Abstract
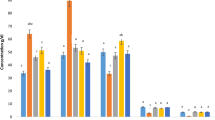
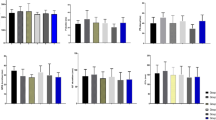
The present study was designed to evaluate the effects of chlorpyriphos, lead acetate and vitamin C alone and in combinations, on various haematological parameters in Wistar rats. Rats of 150–200 g body weight were divided into eight groups of six animals each and were subjected to various daily oral treatment regimes for 98 days. Group C served as control receiving only corn oil, group CP received chlorpyriphos at 5.5 mg/kg in corn oil and group L received lead acetate at100 ppm in water, whereas animals in group CP + L received a combination of chlorpyriphos at 5.5 mg/kg in corn oil and lead acetate at 100 ppm in water. Group VC received vitamin C at 100 mg/kg in water; group CP + VC received a combination of chlorpyriphos at 5.5 mg/kg and vitamin C at 100 mg/kg; group L + VC received lead acetate at 100 ppm in water and vitamin C at 100 mg/kg and group CP + L + VC received chlorpyriphos at 5.5 mg/kg, lead acetate at 100 ppm in water and vitamin C at 100 mg/kg. Blood samples were collected on days 0, 30, 60 and 98 post exposure and analysed for packed cell volume (PCV), total erythrocyte count (TEC), haemoglobin (Hb), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), total leucocyte count (TLC) and differential leucocyte count. A significant decrease in TEC, PCV and Hb and a significant increase in ESR values were observed. However, lead acetate caused an increase in TLC while chlorpyriphos resulted in a decrease in TLC. Both of these toxicants potentiated toxicity of each other. The study demonstrated that treatment of chlorpyriphos- and lead-treated rats with vitamin C significantly altered some of the important haematological parameters revealing the protective effect of this vitamin against haematological alterations induced by chlorpyriphos and lead.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal R, Chaurosia JP (1989) Chronic effects of mercuric chloride ingestion on rat adenocorticol function. Bulls Environ Contam Toxicol 43:481–484
Ahmed NS, Mohamed AS, Abdel-Wahhab MA (2010) Chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress and histological changes in retinas and kidney in rats: protective role of ascorbic acid and alpha tocopherol. Pestic Biochem Physiol 98:33–38
Ambali SF (2009) Ameliorative effects of vitamins C and E on neurotoxicological, haematological and biochemical changes induced by chronic chlorpyriphos in wistar rats. PhD dissertation, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria
Ambali SF, Abudkar AT, Yaqub LS, Anafi SB, Abdullahi A (2010) Chlorpyriphos induced alteration of haematological parameters in wistar rats: ameliorative effect of zinc. Environ Toxicol 4:55–66
Ambali S, Akanbi O, Igbokwe N, Shittu M, Kawu AJ (2007) Evaluation of sub-chronic chlorpyriphos poisoning on haematological and serum biochemical changes in mice and protective effect of vitamin C. J Toxicol Sci 32(2):111–120
Canadas F, Cardona D, Dávila E, Sánchez-Santed F (2005) Long-term neurotoxicity of chlorpyriphos; spatial learning impairment on repeated acquisition in a water maze. Toxicol Sci 85:944–951
Casida JE, Quinstad GB (2004) Organophosphate toxicol: safety aspects of non-acetylcholine cholinesterase secondary targets. Chem Res Toxicol 17:983–998
Costa L (2006) Current issues in organophosphate toxicology. Clin Chem Acta 306:1–13
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 11:1–42
Flora SJ, Tandon SK (1986) Preventive and therapeutic effects of thiamine, vitamin and their combination in lead intoxication. Acta Pharm Toxicol 58:374–378
Freeman R (1970) Chronic lead poisoning in children: a review of 90 children diagnosed in Sydney, 1948–67. 2. Clinical features and investigations. Med J Aust 1:648–651
Goel A, Chauhan DP, Dhawan DK (2000) Protective effects of zinc in chlorpyriphos induced hepatotoxicity: a biochemical and trace elemental study. Biol Trace Elem Res 74:171–183
Gosset KA (2004) Anemias associated with drugs and chemicals. In: Feldman BF, Zinkl JG, Jain NC (eds) Schalm's veterinary haematology, 5th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 185–189
