Abstract
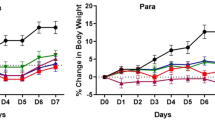
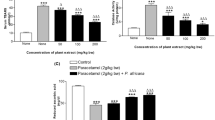
The leaf of Ficus exasperata has been used locally in managing liver toxicity. Hence, this study was designed to assess the effect of ethanol leaf extract of Ficus exasperata in acetaminophen (paracetamol)-induced albino rats. Hence, qualitative phytochemical screening and HPLC analysis of this extract were carried out using an established protocol. Toxicity was achieved when 2 g/kg body weight of acetaminophen was administered to the albino rats. In addition, different biochemical parameters of liver and kidney were assessed to determine the efficacy of ethanol leaf extract of Ficus exasperata in acetaminophen-induced albino rats. The results obtained showed that phytochemicals such as alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, saponins, phlobatannins, phenols, terpenoids and reducing sugars were detected. The HPLC further revealed compounds such as orientin, α-caryophyllene, quercetin and myricetin, among others. Furthermore, for in vivo studies, there was a significant (P < 0.05) reduction in the activities of ALP, AST and ALT as well as concentrations of uric acid, urea and creatinine kinase when compared with positive control. Also, a significant (P < 0.05) increase in the activities of antioxidant biomarkers in both liver and kidney of the acetaminophen-induced albino rats administered extract in groups III–VIII were observed when compared with the positive control group I. The extracts were able to reverse the damage caused in the histopathological architectures of the liver and kidney of acetaminophen-induced albino rats. The ethanol leaf extract of F. exasperata was able to ameliorate the toxicity induced by acetaminophen in rats. This observation therefore supports its traditional use in the treatment of liver problems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluma JR, Kaboggoza JR, Mubaala SA (2012) Tree Tales from Uganda Honey Bee 3(4):14–56
Akah PA, Orisakwe OE, Gamaniel KS, Shittu A (2008) Evaluation of Nigerian traditional medicines II effects of some Nigerian folk remedies on peptic ulcer. J Ethnopharmacol 6(2):123–127
American Liver Foundation (2016) Liver function tests; Available from: http://www.liverfoundation.org/abouttheliver/info/liverfunctiontests.
Avwioro OG (2010) Histochemistry and tissue pathology, principle and techniques Claverianum press. Nigeria 978–35627-9-7
Bafor EE, Igbinuwen ZA (2009) Traditional medicine and pharmacopoeia: contribution to the revision of ethnobotanical and floristic studies in Ghana Accra Institute for Scientific and Technological Information. J Sci 9(4):900–919
Berg CC, Wiebes JT (1992) African Fig Trees and Fig Wasps. Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, Verhandelingen Afdelin Natuurkunde, Tweede Reeks, Deel 89, Amsterdam
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood Glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Blench R (2018) Nupe plants and trees, their names and uses. 20(4):56–78
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2016) Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Epstein-Barr. Virus and Infectious Mononucleosis. https://www.cdc.gov/epstein-barr/about-mono.html.
De Martino M, Chiarugi A (2015) Recent advances in pediatric use of oral paracetamol in fever and pain management. J Health 4(2):149–168
Englehardt A (1970) Measurement of alkaline phosphatase. Aerdti or Aerzti Labor 16:42–43
Farrugia A (2010) Albumin usage in clinical medicine: tradition or therapeutic? Transfus Med Rev 24(1):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmrv.2009.09.005.PMID19962575
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, Squadrito F, Altavilla D Bitto A (2017) Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Longev 8416763. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8416763
Ghouri N, Preiss D, Sattar N (2010) Liver enzymes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and incident cardiovascular disease: a narrative review and clinical perspective of prospective data" Hepatology 52(3):1156–1161. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23789.PMID20658466.S2CID5141849
Giannini EG, Testa R, Savarino V (2005) Liver enzyme alteration: a guide for clinicians" Can Med Assoc J 172(3):367–379. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.1040752.PMC545762.PMID15684121
Grant GH, Dumas BT, Watson WA (1987) Fundamentals of clinical chemistry. WB Saunders Company, p. 328–329
GRIN Germplasm Resources Information Network (2013) USDA, ARS, National Genetic Resources Program, National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.www.germplasm.com.
Hamilton RJ (2013) Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2013 Classic Shirt Pocket Edition, Jones & Bartlett Learning, Burlington, 27th ed.
