Abstract
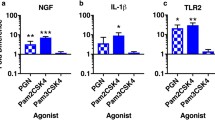
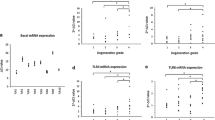
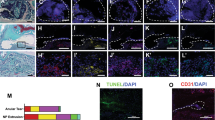
Inflammation and irritation of the nerve roots has been indicated as an important factor in the pain associated with symptomatic disc herniations. Tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) is now believed to be involved in this pathway. TNFα causes connective tissue cells in culture to synthesise a glycoprotein, TNFα-stimulated gene-6 (TSG-6). TSG-6 is found in inflammatory diseases of related connective tissues, such as articular cartilage in rheumatoid arthritis, but is not present in unaffected individuals. In order to determine if TSG-6 occurred in intervertebral disc (and cartilage endplate), we have investigated the presence of TSG-6 and its binding protein, inter-α-inhibitor (IαI), in 58 herniated and 15 non-herniated discs. Immunostaining for the cytokines, IL-1α, IL-1β and TNFα, has also been carried out. We have demonstrated that both TSG-6 and IαI occur commonly in human intervertebral disc matrix with at least some TSG-6 in 98% of discs studied and IαI in all of them. Staining for TSG-6 was greatest in herniated discs, particularly close to blood vessels. IαI immunostaining was frequently widespread throughout the disc but there was little in the cartilage endplate. It has been proposed that these molecules have widespread effects, including extracellular matrix stabilisation, down-regulation of the protease network and reduction of inflammation. Hence, the occurrence of TSG-6 and IαI in disc tissue could have implications in the aetiopathogenesis and future therapeutics of intervertebral disc disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn SH, Cho YC, Ahn MW, Jang SH, Sohn YK, Kim HS (2002) mRNA expression of cytokines and chemokines in herniated lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine 27:911–917
Bayliss MT, Howat SLT, Dudhia J, Murphy JM, Barry FP, Edwards JCW, Day AJ (2001) Up-regulation and differential expression of the hyaluronan-binding protein TSG-6 in cartilage and synovium in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 9:42–48
Blundell CD, Mahoney DJ, Almond A, DeAngelis PL, Kahmann JD, Teriete P, Pickford AR, Campbell ID, Day AJ (2003) The link module from ovulation- and inflammation-associated protein TSG-6 changes conformation on hyaluronan binding. J Biol Chem 278:49261–49270
Crean JKG, Roberts S, Jaffray DC, Eisenstein SM, Duance VC (1997) Matrix metalloproteinases in the human intervertebral disc: Role in disc degeneration and scoliosis. Spine 22:2877–2844
Fujimoto T, Savani RC, Watari M, Day AJ, Strauss JF (2002) Induction of the hyaluronic acid-binding protein, TSG-6, in cervical smooth muscle cells by pro-inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandin E2. Am J Pathol 160:1495–1502
Fülöp C, Szántó S, Mukhopadhyay D, Bárdos T, Kamath RV, Rugg MS, Day AJ, Salustri A, Hascall VC, Glant TT, Mikecz K (2003) Impaired cumulus mucification and female sterility in tumor necrosis factor-induced protein-6 deficient mice. Development 130:2253–2261
Getting SJ, Mahoney DJ, Cao T, Rugg MS, Fries E, Milner CM, Perretti M, Day AJ (2002) The link protein module from human TSG-6 inhibits neutrophil migration in a hyaluronan and inter-α-inhibitor-independent manner. J Biol Chem 277:51068–51076
Glant TT, Kamath RV, Bardos T, Gal I, Szanto S, Murad YM, Sandy JD, Mort JS, Roughley PJ, Mikecz K (2002) Cartilage-specific constitutive expression of TSG-6 protein (product of tumour necrosis factor α-stimulated gene 6) provides a chondroprotective, but not antiinflammatory, effect in antigen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:2207–2218
Habtemariam A, Gronblad M, Virri J, Seitsalo S, Ruuskanen M, Karahaharju E (1996) Immunocytochemical localization of immunoglobulins in disc herniations. Spine 21:1864–1869
Igarashi T, Kikuchi S, Shubayev V, Myers RR (2000) 2000 Volvo Award Winner in Basic Science Studies: Exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha mimics nucleus pulposus-induced neuropathology. Spine 25:2975–2980
Karppinen J, Korhonen T, Malmivaara A, Paimela L, Kyllönen E, Lindgren KA, Rantanen P, Tervonen O, Niinimäki J, Seitsalo S, Hurri H (2003) Tumor necrosis factor-a monoclonal antibody, infliximab, used to manage severe sciatica. Spine 28:750–754
Kida D, Yoneda M, Miyaura S, Ishimaru T, Yoshida Y, Ito T, Ishiguro N, Iwata H, Kimata K (1999) The SHAP-HA complex in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 26:1230–1238
Kohda D, Morton CJ, Parkar AA, Hatanaka H, Inagaki FM, Campbell ID, Day AJ (1996) Solution structure of the link module: a hyaluronan-binding domain involved in extracellular matrix stability and cell migration. Cell 86:767–775
