Abstract
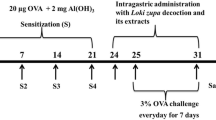
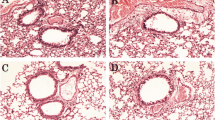
Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the respiratory system affecting over 300 million people worldwide. Lavandula has been traditionally used to treat inflammatory diseases and has also several medical applications. We aimed to explore the anti-inflammatory effects of Lavandula extract on a murine model of asthma. Twenty-eight Balb/c mice were divided into four groups of seven animals. The negative control group was treated with Phosphate-buffered saline, and the remaining three groups received ovalbumin to induce asthma. Subsequently, two asthmatic groups received budesonide or Lavandula extract. Afterward, the changes in the number of eosinophils, gene expressions, and the levels of interleukins 5, 13, and 33 were quantified in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of animals. Histopathological alterations of goblet cells, mucus secretion, and peribronchial and perivascular inflammations were examined in lung tissues of all animals. Eosinophils count and the levels of interleukins 5, 13, and 33 in BALF specimens were significantly reduced. Hyperplasia of goblet cells, mucus hypersecretion, and peribronchial and perivascular inflammations were inhibited in mice treated with Lavandula compared to asthmatic group. Interestingly, Lavandula was more effective than budesonide in alleviating inflammatory responses of asthma. The present study is the first report of anti-inflammatory and antiasthmatic activities of Lavandula extract in the Balb/c mouse model of ovalbumin-induced asthma. Lavandula antiasthmatic effects were mediated by modulating eosinophil counts, type 2 inflammatory responses, mucus secretion, and histological alterations of the lung due to inflammation, proposing it as a therapeutic modality to attenuate inflammatory complications of asthma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah AAM, Nasr El-Deen NAM, Abd El-Aziz HI, Neamat-Allah ANF (2020a) Effect of the aqueous root extract of Curcuma longa L. (turmeric) against thermally oxidized oil-induced hematological, biochemical and histopathological alterations. Comp Clin Pathol 29:837–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-020-03108-w
Abdallah AAM, Nasr El-Deen NAM, Neamat-Allah ANF, Abd El-Aziz HI (2020b) Evaluation of the hematoprotective and hepato-renal protective effects of Thymus vulgaris aqueous extract on thermally oxidized oil-induced hematotoxicity and hepato-renal toxicity. Comp Clin Pathol 29:451–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-03078-8
Asamoah F, Kakourou A, Dhami S, Lau S, Agache I, Muraro A, Roberts G, Akdis C, Bonini M, Cavkaytar O, Flood B, Izuhara K, Jutel M, Kalayci Ö, Pfaar O, Sheikh A (2017) Allergen immunotherapy for allergic asthma: a systematic overview of systematic reviews. Clin Transl Allergy 7:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13601-017-0160-0
Bakakos A, Loukides S, Bakakos P (2019) Severe eosinophilic asthma. J Clin Med 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091375
Bok SH, Seo JH, Bae CS, Kang B, Cho SS, Park DH (2019) Allium hookeri root extract regulates asthmatic changes through immunological modulation of Th1/Th2-related factors in an ovalbumin-induced asthma mouse model. Mol Med Rep 20:3215–3223. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10560
Chakir J, Shannon J, Molet S, Fukakusa M, Elias J, Laviolette M, Boulet LP, Hamid Q (2003) Airway remodeling-associated mediators in moderate to severe asthma: effect of steroids on TGF-beta, IL-11, IL-17, and type I and type III collagen expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:1293–1298. https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2003.1557
Chan BCL, Lam CWK, Tam LS, Wong CK (2019) IL33: Roles in allergic inflammation and therapeutic perspectives. Front Immunol 10:364. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00364
Chung KF (2016) Asthma phenotyping: a necessity for improved therapeutic precision and new targeted therapies. J Intern Med 279:192–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12382
de Almeida DA et al (2017) Mandevilla longiflora (Desf.) Pichon improves airway inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma. J Ethnopharmacol 200:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.02.015