Goyer RA, Cherion N (1979) Lead toxicity: from overt to sub-clinical to subtle health effects. EnvironHealth Perspect 86:177–181
Halliwell B (1996) Vitamin C: antioxidant or proxidant in vivo? Free Radic Res 25:439–454
Iqbal K, Khan A, Khattak MAK (2004) Biological significance of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) in human health—a review. Pak J Nutr 3(1):5–13
Klassen CD (2001) Casarett and Doull's toxicology: the basic science of poisons, 6th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 812–841
Malla G, Sharma S, Singh (2009) Chlorpyrifos pesticide toxicity on erythrocyte sedimentation rate in fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch.). Biol Med (09748369) 1(2):54–55
Okediran BS, Ajibola ES, Thomas FC, Abam OE, Biobaku KT, Olaniyi MO, Rahman S (2010) Investigation on subchronic lead intoxication on blood indicies of male rats. Global Veterinaria 4(5):532–535
Pope CN, Chakraborti TK, Chapman ML, Farrar JD (1992) Long-term neurochemical and behavioural effects induced by acute chlorpyriphos treatment. Pharmacol Biochem of Behav 42:251–256
Rahman MF, Mahboob M, Danadevi K, Saleha BB, Grover P (2003) Assessment of genotoxic effects of chloropyriphos and acephate by the comet assay in mice leucocytes. Mutat Res 516(1–2):139–147
Rahimi R, Nikfar S, Abdollahi M (2006) Increased morbidity and mortality in acute human organophosphate-poisoned patients treated by oximes: a meta-analysis of clinical trials. Hum Exp Toxicol 25:157–162
Rodak LC (1995) Routine testing in haematology. In: Rodak LC (ed) Diagnostic haematology. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 128–144
Sayers MH, Lynch SR, Jacobs P (1973) The effects of ascorbic acid supplementation on the absorption of iron in maize, wheat and soya. Br J Haematol 4:209–218
Shalan MG, Mostafa MS, Hasouna MM, Nabi SE, Refaie A (2005) Amelioration of lead toxicity on rat liver with vitamin C and silymarin supplements. Toxicology 206:1–15
Sharaf NE, Zaki MS, Gomaa WR, Batrawy NEI, Fawzi OM (2008) Some clinicopathological and microbiological studies on lead toxicity in bull. Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 3(2):165–168
Singh S, Bhati DPS (1991) Effect of zinc chloride on the morphology of blood in Channa punctatus (Bloch.). Nature Environ 8:27–32
Shadnia S, Azizi E, Hosseini R, Khoei S, Fouladdel S, Pajoumand A, Jalali N, Abdollahi M (2005) Evaluation of oxidative stress and genotoxicity in organophosphorus insecticide formulators. Hum Exp Toxicol 24:439–445
Wade MG, Fosler WG, Younglal EV, Macmohan A, Leingartner K, Yogmwas A (2002) Effects of subchronic exposure to a complex mixture of persistent chemicals in male rats. Toxicol Sci 67:131–143
Van Kampen JE, Zilista WG (1961) Standardisation of haemoglobinometry–haemoglobin-cyanide method. Clin Chem Acta 6:538–544
Wardlaw GM (1999) Perspectives in Nutrition. 4th Ed. McGraw-Hill, USA
Westergren (1986) A technique of red cell sedimentation reaction. American Review Journal 14:94–101
Yagminas AP, Franklin CA, Villeneuve DC, Gilman AP, Little PB, Valli VE (1990) Subchronic oral toxicity of triethyl lead in the male weaning rat. Clinical, biochemical, hematological and histopathological effects. Fundamentals of Applied Toxicology 15:580–596
Yurumez Y, Cemek M, Yavuz Y, Birdane YO (2007) Beneficial effect of N-acetylcysteine against organophosphate toxicity in mice. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 30:490–494
Zhang JL, Qiao CL, Lan WS (2004) Detoxification of organophosphorus compounds by recombinant carboxylesterase from an insecticide-resistant mosquito and oxime-induced amplification of enzyme activity. Inc Environ Toxic 19:154–159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nisar, N.A., Sultana, M., Baba, N.A. et al. Ameliorative effect of vitamin C on the haematological changes induced by exposure of chlorpyriphos and lead acetate in Wistar rats. Comp Clin Pathol 23, 829–834 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-013-1697-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-013-1697-5