Abstract
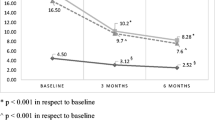
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune inflammatory disease that mainly affects joint damage followed by increased morbidity and mortality rates. The progressive increase of inflammation factors, especially IL-6, is seen during the course of this condition. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of tocilizumab (TCZ) in patients with severe to moderate resistant RA with an inadequate response to treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). We also reviewed the safety of the drug and related complications. Twelve selected RA patients received 8 mg/kg of TCZ every 4 weeks for over 24 weeks; we evaluated inflammatory factor like ESR, lipid profile, comprehensive physical exam, and RA activity like Disease Activity Score (DAS) 28, Short Form (36) Health Survey (SF-36), and ACR50 to calculate the swollen and tender joint counts. DMARDs were simultaneously administered. First-level response and secondary response were defined as reaching the American College of Rheumatology 20% response criteria (ACR20) within 24 weeks of treatment and Disease Activity Score (DAS) 28, Short Form (36) Health Survey (SF-36), and ACR50, respectively. All patients achieved ACR20 after 24 weeks and 83% reached ACR50 (p < 0.001). DAS28 decreased from 6.93 ± 2.11 at baseline to 1.29 ± 0.95 at the end of 28 weeks (p < 0.001). SF-36 increased from 28 ± 1.43 to 61.42 ± 15.66 at the end of the study (p < 0.001). SF-36 physical component summary scores also increased from 42 ± 4.98 at baseline to 88.17 ± 2.96 at the end of the study (p < 0.001). We observed that TCZ caused a rapid and sustained improvement in all disease activity indicators such as CRP, ESR, swelling and tender joint count, and morning stiffness duration in RA patients’ refractory to methotrexate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 31(3):315–324
Dougados M, Kissel K, Sheeran T, Tak PP, Conaghan PG, Mola EM et al (2013) Adding tocilizumab or switching to tocilizumab monotherapy in methotrexate inadequate responders: 24-week symptomatic and structural results of a 2-year randomised controlled strategy trial in rheumatoid arthritis (ACT-RAY). Ann Rheum Dis 72(1):43–50
Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, Cantagrel A, Van Vollenhoven R, Sanchez A, Alecock E, Lee J, Kremer J (2008) IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1516–1523
Feely MG, O’Dell JR (2010) Update on the use of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 22(3):316–320
Genovese MC, McKay JD, Nasonov EL, Mysler EF, da Silva NA, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Gomez-Reino JJ (2008) Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 58(10):2968–2980
Gottenberg J-E, Dayer J-M, Lukas C, Ducot B, Chiocchia G, Cantagrel A et al (2012) Serum IL-6 and IL-21 are associated with markers of B cell activation and structural progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: results from the ESPOIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 71(7):1243–1248
Jones G, Sebba A, Gu J, Lowenstein MB, Calvo A, Gomez-Reino JJ et al (2010) Comparison of tocilizumab monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION study. Ann Rheum Dis 69(01):88–96
Katchamart W, Trudeau J, Phumethum V, Bombardier C 2010. Methotrexate monotherapy versus methotrexate combination therapy with non-biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. The Cochrane Library
Kume K, Amano K, Yamada S, Hatta K, Ohta H, Kuwaba N (2011) Tocilizumab monotherapy reduces arterial stiffness as effectively as etanercept or adalimumab monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: an open-label randomized controlled trial. J Rheumatol 38(10):2169–2171
McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365(23):2205–2219
Nakashima Y, Kondo M, Fukuda T, Harada H, Horiuchi T, Ishinishi T et al (2014) Remission in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis by tocilizumab treatment in routine clinical practice: results from 3 years of prospectively registered data. Mod Rheumatol 24(2):258–264
Salliot C, van der Heijde D 2008. Long term safety of methotrexate monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a systematic literature research. Annals of the rheumatic diseases
Sangha O (2000) Epidemiology of rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology 39(2):3–12
Sebba A (2008) Tocilizumab: the first interleukin-6-receptor inhibitor. Am J Health Syst Pharm 65(15):1413–1418
Silman AJ, Pearson JE (2002) Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis research & therapy 4(3):1
Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E et al (2008) Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 371(9617):987–997
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, Breedveld FC, Boumpas D, Burmester G et al (2010) Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis 69(4):631–637
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all our colleagues in rheumatology clinics in Hazrat-e-Rasoul Akram and Imam Khomeini hospitals, Iran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the local ethics committee of the Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients and normal individuals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajae, E., Bidari, A., Zadeh, J.F. et al. The effect of tocilizumab on clinical signs and laboratory findings in rheumatoid arthritis patients resistant to methotrexate. Comp Clin Pathol 26, 1221–1226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2513-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2513-4