Abstract
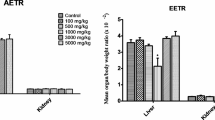
The abundance of medicinal plants does not guaranteed that they are safe, as there is dearth of data on their toxicity and safety. The present study evaluated the oral acute toxicity of methanolic leaf extract of Guiera senegalensis J.F. Gmel (GS), a plant used traditionally for the treatment of epilepsy. In phase one, 12 rats were divided in to 4 groups (n = 3) and orally administered with water, 10 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, and 1000 mg/kg of GS respectively. In phase two, four rats were divided into four groups (n = 1) and orally administered with water, 1600 mg/kg, 2900 mg/kg, and 5000 mg/kg of GS extract respectively. Rats were monitored for 24 h and subsequently for 14 days for any signs of toxicity or mortality. Liver and kidney function parameters as well as their histology were evaluated. No mortality was recorded even at the highest dose of GS extract, 5000 mg/kg. A significant increase (p < 0.05) was observed in serum level of aminotransferase (AST) and decrease (p < 0.05) in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in rats that received 10 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, and 1000 mg/kg of GS extract when compared to the control. Further, significant decrease (p < 0.05) in serum levels of creatinine and urea was also observed in the same set of rats when compared to the control rats. Histology results showed no damages to both the kidneys and livers. Conclusively, the LD50 of GS extract administered through oral route is above 5000 mg/kg per body weight.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou S, Howida S (2016) Physiological changes due to hepatotoxicity and the protective role of some medicinal plants. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 5:134–146
Ajiboye BO, Oyinloye BE, Essien PE, Onikanni SA, Ojo OA, Kappo AP (2021) Ameliorative potential of Sterculia tragacantha aqueous extract on renal gene expression and biochemical parameters in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Pharm Investig 51:103–113
Al-Rasheed NM, Fadda LM, Ali HM, Abdel Baky NA, El-Orabi NF, Al-Rasheed NM, Yacoub HI (2016) New mechanism in the modulation of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity in rats using different natural antioxidants. Toxicol Mech Methods 26:243–250
Auti ST, Kulkarni YA (2019) Acute and 28-day repeated dose oral toxicity study of caraway oil in rats. Drug Metab Personalized Ther 2019:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1515/dmpt-2019-0011
Balogun FO, Ashafa AO (2016) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of Dicoma anomala Sond. aqueous root extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in Wistar rats. J Tradit Chin Med 36:504–513
Dénou⃰ A, Togola A, Haïdara M, Sanogo R, Diallo D, Koumaré M (2016) Review on phytochemistry and pharmacological aspects of Guiera senegalensis JF Gmel (Combretaceae)
Deshmukh SA, Gaikwad DK (2014) A review of the taxonomy, ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Basella alba (Basellaceae). J Appl Pharm Sci 4:153–65
Devi N, Sangeetha R (2019) Acute and Sub-Acute Toxicity Assessment of the Hydroalcoholic Extract of MadhucaLongifolia Leaves in Wistar Rats, Journal of Herbs, Spices and Medicinal Plants 25(3):287–297
Dibal NI, Garba SH, Jacks TW (2020a) Acute toxicity of quercetin from onion skin in mice. Pharm Biomed Res 6(4):269–276
Dibal NI, Garba SH, Jacks TW (2020b) Repeated 28-day oral dose toxicity of onion skin quercetin in mice. Comp Clin Pathol 6:1219–1227
Dirar AI, Devkota HP (2021) Ethnopharmacological uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of Guiera senegalensis JF Gmel. (Combretaceae). J Ethnopharmacol 267:113433
Ekakitie L, Ajiboye BO, Oyinloye BE, Owero-ozeze OS, Onikanni SA, Ojo OA (2021) Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy in alloxan-induced diabetic rats by Solanum macrocarpon Linn aqueous leaves extract. Comp Clin Pathol 2:173–179