Ez zoubi Y, Bousta D, Farah A (2020) A phytopharmacological review of a Mediterranean plant: Lavandula stoechas L. Clin Phytosci 6:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-019-0142-y
Fahy JV (2015) Type 2 inflammation in asthma--present in most, absent in many. Nat Rev Immunol 15:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3786
Galeone C, Scelfo C, Bertolini F, Caminati M, Ruggiero P, Facciolongo N, Menzella F (2018) Precision medicine in targeted therapies for severe asthma: is there any place for “omics” technology? Biomed Res Int 2018:4617565–4617515. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4617565
Hashem MA, Neamat-Allah ANF, Hammza HEE, Abou-Elnaga HM (2020) Impact of dietary supplementation with Echinacea purpurea on growth performance, immunological, biochemical, and pathological findings in broiler chickens infected by pathogenic E. coli. Trop Anim Health Prod 52:1599–1607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-019-02162-z
Jeon WY, Shin HK, Shin IS, Kim SK, Lee MY (2015) Soshiho-tang water extract inhibits ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation via the regulation of heme oxygenase-1. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:329. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0857-3
Korsgaard J, Ledet M (2009) Potential side effects in patients treated with inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta2-agonists. Respir Med 103:566–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2008.10.028
Leonard P, Sur S (2002) Asthma: future directions. Med Clin North Am 86:1131–1156. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-7125(02)00037-8
Lin SC, Shi LS, Ye YL (2019) Advanced molecular knowledge of therapeutic drugs and natural products focusing on inflammatory cytokines in asthma Cells 8. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070685
López-Expósito I, Srivastava KD, Birmingham N, Castillo A, Miller RL, Li XM (2015) Maternal antiasthma simplified herbal medicine intervention therapy prevents airway inflammation and modulates pulmonary innate immune responses in young offspring mice. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 114:43-51.e41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2014.10.018
Loureiro CC, Amaral L, Ferreira JA, Lima R, Pardal C, Fernandes I, Semedo L, Arrobas A (2018) Omalizumab for severe asthma: beyond allergic asthma. Biomed Res Int 2018:3254094–3254010. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3254094
Mahmoud EA, El-Sayed BM, Mahsoub YH, El-Murr AEI, Neamat-Allah ANF (2020) Effect of Chlorella vulgaris enriched diet on growth performance, hemato-immunological responses, antioxidant and transcriptomics profile disorders caused by deltamethrin toxicity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 102:422–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.04.061
Mathur SK, Viswanathan RK (2014) Relevance of allergy in adult asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 14:437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-014-0437-5
McBrien CN, Menzies-Gow A (2017) The biology of eosinophils and their role in asthma. Front Med (Lausanne) 4:93. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2017.00093
Mesnil C, Raulier S, Paulissen G, Xiao X, Birrell MA, Pirottin D, Janss T, Starkl P, Ramery E, Henket M, Schleich FN, Radermecker M, Thielemans K, Gillet L, Thiry M, Belvisi MG, Louis R, Desmet C, Marichal T, Bureau F (2016) Lung-resident eosinophils represent a distinct regulatory eosinophil subset. J Clin Invest 126:3279–3295. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci85664
Moßhammer MR, Stintzing FC, Carle R (2006) Evaluation of different methods for the production of juice concentrates and fruit powders from cactus pear. Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 7:275–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2006.04.003
Neamat-Allah ANF, Abd El Hakim Y, Mahmoud EA (2020) Alleviating effects of β-glucan in Oreochromis niloticus on growth performance, immune reactions, antioxidant, transcriptomics disorders and resistance to Aeromonas sobria caused by atrazine. Aquac Res 51:1801–1812. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14529
