopy. An oblique osteotomy including the lateral and posterior cortex is performed above and below the pedicle under imaging. The osteotomy site is closed through unilateral compression.
Conclusion
Satisfactory correction of coronal deformity can be achieved with APSO from an isolated posterior approach. In contrast to sagittal osteotomies, blunt dissection along the anterior cortex is necessary to allow safe resection of anterior cortical bone for closure of the wedge.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridwell KH (2006) Decision making regarding Smith-Petersen vs. pedicle subtraction osteotomy vs vertebral column resection for spinal deformity. Spine 31:S171–S178
Thomasen E (1985) Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop 194:142–152
Dorward IG, Lenke LG (2010) Osteotomies in the posterior-only treatment of complex adult spinal deformity: a comparative review. Neurosurg Focus 28(3):E4
Bakaloudis G, Lolli F, Di Silvestre M, Greggi T, Astolfi S, Martikos K, Vommaro F, Barbanti-Brodano G, Cioni A, Giacomini S (2011) Thoracic pedicle subtraction osteotomy in the treatment of severe pediatric deformities. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl):S95–S104
Wang Y, Lenke LG (2011) Vertebral column decancellation for the management of sharp angular spinal deformity. Eur Spine J 20:1703–1710
Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Rinella A, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K (2004) Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Essent Surg Tech 86(Suppl):1
Wang MY, Sigurd BH (2007) Lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Neurosurgery 60(2):p140–p146
Suk S, Chung E, Lee S, Lee J, Kim S, Kim J (2005) Posterior vertebral column resection in fixed lumbosacral deformity. Spine 30:E703–E710
Bradford DS, Tribus CB (1997) Vertebral column resection for the treatment of rigid coronal decompensation. Spine 22:1590–1599
Polly DW, Rosner MK, Monacci W, Moquin RR (2003) Thoracic hemivertebra excision in adults via a posterior-only approach. Report of two cases. Neurosurg Focus 14:1–4
Halm H (2011) Transpedicular hemivertebra resection and instrumented fusion for congenital scoliosis. Eur Spine J 20:993–994
Arun R, Dabke HV, Mehdian H (2011) Comparison of three types of lumbar osteotomy for ankylosing spondylitis: a case series and evolution of a safe technique for instrumented reduction. Eur Spine J 20:2252–2260
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thambiraj, S., Boszczyk, B.M. Asymmetric osteotomy of the spine for coronal imbalance: a technical report. Eur Spine J 21 (Suppl 2), 225–229 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2171-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2171-9