Abstract
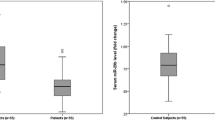
In colorectal cancer (CRC), dysregulation of noncoding RNA expression is a distinguishing factor. Owing to the conflicting results and the insufficient studies on serum microRNA-378 (miR-378) and long intragenic noncoding RNA00641 (LINC00641) expression patterns, we aimed to explore their expression profiles and diagnostic ability in colorectal cancer. Blood samples were collected from 30 healthy controls and 70 CRC patients. miR-378 and LINC00641 expression levels were determined using quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels assessed by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. The expression levels of the studied miR-378 and LINC00641 correlated with patients’ CEA levels. LINC00641 expression was dramatically upregulated, and miR-378 expression was significantly downregulated in colorectal cancer compared to the healthy controls. The differential expression of miR-378 and LINC00641 was inversely correlated, whereas the expression folds of both LINC00641 and CEA directly correlated with the advanced stages of colorectal cancer. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve analysis disclosed the highest diagnostic potential for LINC00641 to discriminate colorectal cancer patients from the control and the highest diagnostic potential for discrimination between colorectal cancer stages.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catela IT, Voss G, Cornella H et al (2017) microRNAs as cancer therapeutics: a step closer to clinical application. Cancer Lett 407:113–122
Elkeleny MR, Abdelbaki TN, Sabry AA et al (2021) Colonoscopic screening in early detection of colorectal cancer in high-risk groups: a prospective study. Egypt J Surg 40(1):3–10
Elshafei A, Shaker O, Abd El-motaal O, Salman T (2017) The expression profiling of serum miR-92a, miR-375, and miR-760 in colorectal cancer: an Egyptian study. Tumor Biol 39(6):1–14
Faltejskova P, Svoboda M, Srutova K et al (2012) Identification and functional screening of microRNAs highly deregulated in colorectal cancer. J Cell Mol Med 2655–66
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I et al (2021) Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int J Cancer 149:778–789
Hu Y, Su Y, Lei X et al (2020) LINC00641/miR-582-5p mediate oxaliplatin resistance by activating autophagy in gastric adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 10(1):14981
Ibrahim AS, Khaled HM, Mikhail NN et al ( 2014). Cancer incidence in Egypt: results of the national population-based cancer registry program. J Cancer Epidemiol 437971
Jarroux J, Morillon A, Pinskay M (2017) History, discover and classification of lncRNAs. Adv Exp Med Biol 1008:1–46
Kanduri C (2016) Long noncoding RNAs: lessons from genomic imprinting. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859:102–111
Khalil EH, Shaker OG, Hasona NA (2022) Impact of rs2107425 Polymorphism and Expression of lncH19 and miR-200a on the susceptibility of colorectal cancer. Ind J Clin Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-022-01052-w
Li Y, Jiang J, Liu W, et al (2018b) microRNA-378 promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(46):E10849–E10858
Liang R, Zhi Y, Zheng G et al (2019) Analysis of long non-coding RNAs in glioblastoma for prognosis prediction using weighted gene co-expression network analysis, Cox regression and L1-LASSO penalization. Onco Targets Ther 12:157–168
Li B, Wang Y, Li S et al (2015) Decreased expression of miR-378 correlates with tumor invasiveness and poor prognosis of patients with glioma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:7016–7021
Li LH, Gao Q, Wang XY et al (2013) miR-378 suppresses HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth by directly targeting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 21:609–613
Li L, Zhao P, Zhao Z et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA LINC00641 suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer by sponging miR-424-5p to upregulate PLSCR4. Cancer Biomark 26:79–91
Li Z, Hong S, Liu Z (2018a) LncRNA LINC00641 predicts prognosis and inhibits bladder cancer progression through miR-197-3p/KLF10/ PTEN/PI3K/AKT cascade. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(3):1825–1829
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods (san Diego Calif) 25(4):402–408
Niu JX, Meng XK, Ren JJ (2015) Studied microRNA gene expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma by microRNA microarray techniques. World J Gastroenterol 21:12605–12611
Parikh A, Lee C, Joseph P et al (2014) microRNA-181a has a critical role in ovarian cancer progression through the regulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat Commun 5:2977
Peng J, Xie Z, Cheng L et al (2015) Paired design study by real-time PCR: miR-378 and miR-145 are potent early diagnostic biomarkers of human colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 15:158
Picard E, Verschoor CP, Grace WM et al (2020) Relationships between immune landscapes, genetic subtypes and responses to immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Front Immunol 6(11):369
Ramzy I, Hasaballah M, Marzaban R et al (2015) Evaluation of microRNAs-29a, 92a and 145 in colorectal carcinoma as candidate diagnostic markers: an Egyptian pilot study. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 39:508–515
Ren D, Jinlong Lu, Han X et al (2021) LINC00641 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell malignancy through FOXD1 upregulation at the post-transcriptional level. Biochem Cell Biol 99(6):750–758
Romano G, Veneziano D, Acunzo M et al (2017) Small non-coding RNA and cancer. Carcinogenesis 38(5):485–491
Sajjadi RS, Modarressi MH, Tabatabaiefar MA (2021) JPX and LINC00641 ncRNAs expression in prostate tissue: a case-control study. Res Pharm Sci 16(5):493–504
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 69:7–34
Stoffel EM, Murphy CC (2020) Epidemiology and mechanisms of the increasing incidence of colon and rectal cancers in young adults. Gastroenterology 158(2):341–353
Schmitt AM, Chang HY (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 29:452–463
Tang Y, Cheung BB, Atmadi Brata B et al (2017) The regulatory role of long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Cancer Lett 391:12–19
Wallace J, Hu R, Mosbruger TL et al (2016) Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen identifies microRNAs that regulate myeloid leukemia cell growth. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0153689
Wang J, Liu Z-H, Yu L-J (2019) Long non-coding RNA LINC00641 promotes cell growth and migration through modulating miR-378a/ZBTB20 axis in acute myeloid leukemia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(17):7498–7509
Wang XB, Wang H, Long HQ et al (2018) LINC00641 regulates autophagy and intervertebral disc degeneration by acting as a competitive endogenous RNA of miR-153-3p under nutrition deprivation stress. J Cell Physiol 234(5):7115–7127
Xue D, Xue YF, Zhang LJ et al (2021) LINC00641 induces the malignant progression of colorectal carcinoma through the miRNA-424 5p/PLSCR4 feedback loop. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 25(2):749–757
Zeng M, Zhu L, Li L et al (2017) miR-378 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells by inhibiting SDAD1. Cell Mol Biol Lett 22:12
Zhang J, Jin S, Xiao W et al (2021) Long noncoding RNA LINC00641 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression via sponging microRNA-340-5p. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):210
Funding
This work was supported by a project funded by Cairo University entitled “long noncoding RNA signature in CRC.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.H. and O.G. conceived and designed the research study; N.A. and O.G. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; N.A. and N.H. analyzed the data; N.H. and N.A. wrote the manuscript. Finally, all authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was performed with the approval of the ethics committee of Al-Kasr Al-Ainy Hospital, Cairo University, Egypt, and The Helsinki Declaration was followed in the current research. All of the participants in this study gave their informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel Hameed, N.A., Shaker, O.G. & Hasona, N.A. Significance of LINC00641 and miR-378 as a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer. Comp Clin Pathol 31, 807–814 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03384-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03384-8