Abstract
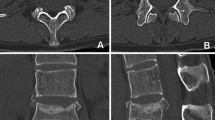
Anterior column reconstruction of the thoracolumbar spine by structural allograft has an increased potential for biological fusion when compared to synthetic reconstructive options. Estimation of cortical union and trabecular in-growth is, however, traditionally based on plain radiography, a technique lacking in sensitivity. A new assessment method of bony union using high-speed spiral CT imaging is proposed which reflects the gradually increasing biological stability of the construct. Grade I (complete fusion) implies cortical union of the allograft and central trabecular continuity. Grade II (partial fusion) implies cortical union of the structural allograft with partial trabecular incorporation. Grade III (unipolar pseudarthrosis) denotes superior or inferior cortical non-union of the central allograft with partial trabecular discontinuity centrally and Grade IV (bipolar pseudarthrosis) suggests both superior and inferior cortical non-union with a complete lack of central trabecular continuity. Twenty-five patients underwent anterior spinal reconstruction for a single level burst fracture between T4 and L5. At a minimum of two years follow up the subjects underwent high-speed spiral CT scanning through the reconstructed region of the thoracolumbar spine. The classification showed satisfactory interobserver (kappa score = 0.91) and intraobserver (kappa score = 0.95) reliability. The use of high-speed CT imaging in the assessment of structural allograft union may allow a more accurate assessment of union. The classification system presented allows a reproducible categorization of allograft incorporation with implications for treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albee F (1911) Transplantation of a portion of the tibia into the spine for Pott’s disease: a preliminary report. JAMA 57:885–886
Bishop RC, Moore KA, Hadley MN (1996) Anterior cervical interbody fusion using allogeneic and allogeneic bone graft substrate: a prospective comparative analysis. J Neurosurg 85:206–210
Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, McEneryKW, Baldus C, Blanke K (1995) Anterior structural allografts in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Spine 20:1410–1418
Butterman GR, Glazer PA, Hu SS, Bradford DS (1997) Revision of failed lumbar fusion: a comparison of anterior autograft and allograft spine. Spine 22:2748–2755
Cloward RB (1952) The treatment of ruptured lumbar intervertebral discs by vertebral fusion III method of use of banked bone. Ann Surg 136:987–992
Cloward RB (1959) Vertebral body fusion for ruptured cervical discs: description of instruments and operative technic. Am J Surg 98:722–727
Cunningham BW, Kanayama M, Parker L.M, Weis JC, Sefter JC, Fedder IL McAfee PC (1999) Osteogenic protein versus autologous interbody arthrodesis in the sheep thoracic spine. Spine 24:509–518
Ehrler DM Vaccaro AR (2000) The use of allograft bone in lumbar spine surgery. Clin Orthop 371:38–45
Engelke K, Graeff W, Meiss L, Hahn M Delling G (1993) High spatial resolution imaging of bone mineral using computed microtomography comparison with microradiography and undecalcified histologic sections. Invest Radiol 28:341–349
Hibbs R (1912) An operation for Pott’s disease of the spine. JAMA 59:43
Hutter G (1983) Posterior intervertebral body fusion a 25 year study. Clin Orthop 179:86–96
Kozak JA, Heilman AE O’Brien JP (1994) Anterior lumber fusion option. Clin Orthop 300:45–51
Kumar A, Kozak JA, Doherty BJ Dickson JH (1993) Interspace distraction and grafts subsidence after anterior lumbar fusion with femoral strut allograft. Spine 18:2393–2400
Landis JR Koch GG (1997) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:154–174
Lewandrowski KU, Hecht AC, DeLaney TF, Chapman PA, Hornicek FJ Pedlow FX (2004) Anterior spinal arthrodesis with structural cortical allograft and instrumentation for spinal tumor surgery. Spine 29:1150–1159
Magerl F, Aebi M, Gertzbein SD, Harms J Nazarian S (1994) A comprehensie classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. Eur Spine J 3:184–201
Martin GJ Jr, Haid RW Jr, MacMillan M, Rodts GE Jr Berkman R (1999) Anterior cervical discectomy with freeze–dried fibula allograft: overview of 317 cases and literature review. Spine 24:852–859
McAfee PC, Boden SD, Brantigan JW, Fraser RD, Kuslich SD, Oxland TR, Panjabi MM, Ray CD Zdeblick TA (2001) Symposium. A critical discrepancy—a criteria of successful arthrodesis following interbody spinal fusions. Spine 26:320–334
Pearcy M, Burrough S (1982) Assessment of bony union after interbody fusion of teh lumbar spine using a biplanar radiographic technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br 64-B:228–322
Santos ERG, Goss DG, Morcom RK Fraser RD (2003) Radiologic assessment of interbody fusion using carbon fiber cages. Spine 28:997–1001
Sarwat AM, O’Brien JP, Renton P Sutcliffe JC (2001) The use of allograft (and avoidance of autograft) in anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a critical analysis. Eur Spine J 10:237–241
Shah RR, Mohammed S, Saifuddin A Taylor B A (2003) Comparison of plain radiographs with CT scan to evaluate interbody fusion following the use of titanium interbody cages and transpedicular instrumentation. Eur Spine J 12:378–385
Singh K, DeWald CJ, Hammerberg KW, DeWald RL (2002) Long structural allografts in the treatment of anterior spinl column defect. Clin Orthop 394:121–129
Tuli SK, Chen P, Eichler ME, Woodard EJ (2004) Reliability of radiologic assessment of fusion: cervical fibular allograft model. Spine 29:856–860
Tuli SK, Tuli J, Chen P, Woodard EJ (2004) Fusion rate: a time-to-event phenomenon. J Neurosurg Spine 1:47–51
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Synthes Asia Pacific, AOSpine Asia Pacific and the QLD Government, Department of State Development. The authors thank Drs Geoff Askin and David Lisle for their involvement in the interobserver study
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, G.H., Goss, B.G., Thorpe, P.J. et al. CT-based classification of long spinal allograft fusion. Eur Spine J 16, 1875–1881 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0376-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0376-0