Abstract
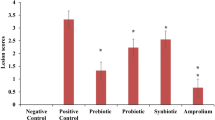
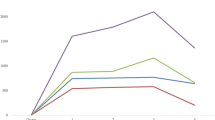
Effects of synbiotic, probiotic and prebiotic supplementation on alterations in haematological parameters of broiler chickens infected with Eimeria tenella was understudied. Ninety-day-old broiler chicks divided into 6 groups (I, II, III, IV, V, VI) containing 15 chicks each were used for the study. Group I served as negative control (non-supplemented, unchallenged). Group II served as positive control (non-supplemented but challenged). Group III was supplemented with prebiotic (sugarcane molasses). Group IV was supplemented probiotic (Antox®). Group V was supplemented synbiotic (Enflorax®) whilst Group VI was given Amprolium prophylactic treatment. Birds were challenged at 21 days with 2.0 × 104 sporulated E. tenella oocysts/chick. Blood samples were taken on days 0, 4, 7, 11 and 14 post-challenge for haematology and serum total protein evaluation according to standard laboratory procedures. Results showed haematological alterations even 4 days post-challenge (dpc) in infected groups. Total leucocyte count rose 4 dpc and was significantly (P < 0.05) high 7 dpc. Heterophil/lymphocyte ratio was significantly high in the infected groups compared with negative control by 7 dpc. Relative monocyte and oesinophil counts also increased significantly (P < 0.05). Packed cell volume, haemoglobin concentration and total erythrocyte counts were significantly lower in infected groups 7 dpc. MCHC and MCV were also low. Serum total protein equally decreased 4 dpc and was significantly (P < 0.05) lower in the infected groups compared with negative control 7 dpc. Supplementation with synbiotic, probiotic and prebiotic products amended haematological alterations associated with experimental Eimeria tenella infection more rapidly and lessened fatalities prompted by caecal coccidiosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated in the current study are available from the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Adamu M, Chaiwat B, Nirat G, Montakan V (2013) Haematological, biochemical, and histopathological changes caused by coccidiosis in chickens. Kasetsart Journal of Natural Science 47:238–246
Adewole SO (2012) The efficacy of drugs in the treatment of coccidiosis in chicken in selected poultries. Int J Adv Res 2:20–24
Akhtar M, Awais MM, Anwar IM, Ehtisham-ul-Haque S, Nasir A, Saleemi KM, Ashraf K (2015) The effect of infection with mixed Eimeria species on hematology and immune responses following Newcastle disease and infectious bursal disease booster vaccination in broilers. Veterinary Quarterly 35(1):21–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/01652176.2014.991048
Ali A, Aslam A, Khan SA, Hashmi HA, Khan KA (2002) Stress management following vaccination against coccidiosis in broilers. Pak Vet J 22:192–196
Anas M, Rizwan HM, Kasib M (2018) Probiotic role in control of coccidiosis in poultry industry. Res Vet Sci 3(1) ISSN 2474–9222
Bagado ALG, Garcia JL, da Silva PFN, Balarin MRS, Junior JDG (2010) Post-challenge hematological evaluation with virulent strain of Eimeria tenella in broilers immunized with attenuated strain or sporozoite proteins from homologous strain. Revista Brasileira De Parasitologia 19:1–6
Basith S, Abdul S, Rajavelu G, Murali MB (2003) Biochemical studies in experimental Eimeria necatrix infection in chickens. Indian Vet J 75:876–878
Blake DP, Knox J, Dehaeck B, Huntington B, Rathinam T, Ravipati V, Ayoade S, Gilbert W, Adebambo AO, Jatau ID, Raman M, Parker D, Rushton J, Tomley FM (2020) Re-calculating the cost of coccidiosis in chickens. Vet Res 51:115. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-020-00837-2
Campbell TW (1988) Avian Haematology and Cytology. Iowa State University Press, Ames, IA, p 101
Campbell TW (2000) Normal haematology of psittacine birds. In: Feldman BF, Zinkl JG, Jain NC (eds) Schalm’s Veterinary Haematology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1155–1160
Campbell TW, Ellis CK (2007) Haematology of birds. In: Campbell TW, Ellis CK (eds) Avian and Exotic Animal Haematology and Cytology, 3rd edn. Blackwell Publishing Professional, Ames (IA), pp 3–50
Campbell TW, Smith SA, Zimmerman KL (2010) Hematology of waterfowl and raptors. In: Weiss DJ, Wardrop KJ, editors. Schalm’s Veterinary Hematology. 6. USA: Wiley-Blackwell. 977–986.
Coles EH (1986) Veterinary pathology, 4th edn. Saunders, London, W.B
Dial AJ (2010) Abnormalities in the red and whites blood cell populations. Clinical Pathology for the Veterinary Team. Willey-Blackwell, USA, pp 45–74
Drabkin DR (1945) Crystallographic and optical properties of human haemoglobin. A proposal for standardization of haemoglobin. Am J Med 209:268–270
Feldmann BV, Zinki JG, Jain NC (2006) Shalmʼs Veterinary Hematology. 5th Ed. Lea and Fibiger, Philadelphia, USA.