Neamat-Allah ANF, El-Murr AI, Abd El-Hakim Y (2019) Dietary supplementation with low molecular weight sodium alginate improves growth, haematology, immune reactions and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in Clarias gariepinus. Aquac Res 50:1547–1556. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14031
Nino G, Grunstein MM (2010) Current concepts on the use of glucocorticosteroids and beta-2-adrenoreceptor agonists to treat childhood asthma. Curr Opin Pediatr 22:290–295. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0b013e328337cb0c
Pavlidis S et al. (2019) "T2-high" in severe asthma related to blood eosinophil, exhaled nitric oxide and serum periostin. Eur Respir J 53. doi:https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00938-2018
Pelaia G, Vatrella A, Busceti MT, Gallelli L, Calabrese C, Terracciano R, Maselli R (2015) Cellular mechanisms underlying eosinophilic and neutrophilic airway inflammation in asthma. Mediat Inflamm 2015:879783–879788. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/879783
Possa SS, Leick EA, Prado CM, Martins MA, Tibério IF (2013) Eosinophilic inflammation in allergic asthma. Front Pharmacol 4:46. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00046
Saffari H, Hoffman LH, Peterson KA, Fang JC, Leiferman KM, Pease LF 3rd, Gleich GJ (2014) Electron microscopy elucidates eosinophil degranulation patterns in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 133:1728-1734.e1721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.11.024
Salehi B et al (2018) Plants of the Genus Lavandula: From Farm to Pharmacy. Natural Product Communications 13:1934578X1801301037. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1801301037
Silkoff PE, Strambu I, Laviolette M, Singh D, FitzGerald JM, Lam S, Kelsen S, Eich A, Ludwig-Sengpiel A, hupp GC, Backer V, Porsbjerg C, Girodet PO, Berger P, Leigh R, Kline JN, Dransfield M, Calhoun W, Hussaini A, Khatri S, Chanez P, Susulic VS, Barnathan ES, Curran M, Das AM, Brodmerkel C, Baribaud F, Loza MJ (2015) Asthma characteristics and biomarkers from the airways disease endotyping for personalized therapeutics (ADEPT) longitudinal profiling study. Respir Res 16:142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-015-0299-y
Srivastava KD, Dunkin D, Liu C, Yang N, Miller RL, Sampson HA, Li XM (2014) Effect of antiasthma simplified herbal medicine intervention on neutrophil predominant airway inflammation in a ragweed sensitized murine asthma model. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 112:339-347.e331-332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2014.01.021
Yang SH, Kao TI, Chiang BL, Chen HY, Chen KH, Chen JL (2015) Immune-modulatory effects of bu-zhong-yi-qi-tang in ovalbumin-induced murine model of allergic asthma. PLoS One 10:e0127636. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127636
Ye Y, Mo S, Feng W, Ye X, Shu X, Long Y, Guan Y, Huang J, Wang J (2019) The ethanol extract of Involcucrum castaneae ameliorated ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation and smooth muscle thickening in guinea pigs. J Ethnopharmacol 230:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2018.10.027
Zhou K, Liu L, Shi S (2014) Qu Feng Xuan Bi Formula attenuates anaphylactic rhinitis-asthma symptoms via reducing EOS count and regulating T cell function in rat ARA models. J Ethnopharmacol 152:568–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.006
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our special thanks to the Vice-Chancellor for Research, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. The author thanks Dr. Jamali for the preparation and analysis of histological sections.
Funding
This study was funded by Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran [Grant No. 196 and 198].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [Majid Tebianian and Rasool Choopani]; Methodology: [Sayyed Shamsadin Athari, Mahboubeh Irani, Tahereh Dargahi]; Formal analysis and investigation: [Zeinab Ghahremanid]; Writing - original draft preparation: [Sadegh Rajabi]; Writing - review and editing: [Mahmood Khodadoost]; Funding acquisition: [Rasool Choopani].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodadoost, M., Rajabi, S., Tebianian, M. et al. Alleviating effects of Lavandula aqueous extract on asthmatic complications in a mouse model. Comp Clin Pathol 30, 199–206 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03207-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03207-2