Everds NE (2015) Evaluation of clinical pathology data: correlating changes with other study data. Toxicol Pathol 43:90–97
Faria J, Ahmed S, Gerritsen KG, Masereeuw MSM, R, (2019) Kidney-based in vitro models for drug-induced toxicity testing. Arch Toxicol 93(12):3397–3418
Hosseinzadeh S, Jafarikukhdan A, Hosseini A, Armand R (2015) The application of medicinal plants in traditional and modern medicine: a review of Thymus vulgaris. Int J Clinic Med 6:635–642. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijcm.2015.69084
Ifijen IH, Mamza AU, Fasina KA, Omoruyi JI, Ikhuoria EU (2019) Phytochemical analysis of guiera senegalensis jF Gmel extract and its anti-plasmodial properties on wister albino mice via oral route. Int J Pharmacol Phytochem Ethnomed 13:35–44
Jafarinia M, Hosseini MS, Kasiri N, Fazel N, Fathi F, Hakemi MG, Eskandari N (2020) Quercetin with the potential effect on allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 16:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-020-00434-0
Lala V, Goyal A, Bansal P, Minter DA (2020) Liver function tests. StatPearls [Internet]. Accessed 15 Oct 2021
Lorke D (1983) A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing. Archives of toxicology 54(4):275–287
Mbaoji FN, Nweze JA (2020) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective potentials of active fractions of Lannea barteri Oliv.(Anarcadiaceae) in rats. Heliyon 6:e04099
Oh RC, Hustead TR (2011) Causes and evaluation of mildly elevated liver transaminase levels. Am Fam Physician 84:1003–1008
Rossignol P, Massy ZA, Azizi M, Bakris G, Ritz E, Covic A…, A-m working group et al (2015) The double challenge of resistant hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Lancet 386(10003):1588–1598
Sombié P, Hafizur R, Kiendrébéogo M, Choudhary M, Nacoulma O (2019) Extracts of Guiera senegalensis JF Gmel (Combretaceae) Galls Ameliorates Streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus rats status. Int J Biochem Res Rev 25:1–11
Wahid A, Hamed AN, Eltahir HM, Abouzied MM (2016) Hepatoprotective activity of ethanolic extract of Salix subserrata against CCl 4-induced chronic hepatotoxicity in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 16:1–10
World Health Organization (2000) General guidelines for methodologies on research and evaluation of traditional medicine. 1:1–74. http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/pdf/whozip42e/whozip42e.pdf. Accessed 7 Oct 2021
Yahaya T, Shehu K, Isah H, Oladele E, Shemishere U (2019) Toxicological evaluation of the leaves of Guiera senegalensis (JF Gme), Cassia occidentalis (Linn), and Ziziphus mauritiana (Lam). Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences 8(1):1–9
Zakawa NN, Akesa TM, Timon D, Yusuf CS, Magga B, Jacob GF (2018) Ethnobotanical survey and phytochemical studies of Guiera senegalensis Lam. In: Mubi local government of Adamawa state
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: all authors. Methodology: NID, SMC, AMA, and HAA; Resources: AMA, HAA, SHG, NID, and SMC; data collection and processing: AMA and HAA; analysis and interpretation: SMC, AMA, HAA, and NID; writing—original draft: AMA and HAA; Critical review and editing: SHG, SMC, and NID; supervision: SHG and SMC.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The research protocol was approved by the Postgraduate Board of Studies, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, University of Maiduguri with reference number: UM/HA/PGR18.19–08801. And it was conducted in accordance to the ARRIVE guidelines for in vivo experiment.
Informed consent
None.
Consent for publication
All the authors gave their consent for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, A.M., Audu, H.A., Garba, S.H. et al. Acute toxicity study of Guiera senegalensis J.F. Gmel methanolic leaf extract in Wistar albino rats through oral administration. Comp Clin Pathol 31, 839–845 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03387-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03387-5