Abstract
The kynurenine pathway (KP) is the main catabolic pathway for the essential amino acid tryptophan (TRP). The imbalance between beneficial and harmful kynurenines was concerned with the pathogenesis and biological mechanisms of various disorders such as diabetes mellitus (DM), obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, depression, and schizophrenia. The present study aimed to determine the levels of biomarkers—TRP, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), kynurenine (KYN) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) to find their association with relevant clinical parameters. Further, aimed to shed light on how coordination amongst the metabolites of KP and BDNF may influence the diagnosis of T2DM and GDM comorbid with depression. One hundred eighty participants were divided into six groups based on glycemic index and depression state. TRP, IDO, KYN and BDNF were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and their association was examined. The biochemical parameters were analysed by fully automated equipment. The levels of TRP, IDO and KYN were significantly higher in diabetic patients when compared to non-diabetic, whereas the BDNF level was lower. Correlation analyses showed that TRP, IDO and KYN were positively associated, whereas BDNF was negatively associated with glycemic index (p < 0.01). Our study correlated the overall association between KYN metabolites and BDNF in the aetiology of T2DM and GDM with depression as a cofactor. According to our findings, TRP, IDO, KYN and BDNF either individually or in combination have the potential to be an effective diagnostic tool for both diabetes and depression.
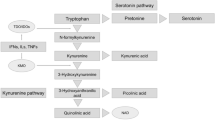
Graphical Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data outside those published and the material presented in this manuscript are available for sharing.
Abbreviations
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- IDO:
-
Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase
- FBS:
-
Fasting blood sugar
- KP:
-
Kynurenine pathway
- KYN:
-
Kynurenine
- MDD:
-
Major depressive disorder
- PPBS:
-
Post prandial blood sugar
- TDO:
-
Tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase
- TRP:
-
Tryptophan
References
Abbkine:abbkine.com/product/human-tryptophan-elisa-kit (2017) Copyright © 2012 - 2017 Abbkine, Inc. - All rights reserved. Available from https://www.abbkine.com/datasheet/KTE63056-B.pdf
Abedi S, Vessal M, Asadian F, Takhshid MA (2021) Association of serum kynurenine/tryptophan ratio with poor glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Metab Disord 20:1521–1527
Atlas ID. Diabetes around the world in (2021) International Diabetes Federation
Badawy AA (2017) Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism: regulatory and functional aspects. Int J Tryptophan Res 9(10):1178646917691938
Bakker L, Ramakers IH, van Boxtel MP, Schram MT, Stehouwer CD, van der Kallen CJ, Dagnelie PC, Van Greevenbroek MM, Wesselius A, Midttun Ø, Ueland PM (2021) Associations between plasma kynurenines and cognitive function in individuals with normal glucose metabolism, prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: the Maastricht Study. Diabetologia 64:2445–2457
Campayo A, De Jonge P, Roy JF, Saz P, De la Cámara C, Quintanilla MA, Marcos G, Santabárbara J, Lobo A (2010) Depressive disorder and incident diabetes mellitus: the effect of characteristics of depression. Am J Psychiatry 167(5):580–588
Chen T, Zheng X, Ma X, Bao Y, Ni Y, Hu C, Rajani C, Huang F, Zhao A, Jia W, Jia W (2016) Tryptophan predicts the risk for future type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 11(9):e0162192
Eyileten C, Mirowska-Guzel D, Milanowski L, Zaremba M, Rosiak M, Cudna A, Kaplon-Cieslicka A, Opolski G, Filipiak KJ, Malek L, Postula M (2019) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor is related to platelet reactivity and metformin treatment in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Can J Diabetes 43(1):19–26
Fiore V, Marci M, Poggi A, Giagulli VA, Licchelli B, Iacoviello M, Guastamacchia E, De Pergola G, Triggiani V (2015) The association between diabetes and depression: a very disabling condition. Endocrine 48:14–24
Immunotag.com/ELISA_Kits/Human_ELISA_kits (2022a) © 2022 Geno Technology Inc., USA. All Rights Reserved. Available from: https://www.immunotag.com/ELISA_Kits/Human_ELISA_kits/datasheet/ITE021805
Immunotag.com/ELISA_Kits/Human_ELISA_kits (2022b) © 2022 Geno Technology Inc., USA. All Rights Reserved. Available from: https://www.immunotag.com/ELISA_Kits/Human_ELISA_kits/datasheet/ITLK09026
Immunotag.com/ELISA_Kits/Human_ELISA_kits (2022c) © 2022 Geno Technology Inc., USA. All Rights Reserved. Available from: https://www.immunotag.com/ELISA_Kits/Human_ELISA_kits/datasheet/ITLK01394
Kiluk M, Lewkowicz J, Pawlak D, Tankiewicz-Kwedlo A (2021) Crosstalk between tryptophan metabolism via kynurenine pathway and carbohydrate metabolism in the context of cardio-metabolic risk. J Clin Med 10(11):2484
