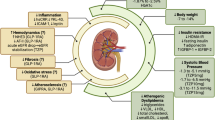
Abstract
Solanum macrocarpon leaf is one of the medicinal plants locally used to manage diabetic nephropathy. This has been established in scientific studies as one of the main factors responsible for kidney damage in diabetes mellitus patients. Hence, our study investigated the attenuation of diabetic nephropathy in alloxan-induced diabetic rats using Solanum macrocarpon Linn aqueous extract leaves. A total of 48 male Wistar rats of 7 to 8 weeks old were used in this study. A single injection of alloxan (150 mg/kg, i.p.) was used to induce diabetes in rats. Induced diabetic rats were then administered different doses (12.45, 24.90 and 49.80 mg/kg body weight) of Solanum macrocarpon (SM) leaves aqueous extract orally for 14 days. Then kidney and serum were subsequently obtained for oxidative stress biomarkers, kidney function indices as well as inflammatory parameters determination using their respective procedures. Induced diabetic rats administered SM leaves aqueous extract showed significant (p<0.05) increase in the activities of catalase (CAT), glutathione S-transferase (GST), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione (GSH), an antioxidant enzymes studied compared with the diabetic control group. However, induced diabetic rats administered SM leaves aqueous extract showed significant (p<0.05) decrease in lipid peroxidation, fasting blood glucose, creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), urea and uric acid levels as well as levels of inflammation compared with the diabetic control group. Our findings provide experimental evidence that SM leaves aqueous extract has an anti-nephropathy ability which might be useful for diabetes mellitus patients globally.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbdElwahab AH, Yousuf AF, Ramadan BK, Elimam H (2017) Comparative effects of Stevia rebaudiana and Aspartame on hepato-renal function of diabetic rats: biochemical and Histological Approaches. J Appl Pharm Sci 7(8):034–042
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods in enzymatic analysis, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 674–684
Ajiboye BO, Akalabu MC, Ojo, OA, Afolabi OB, Okesola MA, Olayide I and Oyinloye BE. 2018. Inhibitory effect of ethyl acetate fraction of Solanum macrocarpon L. leaves on cholinergic, monoaminergic, and purinergic enzyme activities. J Food Biochem e12643
Ajiboye BO, Oyinloye BE, Agboinghale PE, Onikanni SA, Asogwa E, Kappo AP (2019) Antihyperglycaemia and related gene expressions of aqueous extract of Gongronema latifolium leaf in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Pharmaceut Biol. 57(1):604–611
Ajiboye BO, Oyinloye BE, Essien PE, Onikanni SA, Ojo OA, Kappo AP (2021) Ameliorative potential of Sterculia tragacantha aqueous extract on renal gene expression and biochemical parameters in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation. 51:103–113
Cheng J, Wang F, Yu DF, Wu PF, Chen JG (2011) The cytotoxic mechanism of malondialdehyde and protective effect of carnosine via protein cross-linking/mitochondrial dysfunction/reactive oxygen species/MAPK pathway in neurons. Euro J Pharmacol. 650:184–194
Ewis SA, AbdelRahman MS (1995) Effect of metformin on glutathione and magnesium in normal and streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. J Appl Toxicol 15:387–390
Gupta P, Sharma P, Shanno K, Jain V, Pareek A, Agarwal P, Singh R, Sharma V (2016) Nephroprotective role of alcoholic extract of Pterocarpus marsupium heartwood against experimentally induced diabetic nephropathy. J Phar & Pharmaco Res. 4(5):174–186
Hemant VK, Bodhankar SL (2013) Trigonelline and sitagliptin attenuates nicotinamide-streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy in Wistar rats. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5(4):583–589
Kikkawa R, Koya D, Haneda M (2003) Progression of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 41:S19–S21
Kono Y (1978) Generation of superoxide radical during autooxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 186(1):189–195
Makita Z, Radoff S, Rayfield EJ, Yang Z, Skolnik E, Delaney V, Friedman EA, Cerami A, Vlassara H (1991) Advanced glycolsylation end products in patients with diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med 25:836–842
Mestry SN, Dhodi JB, Kumbhar SB, Juvekar AR (2017) Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by Punica granatum Linn. leaves extract. J Trad and Compl Med. 7(3):273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.06.008
Moin VM (1986) Simple and specific method of measurement of glutathione peroxidase activity in the erythrocytes. Lab Manuals. 12(724):727
Morgon MS, Depirre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione Stransferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochem Biophys Acta. 582(67):78
Naik P (2010) Biochemistry textbook, 3rd edn. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd., New Delhi (India)
Nishi, Amjid A, Pawan K (2013) Protective effect of chlorogenic acid against diabetic nephropathy in high fat diet/streptozotocin induced type-2 diabetic rats. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5(2):489–495
Ojo O, Ajiboye BO, Imere O, Adeyonu O, Olayide I, Fadaka AO (2018) Antioxidative Properties of Blighia sapida K.D. Koenig stem bark extract and inhibitory effects on carbohydrate hydrolyzing enzymes associated with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Pharmaco J 10:376–383
Onuora EEO, Okafor CN (2016) Efficacy of extracts of African eggplant and Okra leaves on alloxan-induced diabetes mellitus adult male albino rats. Pak J Nut 15:551–555
Sugumar M, Doss DVA, Maddisetty PNP (2016) Hepato-renal protective effects of hydroethanolic extract of Senna alata on enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant systems in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Integr Med Res 5:276–283
Young EC, Soo KA, Won TL, Jong EL, Seung HP, Bang BY, Kyung AP (2010) Soybeans ameliorate diabetic nephropathy in rats. Adv Acc Pub 7(4):433–440
Zhufeng W, Xie Z, Liu J, Wu Q, Wang X (2017) Renoprotective effect of berberine on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rats. Inter J Pharm 13:247–256
Funding
This manuscript was funded by all the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This research was conducted in line with the directive of the Animal Ethical Committee of Afe Babalola University, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria. The Ethical approval number is ABUAD/SCI/19/016.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ekakitie, L., Ajiboye, B.O., Oyinloye, B.E. et al. Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy in alloxan-induced diabetic rats by Solanum macrocarpon Linn aqueous leaves extract. Comp Clin Pathol 30, 173–179 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03220-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03220-5