Fukata T, Komba Y, Sasai K, Baba E, Arakaw A (1997) Evaluation of plasma chemistry and haematological studies on chickens infected with Eimeria tenella and E. acervulina. Veterinary Record 141:44–46
Gibson GR, Scott KP, Rastall RA, Tuohy KM, Hotchkiss A, Dubert-Ferrandon A, Gareau M, Murphy EF, Saulnier D, Loh G (2010) Dietary prebiotics: current status and new definition. Food Science and Technology Bulletin - Functional Foods 7:1–19
Gotep JG, Tanko JT, Forcados GE, Muraina IA, Ozele N, Dogonyaro BB, Oladipo OO, Makoshi MS, Akanbi OB, Kinjir H, Samuel AL, Onyiche TE, Ochigbo GO, Aladelokun OB, Ozoani HA, Viyoff VZ, Dapuliga CC, Atiku AA, Okewole PA, Shamaki D, Ahmed MS, Nduaka CI (2016) Therapeutic and safety evaluation of combined aqueous extracts of Azadirachta indica and Khaya senegalensis in chickens experimentally infected with Eimeria oocysts. J Parasitol Res 2016 Article ID 4692424, 9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4692424.
Hashem MA, Neamat-Allah ANF, Hammza HEE, Abou-Elnaga MH (2020) Impact of dietary supplementation with Echinacea purpurea on growth performance, immunological, biochemical, and pathological findings in broiler chickens infected by pathogenic E. coli. Trop Anim Health Prod 52:1599–1607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-019-02162-z
Hassan ER, Zeinab KME, Girh MA, Mekky HM (2012) Comparative studies between the effects of antibiotic (oxytetracycline); probiotic and acidifier on E. coli infection and immune response in broiler chickens. J Am Sci 8:795–801
Hector M, Cervantes LRM, Mark CJ (2020) Coccidiosis. Diseases of Poultry, 14th edn. John and Wiley. Sons Inc., USA, pp 1193–1217
Hirani ND, Hasnani JJ, Pandya SS, Patel PV (2018) Haematological changes in broiler birds with induced caecal coccidiosis following prophylaxis with different coccidiostats. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7(04): 1094–1100. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.119
Irizaary-Rovira AR (2004) Avian and reptilian clinical pathology (Avian haematology and biochemical analysis), Section XI, In R.L. Cowell, (ed.). Veterinary clinical pathology secrets. Elsevier Inc. St. Louis, MO, USA., 282–313.
Jatau ID, Lawal IA, Kwaga JK, Tomley FM, Blake DP, Nok AJ (2016) Three operational taxonomic units of Eimeria are common in Nigerian chickens and may undermine effective molecular diagnosis of coccidiosis. BMC Vet Res 12:86
Jatau ID, Sulaiman NH, Musa IW, Lawal AI, Okubanjo OO, Isah I, Magaji Y (2012) Prevalence of Coccidia infection and preponderance Eimeria species in free-range indigenous and intensively managed exotic chickens during the hot-wet season, in Zaria, Nigeria. Asian J Poult Sci 6:79–88
Kaingu F, Liu D, Wang L, Tao J, Waihenya R, Kutima H (2017) Anticoccidial effects of Aloe secundiflora leaf extract against Eimeria tenella in broiler chicken. Trop Anim Health Prod 49(4):823–828
Kasper LH, Buzoni-Gatel D (2001) Ups and downs of mucosal cellular immunity against protozoan parasites. Infect Immun 69(1):1–8
Kheirabdi PK, Jahangir KK, Shahab B, Jaime AT, Amir DS, Mehdi CB (2014) Comparison of the anticoccidial effect of granulated extract of Artemisia sieberi with monensin in experimental coccidiosis in broiler chickens. Exp Parasitol 141:129–133
Kogut MH, Gore TC, Long PL (2005) E. tenella, E. necatrix and E. adenoeides: peripheral blood leukocyte response of chickens and turkeys to strains adapted to the turkey embryo. Exp Parasitol, Orlando 58:63–71
Koinarski V, Georgieva N, Gadjeva V, Petkov P (2005) Antioxidant status of broiler-chickens infected with Eimeria acervulina. Revue De Médecine Vétérinaire 156:1268–1274
Malik TA, Kamili AN, Chishti MZ, Tanveers S, Ahad S, Johri RK (2016) Synergistic approach for the treatment of chicken coccidiosis using berberine — a plant natural product. Microb Pathog 93:56–62
Meskerem A, Chaiwat B, Nirat G, Montakan V (2013) Hematological, biochemical, and histopathological changes caused by coccidiosis in chickens. Kasetsart Journal-Natural Science 47:238–246
Minias P (2019) Evolution of heterophil/ lymphocyte ratios in response to ecological and life-history traits: a comparative analysis across the avian tree of life. J Anim Ecol 88:554–565. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.1294
Mitchell EB, Johns J (2008) Avian hematology and related disorders. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Exotic Animal 23. 11(3):501–22
Mohammed AK (2012) Study of haematological and some biochemical values changing with the administration of Salinomycin and Poultry star probiotics in broiler chickens challenged with Cocciodsis (E. tenella). J Vet Med Sci 11:1–8