Kozieł K, Urbanska EM (2023) Kynurenine pathway in diabetes mellitus—novel pharmacological target? Cells 12(3):460
Kubacka J, Staniszewska M, Sadok I, Sypniewska G, Stefanska A (2022) The kynurenine pathway in obese middle aged women with normoglycemia and type 2 diabetes. Metabolites 12(6):492
Malina HZ, Richter C, Mehl M, Hess OM (2001) Pathological apoptosis by xanthurenic acid, a tryptophan metabolite: activation of cell caspases but not cytoskeleton breakdown. BMC Physiol 1:1–8
Meyramov G, Korchin V, Kocheryzkina N (1998) Diabetogenic activity of xanthurenic acid determined by its chelating properties. InTransplantation proceedings 30(6):2682-2684
Musselman DL, Betan E, Larsen H, Phillips LS (2003) Relationship of depression to diabetes types 1 and 2: epidemiology, biology, and treatment. Biol Psychiat 54(3):317–329
Noto Y, Okamoto H (1978) Inhibition by kynurenine metabolites of proinsulin synthesis in isolated pancreatic islets. Acta Diabetol Lat 15:273–282
Nurjono M, Lee J, Chong SA (2012) A review of brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a candidate biomarker in schizophrenia. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci
Okuda S, Nishiyama N, Saito H, Katsuki H (1998) 3- Hydroxykynurenine, an endogenous oxidative stress generator, causes neuronal cell death with apoptotic features and region selectivity. J Neurochem 70(1):299–307
Oxenkrug GF (2015a) Increased plasma levels of xanthurenic and kynurenic acids in type 2 diabetes. Mol Neurobiol 52:805–810
Oxenkrug GF (2015b) Role of kynurenine pathway in insulin resistance: toward kynurenine hypothesis of insulin resistance and diabetes. Targeting the broadly pathogenic kynurenine pathway. 169–78
Pillai A, Kale A, Joshi S, Naphade N, Raju MS, Nasrallah H, Mahadik SP (2010) Decreased BDNF levels in CSF of drug-naive first-episode psychotic subjects: correlation with plasma BDNF and psychopathology. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13(4):535–539
Pouwer F, Beekman AT, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, Snoek FJ, Kostense PJ, Heine RJ, Deeg DJ (2003) Rates and risks for co-morbid depression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from a community-based study. Diabetologia 46:892–898
Rogers KS, Evangelista SJ (1985) 3-Hydroxykynurenine, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid, and o-aminophenol inhibit leucine-stimulated insulin release from rat pancreatic islets. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 178(2):275–278
Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Kroenke KJ (2014) Test review: patient health questionnaire–9 (PHQ-9). Rehabil Couns Bull 57(4):246–248
Tutakhail A, Boulet L, Khabil S, Nazari QA, Hamid H, Coudoré F (2020) Neuropathology of kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism. Curr Pharmacol Rep 6:8–23
Williams MM, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ (2006) Treating depression to prevent diabetes and its complications: understanding depression as a medical risk factor. Clin Diabetes 24(2):79–86
Yamanaka M, Itakura Y, Tsuchida A, Nakagawa T, Taiji M (2008) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) prevents the development of diabetes in prediabetic mice. Biomed Res 29(3):147–153
Yu E, Papandreou C, Ruiz-Canela M, Guasch-Ferre M, Clish CB, Dennis C, Liang L, Corella D, Fito M, Razquin C, Lapetra J (2018) Association of tryptophan metabolites with incident type 2 diabetes in the PREDIMED trial: a case–cohort study. Clin Chem 64(8):1211–1220
Zhen YF, Zhang J, Liu XY, Fang H, Tian LB, Zhou DH, Kosten TR, Zhang XY (2013) Low BDNF is associated with cognitive deficits in patients with type 2 diabetes. Psychopharmacology 227:93–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept or design: P.S; acquisition, analysis or interpretation of data: P.S; supervision and support: V.P, K.J.S, A.M and A.S.R; drafting the work or revising: P.S and V.P; final approval of the manuscript: P.S and V.P. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of the SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre (SRM MCH & RC) IEC no: 3065/IEC/2022.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study.
Consent for publication
It is affirmed that the person/s named above are the sole author/s of the work titled as below, that neither this work nor portions thereof have been published elsewhere and that this work will not be submitted elsewhere until the Journal’s editorial process is completed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Prasanth Subramanian is the first author of this work
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Subramanian, P., Prabhu, V., S, K.J. et al. Circulating biomarkers of upstream kynurenine pathway and brain-derived neurotropic factor in the diagnosis of type 2 and gestational diabetes mellitus with depression. Comp Clin Pathol 33, 247–255 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03546-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03546-2