Lee TH, Wisniewski HG, Vilcek J (1992) A novel secretory tumor necrosis factor-inducible protein (TSG-6) is a member of the family of hyaluronate binding proteins, closely related to the adhesion receptor CD44. J Cell Biol 116:545–557
Lesley J, English NM, Gal I, Mikecz K, Day AJ, Hyman R (2002) Hyaluronan binding properties of a CD44 chimera containing the link module of TSG-6. J Biol Chem 277:26600–26608
Maier R, Wisniewski HG, Vilcek J, Lotz M (1996) TSG-6 expression in human articular chondrocytes. Possible implications in joint inflammation and cartilage degradation. Arthritis Rheum 39:552–559
Maroudas A (1976) Balance between swelling pressure and collagen tension in normal and degenerate cartilage. Nature 260:808–809
Melrose J, Ghosh P, Taylor TKF, Andrews JL (1992) The serine proteinase inhibitory proteins of the human intervertebral disc: their isolation, characterization and variation with ageing and degeneration. Matrix 12:456–470
Melrose J, Taylor TKF, Ghosh P (1997) The serine inhibitory proteins of the chondrodystrophoid (beagle) and non- chondrodystrophoid (greyhound) canine intervertebral disc. Electrophoresis 18:1059–1063
Milner CM, Day AJ (2003) TSG-6: a multifunctional protein associated with inflammation. J Cell Sci 116, 1863–1873
Mindrescu C, Dias AAM, Olszewski RJ, Klein MJ, Reis LFL, Wisniewski HG (2002) Reduced susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 J mice expressing the TSG-6 transgene. Arthritis Rheum 46:2453–2464
Moore RJ, Vernon-Robert B, Freemont AJ, Osti OL, Schembri M (1996) The origin and fate of herniated lumbar intervertebral disc tissue. Spine 21:2149–2155
Nentwich HA, Mustafa Z, Rugg MS, Marsden BD, Cordell MR, Mahoney DJ, Jenkins SC, Dowling B, Fries E, Milner CM, Loughlin J, Day AJ (2002) A novel allelic variant of the human TSG-6 gene encoding an amino acid difference in the CUB module. Chromosomal localization, frequency analysis, modeling, and expression. J Biol Chem 277:15354–15362
Olmarker K, Rydevik B, Nordborg C (1993) Autologous nucleus pulposus induces neurophysiologic and histologic changes in porcine cauda equina nerve roots. Spine 18:1425–1432
Parkar AA, Day AJ (1997) Overlapping sites on the link module of human TSG-6 mediate binding to hyaluronan and chondroitin 4-sulphate. FEBS Lett 410:413–417
Parkar AA, Kahmann JD, Howat SL, Bayliss MT, Day AJ (1998) TSG-6 interacts with hyaluronan and aggrecan in a pH-dependent manner via a common functional element: implications for its regulation in inflamed cartilage. FEBS Lett 428:171–176
Plow EF, Herren T, Redlitz A, Miles LA, Hoover-Plow JL (1995) The cell biology of the plasminogen system. FASEB J 9:939–945
Saal JS, Franson RC, Dobrow R, Saal JA, White AH, Goldthwhaite N (1990) High levels of inflammatory phospholipase A2 activity in lumbar disc herniations. Spine 15:674–678
Thompson JP, Pearce RH, Schechter MT, Adams ME, Tsang IKY, Bishop PB (1990) Preliminary evaluation of the scheme for grading the gross morphology of the human intervertebral disc. Spine 15:411–415
Wisniewski HG, Maier R, Lotz M, Lee S, Klampfer L, Lee TH, Vilcek J (1993) TSG-6: A TNF-, IL-1-, and LPS-inducible secreted glycoprotein associated with arthritis. J Immunol 151:6593–6601
Wisniewski HG, Burgess WH, Oppenheim JD, Vilcek J (1994) TSG-6, an arthritis-associated hyaluronan binding protein, forms a stable complex with the serum protein inter-alpha-inhibitor. Biochemistry 33:7423–7429
Wisniewski HG, Hua JC, Poppers DM, Naime D, Vilcek J, Cronstein BN (1996) TNF/IL-1-inducible protein TSG-6 potentiates plasmin inhibition by inter-alpha-inhibitor and exerts a strong anti-inflammatory effect in vivo. J Immunol 156:1609–1615
Wisniewski HG, Vilcek J (1997) TSG-6: An IL-1/TNF-inducible protein with anti-inflammatory activity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8:143–156
Ye L, Mora R, Akhayani N, Haudenschild CC, Liau G (1997) Growth factor and cytokine-regulated hyaluronan protein TSG-6 is localized to the injury-induced rat neointima and confers enhanced growth in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 81:289–296
Acknowledgement
We are very grateful to the Arthritis Research Campaign, UK, for financial support for this project (SR, HE, JM, CMM, JU and AJD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, S., Evans, H., Menage, J. et al. TNFα-stimulated gene product (TSG-6) and its binding protein, IαI, in the human intervertebral disc: new molecules for the disc. Eur Spine J 14, 36–42 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-004-0798-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-004-0798-x