Hinson JA, Roberts DW, James LP (2010) Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver necrosis. Handb Exp Pharmacol 196:369–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00663-0_12
Hinkle J, Cheever KB, Suddarth (2014) Hinkle J, Cheever K. Brunner & Suddarth’s handbook of laboratory and diagnostic tests. 2nd Ed, Kindle. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Aspartate Aminotransferase; p. 68–69
Hoilat GJ, John S (2021) Bilirubinuria. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557439/
Jendrassik L, Grof P (1938) Colorimetric method of determination of bilirubin. Biochemical, 297:81–89
Joseph B, Raj SJ (2010) Phytopharmacological and phytochemical properties of three Ficus species - an overview. International Journal Pharmacology Bio Sci 1(4):246–253
Kaplan A (1969) The determination of urea, ammonia, and urease. Methods Biochem Anal 17:311–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470110355.ch7
Kerharo J (2015) Historic and ethnopharmacognosic review on the belief and traditional practices in the treatment of sleeping sickness in West Africa 1(9):400–410
Lala V, Goyal A, Bansal P, Minter D (2020) Liver function tests. Stat Pearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMIDL:29494096
Lansky EP, Paavilainen HM (2011) The genus Ficus. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press 2(5):65
Leopoldino AO, Machado GC, Ferreira PH, Pinheiro MB, Day R, McLachlan AJ, Hunter DJ, Ferreira ML (2019) Paracetamol versus placebo for knee and hip osteoarthritis Cochrane. Database System Rev 6:10–24
Loeser E, DelaCruz M, Madappalli V (2011) Solubility of urea in acetonitrile–water mixtures and liquid–liquid phase separation of urea-saturated acetonitrile–water mixtures. J Chem Eng Data 56(6):2909–2913. https://doi.org/10.1021/je200122b
Ludwig J, McWhinnie H (2019) Antipyretic drugs in patients with fever and infection: literature review. British Journal of Nursing (Mark Allen Publishing) 28(10): 610–618. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2019.28.10.610
Macfoy CA (2013) Medicinal plants and traditional medicine in Sierra Leone; iUniverse: Bloomington. IN, USA
Marmura MJ, Silberstein SD, Schwedt TJ (2015) The acute treatment of migraine in adults: the American headache society evidence assessment of migraine pharmacotherapies. Headache 55(1):3–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.12499
Mattenheimer H (1981) CK-MB methods and clinical significance. Proceedings of the CK-MB Symposium, Philadelphia 1981(51):57
Mayans L, Walling A (2018) Acute migraine headache: treatment strategies. Am Fam Physician 97(4):243–251
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and s simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247(10):3170–3175
Moghadam-Kia S, Oddis CV, Aggarwal R (2016) Approach to asymptomatic creatine kinase elevation. Clevel Clin J Med 83(1):37–42. https://doi.org/10.3949/ccjm.83a.14120.PMC4871266.PMID26760521
Moriles KE, Azer SA (2021) Alanine amino transferase. StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559278/. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559278.
Naidoo U (2016) Sugar: its many disguises. Harvard Health Publishing, Harvard Medical School. https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/sugar-many-disguises-201605189590
Odebiyi A, Sofowora AE (1978) Phytochemical screening of Nigerian medicinal plants, Part III. Lloydia 41:234–246
Ojo OA, Ajiboye BO, Ojo AB, Olayide II, Akinyemi AJ, Fadaka AO, Adedeji EA, Boligon AA, Anraku de Campos MM (2017) HPLC-DAD fingerprinting analysis, antioxidant activity of phenolic extracts from Blighia sapida bark and its inhibition of cholinergic enzymes linked to Alzheimer’s disease. Jordan J Biol Sci 10(4):257–264
Oladosu IA, Zubair MF, Ali MS, Olawore NO (2009) Anticandidal activity of volatile compounds from the root bark of Ficus exasperata Vahl-Holl (Moraceae). J Essent Oil Bear Plants 12(5):562–568.https://aperta.ulakbim.gov.tr/record/39139adresindenerişildi
Rajendran P, Nandakumar N, Rengarajan T, Palaniswami R, Gnanadhas EN, Lakshminarasa U (2014) Antioxidants and human diseases. Clinical Chimica Acta 436:332–347
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Amer J Clin Path 28(1):56–63
Sherlock S (1951) Liver Disease (Determination of Total and Direct Bilirubin, Colorimetric Method). Churchill, London, p. 204
Sinha AK (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. J Anal Biochem 47:389–394
Sofowora A (1993) Medicinal plants and traditional medicines in Africa. 2nd edition. Specrum Book Limited (Publisher) Ibadan, Nigeria. pp.134–56
Sun S, Zhou JY, Yang W, Zhang H (2014) Inhibition of protein carbamylation in urea solution using ammonium-containing buffers" Anal Biochem 446:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2013.10.024.PMC4072244.PMID24161613
Tweheyo M, Lye KA, Weladji RB (2004) Chimpanzee diet and habitat selection in the Budongo Forest Reserve, Uganda. J Forest Ecol 8(8):267–278
University of Rochester Medical Center Rochester (NY) (2019) University of Rochester Medical Center; Health Encyclopedia: Creatine Kinase (Blood). https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=167&ContentID=creatine_kinase_blood
Lushchak VL (2014) Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem Biol Interact 224:164–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2014.10.01
Warwick C (2008) Paracetamol and fever management. J Health 12(6):320–326
Weichselbaum RR, Hellman S (2011) Oligometastases revisited. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8(6):378–382. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.44
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the authority of Federal University Oye-Ekiti (FUOYE) for giving us the enabling environment to conduct this research in the Department of Biochemistry of the Institution. We also appreciate the help rendered by technologists in the Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, FUOYE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the authors.
Conflict of interest
This was sponsored by all the authors.
Ethical approval
The handling and treatment of the experimental rats were in line with the FUOYE Faculty of Science Ethical Committee.
Informed consent
“For this type of study informed consent is not required.”
Consent for publication
“For this type of study consent for publication is not required.”
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bamisaye, F.A., Ajiboye, B.O., Falode, J.O. et al. Ameliorative potential of ethanol leaf extract of Ficus exasperata in acetaminophen-induced toxicity in albino rats. Comp Clin Pathol 32, 99–108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03419-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03419-0