Abstract
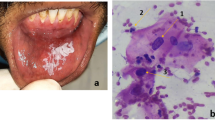
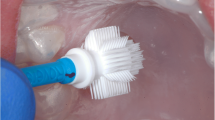
Lichen planus is a mucocutaneous chronic inflammatory lesion with a potential for malignant transformation. Exfoliative cytology is a cheaper and less aggressive method for early diagnosis. The study was conducted to evaluate cytomorphometric changes of exfoliated cells of oral lichen planus lesions. This case-control study was accomplished on 33 patients with oral lichen planus and 50 patients who did not have any lesions as the control group. Buccal mucosa cells which were provided by five to ten reciprocating motion of hard toothbrush with constant tolerable pressure were spread on a slide; then, the samples were fixed within an hour and stained with papanicolau method. The cytomorphometric parameters including the diameter of the nucleus (ND), the diameter of cytoplasm (CD), and nuclear-cytoplasmic diameter ratio of each cell were measured. Our findings showed a significant increase in nuclear diameter of case group cells and a significant decrease in cytoplasmic diameter of the same group; so, the N/C ratio in this group was clearly higher than the control group. Oral mucosa brush biopsy can be an inexpensive, sensitive, simple, and safe method of screening the dysplastic and malignant changes. It serves as an adjuvant method which is precise, objective, and repeatable.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acha-Sagredo A, Jiménez Y, Bagán J, Echebarria-Goicouria M, Aguirre-Urizar J (2011) Cytometric analysis of oral scrapings of patients with oral lichen planus. Cytopathology 22(2):106–110
Amanat D, Ebrahimi H, Zahedani MZ, Zeini N, Pourshahidi S, Ranjbar Z (2014) Comparing the effects of cryotherapy with nitrous oxide gas versus topical corticosteroids in the treatment of oral lichen planus. Indian J Dent Res 25(6):711–716
Cançado RP, Yurgel LS, Sant’Anna Filho M (2004) Comparative analyses between the smoking habit frequency and the nucleolar organizer region associated proteins in exfoliative cytology of smokers’ normal buccal mucosa. Tob Induc Dis 2(1):1
Cowpe J, Longmore R (1981) Nuclear area and Feulgen DNA content of normal buccal mucosal smears. J Oral Pathol Med 10(2):81–86
Davarmanesh M, Samsami Dehaghani A, Deilami Z, Monabbati A, Dastgheib L (2012) Frequency of genital involvement in women with oral lichen planus in southern Iran. Derm Res Pract 2012:1–6
Diniz-Freitas M, García-García A, Crespo-Abelleira A, Martins-Carneiro J, Gándara-Rey J (2003) Applications of exfoliative cytology in the diagnosis of oral cancer. Medicina Oral: Organo oficial de la Sociedad Española de Medicina Oral y de la Academia Iberoamericana de Patología y Medicina Bucal 9(4):355–361
Epstein JB, Wan LS, Gorsky M, Zhang L (2003) Oral lichen planus: progress in understanding its malignant potential and the implications for clinical management. Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Pathol, Oral Radiol, Endodontol 96(1):32–37
Folsom TC, White CP, Bromer L, Canby HF, Garrington GE (1972) Oral exfoliative study: review of the literature and report of a three-year study. Oral Surg, Oral Med Oral Pathol 33(1):61–74
Ghabanchi J, Fattahi MJ, Mardani M, Tadbir AA, Paydar AA (2009) Polymorphism of tumor protein P53 codon 72 showed no association with oral lichen planus in Shiraz, Iran. J Craniofac Surg 20(6):2168–2170
GÖREGEN M, AKGÜL HM, GÜNDOĞDU C (2011) The cytomorphological analysis of buccal mucosa cells in smokers. Turkish J Med Sci 41(2):205–210
Hayes RL, Berg GW, Ross WL (1969) Oral cytology: its value and its limitations. J Am Dent Assoc 79(3):649–657
Hegde V (2011) Cytomorphometric analysis of squames from oral premalignant and malignant lesions. J Clin Exp Dent 3(5):e441–e444
Jaafari-Ashkavandi Z, Mardani M, Pardis S, Amanpour S (2011) Oral mucocutaneous diseases: clinicopathologic analysis and malignant transformation. J Craniofac Surg. 22(3):949–951
Jin Y, Yang L, White F (1995) Preliminary assessment of the epithelial nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio and nuclear volume density in human palatal lesions. J Oral Pathol Med 24(6):261–265
Joshi PS, S M K i (2013) Cytomorphometric analysis of oral premalignant and malignant lesions using Feulgen stain and exfoliative brush cytology. J Interdiscipl Histopathol 1(4):204–211
Khandelwal S, Solomon MC (2010) Cytomorphological analysis of keratinocytes in oral smears from tobacco users and oral squamous cell carcinoma lesions—a histochemical approach. Int J Oral Sci 2(1):45–52
Khoo S-P, Primasari A, Saub R (2001) Nuclear and cellular volumetric alterations in oral lichen planus and lichenoid lesions: a histomorphometric study. J Oral Sci 43(3):151–157