Mohiti-Asli M, Ghanaatparast-Rashti M (2015) Dietary oregano essential oil alleviates experimentally induced coccidiosis in broilers. Prev Vet Med 120:195–202
Mondal DK, Chattopadhyay S, Batabyal S, Bera AK, Bhattacharya K (2011) Plasma biochemical indices at various stages of infection with a field isolate of Eimeria tenella in broiler chicken. Veterinary World 4(9):404–409
Musa IW, Sa’idu L, Jatau JT, Adamu J, Out MO, Abdu PA (2010) An outbreak of coccidiosis in 5-day old commercial breeder flock in Zaria. Nigeria. Int J Poult Sci 9(12):1112–1115
Ogbe AO, Atawodi SE, Abdu PA, Oguntayo BO, Noel D (2010) Oral treatment of Eimeria tenella infected broilers using aqueous extract of wild mushroom (Ganoderma Sp): effect on haematological parameters and histopathology lesions. Afr J Biotech 9:8923–8927
Owai PU, Mgbere G (2010) Effects of components of Melia azadirachta on coccidia infections in broilers in Calabar. Int J Poult Sci 9(10):931–934
Patra G, Ayoub M, Chanu K, Jonathan L, Joy L, Pravo M, Das G, Dvel K (2010) Diagnosis of E. tenella infection in broiler chicken. Int J Poult Sci 9(8):813–818
Patra G, Rajkhow TK, Ali MA, Tiwari JG, Sailo L (2010b) Studies on clinical, gross, histopathological and biochemical parameters in Broiler Birds suffered from Eimeria necatrix infection in Aizwal District of Mizoram. Int J Poult Sci 9(12):1120–1124
Pop L, Gyorke A, Taraban AF, Dumitrache MO, Kalmar Z, Mircean V, Zagon D, Balea A, Cozma V (2015) Effects of artemisin in broiler chickens challenged with Eimeria acervulina, E. maxima and E. tenella in battery trials. J Vet Parasitol 214:264–271
Portugaliza HP, Fernandez TJ (2012) Growth performance of Cobb broilers given varying concentrations of malunggay (Moringa oleifera lam) aqueous leaf extract. J Anim Feed Sci 2(6):465–469
Qureshi MA (2003) Avian macrophage and immune response: an overview. Poult Sci 82(5):691–698
Razzaq A, Hashmi HA, Kamran A, Rehman H, Khan H (2003) Clinical and haematological effects of experimentally induced coccidiosis and its prophylactic control in commercial quails. Pak J Sci 55:23–26
Rehman H, Abbas S, Lohahet N (2003) Laboratory Manual of Physiology, (vol. 1). Society of Veterinary Physiology, Lahore, Pakistan.
Samrawit M, Mersha C, Mulat A (2018). Haematological changes caused by coccidiosis in experimentally infected broiler chickens. Int J Adv Res Biol Sci 5(5): 196–202. https://doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.05.02
Sekhon BS, Jairath S (2010) Prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics: an overview. Indian J Pharm Educ Res 1:13–36
Sirois M (1995) Veterinary clinical laboratory procedures (1st edition). Mosby Year Book, Inc. Pp. 23–67.
Trafalka E, Grazy BK (2004) An alternative to antibiotics? Journal of Poultry Science 57:491–498
Wakenell PS (2010) Haematology of chickens and turkeys. In: Weiss, D. J. and Wardrop, K. J. (eds.) Veterinary haematology 6th ed. John Wiley & Sons. Ames, Iowa, USA. 957–967.
Yang, B, Ping, L, Mei-Xuan, L, Xiao-Ling, C, Wan-Yuan, X, Huai-Jing, H, Xiao-Qin, H (2019) A meta-analysis of the effects of probiotics and synbiotics in children with acute diarrhea. Med 98:37 https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000016618
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ogwiji Matthew, Jatau Isa Danladi, Natala Audu Joseph and Sani Dahiru came up with the research concept and design; Ogwiji Matthew, Andamin Danlami Aliyu, Abdulmajeed Isiaku, Kyari Stephen and Gasaliyu Abidemi Khadijat were involved in the laboratory work as well as statistical analysis of result under the supervision of Jatau Isa Danladi and Natala Audu Joseph. All authors contributed in the discussion of the results.
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The use of broiler chickens in the study were in accordance with international ethical guidelines and the Ahmadu Bello University Committee on Animal Use and care (ABUCAUC) which approved their use.
Consent to participate
Authors have permission to participate.
Consent for publication
Authors have permission for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matthew, O., Danladi, J.I., Joseph, N.A. et al. Effects of synbiotic probiotic and prebiotic supplementation on haematology and serum total proteins of broiler chickens challenged with Eimeria tenella. Comp Clin Pathol 31, 53–66 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03305-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03305-1