Abstract
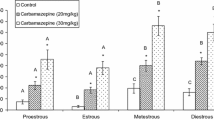
Catamenial epilepsy is one of the central brain-related disorders associated with a menstrual cycle in some epileptic women. This study aimed to determine the effects of berberine on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures during the estrus cycle in rats. A total of 30 adult female Wistar rats were randomly allocated into 5 groups control (saline), valproic acid (75 mg/kg), berberine (10 mg/kg), berberine (20 mg/kg), and berberine (30 mg/kg). Each contains proestrus, estrus, metestrus, and diestrus. Then, each group followed the i.p. administration of saline or vehicle intraperitoneal administration of PTZ (80 mg/kg). Then, initiation time of myoclonic seizures (ITMS), initiation time of tonic–clonic seizures (ITTS), and seizure duration (SD) were recorded. According to the results, berberine (20 and 30 mg/kg) significantly increased the ITTS and ITMS during various phases of the estrous cycle compared to the controls (P < 0.05). Seizure duration significantly decreased using berberine (20 and 30 mg/kg) compared to the controls (P < 0.05). Berberine (20 and 30 mg/kg) significantly increased the onset of ITMS and ITTS in metestrus and diestrus compared to proestrus and estrus (P < 0.05). Findings suggested that berberine has anticonvulsant effects in the model of PTZ rats, and it was more prominent during the luteal phase than the follicular phase.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available by request after acceptance.
References
Amado D, Cavalheiro EA (1998) Hormonal and gestational parameters in female rats submitted to the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 32:266–274
Baluchnejad Mojarad T, Roghani M (2014) The anticonvulsant and antioxidant effects of berberine in kainate-induced temporal lobe epilepsy in rats. Basic Clin Neurosci 5(2):124
Bhutada P, Mundhada Y, Bansod K, Dixit P, Umathe S, Mundhada D (2010) Anticonvulsant activity of berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid in mice. Epilepsy & Behav 18(3):207–210
Bi D, Wen L, Wu Z, Shen Y (2020) GABAergic dysfunction in excitatory and inhibitory (E/I) imbalance drives the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 16(9):1312–1329
Fatehi M, Saleh TM, Fatehi-Hassanabad Z, Farrokhfal K, Jafarzadeh M, Davodi S (2005) A pharmacological study on Berberis vulgaris fruit extract. J Ethnopharmacol 31;102(1):46–52.
Frank S, Tyson NA (2020) A clinical approach to catamenial epilepsy: a review. The Permanente J 24
Guille C, Spencer S, Cavus I et al (2008) The role of sex steroids in catamenial epilepsy and premenstrual dysphoric: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Epilepsy Behav 13:12–24
Hoffmann KM, Herbrechter R, Ziemba PM, Lepke P, Beltrán L, Hatt H, Werner M, Gisselmann G (2016) Kampo medicine: evaluation of the pharmacological activity of 121 herbal drugs on GABAA and 5-HT3A receptors. Frontiers Pharmacol 7:219
Imanshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H (2008) Pharmacological and therapeutic effects of Berberis vulgaris and its active constituent, berberine. Phytotherapy Res 22(8):999–1012
Kaboutari J, Zendehdel M, Habibian S, Azimi M, Shaker M, Karimi B (2012) The antiepileptic effect of sodium valproate during different phases of the estrous cycle in PTZ-induced seizures in rats. J Physiol Biochem 68:155–161
Kulkarni SK, Dhir A (2010) Berberine: a plant alkaloid with therapeutic potential for central nervous system disorders. Phytotherapy Research: an Int J Devoted to Pharmacol Toxicol Evaluation of Natural Product Derivatives 24(3):317–324
Kumar D, Iltaf Sr S, Umer A, Fatima M, Zaheer M, Waqar K, Girdhari K (2020) The frequency of catamenial epilepsy in female epileptic patients of reproductive age group presented to the tertiary care hospital. Cureus 12(11)
Lin X, Zhang N (2018) Berberine: pathways to protect neurons. Phytotherapy Res 32(8):1501–1510
Mattson RH, Cramer JA (1985) Epilepsy, sex hormones and antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia 26:40–51
Radu BM, Epureanu FB, Radu M, Fabene PF, Bertini G (2017) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in clinical and experimental epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 131:15–27
Reddy DS, Carver CM, Clossen B, Wu X (2019) Extrasynaptic GABA-A receptor-mediated sex differences in the antiseizure activity of neurosteroids in status epilepticus and complex partial seizures. Epilepsia 60(4):730
Sadeghnia HR, Taji AR, Forouzanfar F, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Berberine attenuates convulsing behavior and extracellular glutamate and aspartate changes in 4-aminopyridine treated rats. Iranian J Basic Med Sci 20(5):588
Van Luijtelaar G, Budziszewska B, Jaworska-Feil L et al (2001) The ovarian hormones and absence epilepsy: a long term EEG study and pharmacological effects in a genetic absence model. Epilepsy Res 46:225–239
Velı´sˇkova´ and DeSantis, (2013) Sex and hormonal influences on seizures and epilepsy. Horm Behav 63:267–277
Voinescu PE (2019) Catamenial epilepsy. In Neurology and psychiatry of women 2019 (pp. 85–94). Springer, Cham
Xue W, Xue F, Jia T, Hao A (2022) Research and experimental verification of the molecular mechanism of berberine in improving premature ovarian failure based on network pharmacology. Bioengineered 13(4):9885–9900
Yang J, Yan H, Li S, Zhang M (2018) Berberine ameliorates MCAO induced cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via activation of the BDNF–TrkB–PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 43(3):702–710
Zanboori A, Tamaddonfard E, Mojtahedin A (2010) The effect of intracerebroventricular injection of histamine in visceral nociception induced by acetic acid in rats. Indian J Pharmacol 42(5):289
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the central laboratory of the Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran, for their cooperation. This research is conducted as a part of the DVM thesis of the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The research committee approved all study protocols of the Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch (IR.IAU.SRB.REC.1401.056).
Informed consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained for every individual person’s data included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Asadollah-salmanpour, Y., Hassanpour, S. & Vazir, B. Effects of berberine on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures during estrus cycle in rats. Comp Clin Pathol 32, 919–924 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03502-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03502-0