Lavaee F, Majd M (2016) Evaluation of the association between oral lichen planus and hypothyroidism: a retrospective comparative study. J Dent 17(1):38–42
Lavaee F, Ghapanchi J, Anjomruz A, Malekzadeh M. (2018) The evaluation of the serum level of IL-10 in OLP patients. Comp Clin Pathol :1–4
Mardani M, Ghabanchi J, Fattahi MJ, Tadbir AA (2012) Serum level of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with different clinical subtypes of oral lichen planus. Iran J Med Sci 37(4):233–237
Messadi DV (2013) Diagnostic aids for detection of oral precancerous conditions. Int J Oral Sci 5(2):59–65
Moshaverinia M, Rezazadeh F, Dalvand F, Moshaverinia S, Samani S (2014) The relationship between oral lichen planus and blood group antigens. World J Med Sci 10:103–105
Nivia M, Sunil SN, Rathy R, Anilkumar TV (2015) Comparative cytomorphometric analysis of oral mucosal cells in normal, tobacco users, oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Cytol/Indian Acad Cytologists 32(4):253–260
Ramaesh T, Mendis B, Ratnatunga N, Thattil R (1999) Diagnosis of oral premalignant and malignant lesions using cytomorphometry. TROPICAL Dent J:23–28
Reddy SG, Kanala S, Chigurupati A, Kumar SR, Poosarla CS, Reddy BVR (2012) The sensitivity and specificity of computerized brush biopsy and scalpel biopsy in diagnosing oral premalignant lesions: a comparative study. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol: JOMFP 16(3):349–353
Rezazadeh F, Shahbazi F, Andisheh-Tadbir A (2017a) Evaluation of salivary level of IL-10 in patients with oral lichen planus, a preliminary investigation. Comp Clin Pathol 26(3):531–534
Rezazadeh F, Ebrahimi R, Andisheh-Tadbir A, Ashraf MJ, Khademi B (2017b) Evaluation of the Ki-67 and MCM3 expression in cytologic smear of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Dent 18(3):207–211
Sankhla B, Shah S,Madhusudhan AS , Bhagat P.(2010) Exfoliative cytology of oral mucosa: cytomorphometric analysis of diabetic patients J Oral Sign 2(2)
Sivapathasundharam B, Kalasagar M (2004) Yet another article on exfoliative cytology. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 8(2):54
Sudbø J, Kildal W, Risberg B, Koppang HS, Danielsen HE, Reith A (2001a) DNA content as a prognostic marker in patients with oral leukoplakia. N Engl J Med 344(17):1270–1278
Sudbø J, Ried T, Bryne M, Kildal W, Danielsen H, Reith A (2001b) RETRACTED: abnormal DNA content predicts the occurrence of carcinomas in non-dysplastic oral white patches. Oral Oncol 37(7):558–565
Sudbø J, Lippman SM, Lee JJ, Mao L, Kildal W, Sudbø A, Sagen S, Bryne M, el-Naggar A, Risberg B, Evensen JF, Reith A (2004) The influence of resection and aneuploidy on mortality in oral leukoplakia. N Engl J Med 350(14):1405–1413
Sudbø J, Ried T, Bryne M, Kildal W, Danielsen H, Reith A. Retraction notice to ‘abnormal DNA content predicts the occurrence of carcinomas in non-dysplastic oral white patches’[oral Oncol. 37 (2001) 558–565]. Oral Oncol 2007;43(4):418
Teja C, Devy AS, Nirmal RM, Sunil P, Deepasree M (2014) Cytomorphometric analysis of exfoliated cells in oral lichen planus. CytoJournal 11(1):3
Venkatesiah SS, Kale AD, Hallikeremath SR, Kotrashetti VS (2013) Histomorphometric analysis of nuclear and cellular volumetric alterations in oral lichen planus, lichenoid lesions and normal oral mucosa using image analysis software. Indian J Dent Res 24(2):277
Verma R, Singh A, Badni M, Chandra A, Gupta S, Verma R (2015) Evaluation of exfoliative cytology in the diagnosis of oral premalignant and malignant lesions: a cytomorphometric analysis. Dental Res J 12(1):83–88
Weigum SE, Floriano PN, Redding SW, Yeh C-K, Westbrook SD, McGuff HS et al (2010) Nano-bio-chip sensor platform for examination of oral exfoliative cytology. Cancer Prev Res 3(4):518–528
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Vice-Chancellor of Shiraz University of Medical Science for supporting this research (Grant no. 9414). This manuscript is based on the thesis written by Dr. Nasim Razavi. The authors also thank Dr. Mohammad Salehi of the Center for Research Improvement of the School of Dentistry for the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures followed in this study were accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lavaee, F., Nazhvani, A.D. & Razavi, N. Cytomorphometric analysis of exfoliated cells in patients with oral lichen planus. Comp Clin Pathol 27, 1073–1077 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2703-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2703-8