Abstract
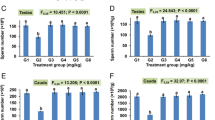
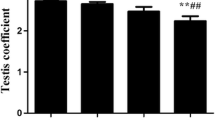
The aim of this study was to evaluate the beneficial effects of vitamin C on epididymal sperm quality following experimentally induced copper poisoning in mice. Forty-eight sexually mature male NMRI mice were divided into four different groups of 12 mice as follows: the first group which is treated by gavage with copper sulfate and distilled water daily via IP injection, the second group which received vitamin C by IP injection and distilled water by gavage, the treatment group which is treated by gavage with copper sulfate and received vitamin C by IP injection, and the control group which received distilled water by gavage and IP injection during experimental period. Sperm, blood, and testicular tissue samples were obtained from six cases of 12 mice of each group during experimental period at the fourth and sixth week. The data obtained revealed that all of parameters in the first group after the sixth week were significantly increased in comparison with group C and there is no significant difference between treatment and control groups.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuja PM, Albertini R (2001) Methods for monitoring oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and oxidant resistance of lipoproteins. Clin Chim Acta 306:1–17
Aitken RJ, Backer HWG, Irvine DS (1995) On the nature of semen quality and infertility. Hum Reprod 10:248–249
Alvarez JG, Touchstone JC, Blasco L, Storey BT (1987) Spontaneous lipid peroxidation and production of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide in human spermatozoa Superoxide dismutase as major enzyme protectant against oxygen toxicity. J Androl 8:348–388
Aydemir B, Kiziler AR, Onaran I, Alici B, Ozkara H, Akyolcu MC (2006) Impact of Cu and Fe concentration on oxidative damage in male infertility. Biol Trace Elem Res 112:193–203
Battersby S, Chandler JA, Morton MS (1982) Toxicity and uptake of heavy metals by human spermatozoa. Fertil Steril 37:230–235
Carlsen E, Giwercman A, Keiding N, Skakkebaek NE (1992) Evidence for decreasing quality of semen during past 50 years. Br Med J 305:609–613
Cummins JM, Jequier AM, Kan R (1994) Molecular biology of human male infertility: links with aging, mitochondrial genetics and oxidative stress? Mol Reprod Dev 37:345
Dawson EB, Harris WA, Powell LC (1990) Relationship between ascorbic acid and male fertility. World Rev Nutr Diet 62:1–26
Devoy J (2002) The diagnosis and pathology of an incident of copper poisoning in dairy replacement calves. Res Vet Sci 72(suppl 1):19
Giralut L, Boudou A, Dufurc EJ (1998) 113Cd-3IP NMR and fluorescence polarization studies of cadmium(II) interactions with phospholipids in model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1414:140–154
Goyer RA (1991) Toxic effects of metals. In: Amdur MO, Doull J, Klaasen CD (eds) Casarett and Doull’s toxicology, 4th edn. Pergamon, New York, pp 653–655
Hamar DW, Bedwell CL, Johnson JL, Schulthesis PC, Raisbeck M, Grotelueschen DM, Williams ES, O’Toole D, Paumer RJ, Vickers MG, Graham TJ (1997) Iatrogenic copper toxicosis induced by administering copper oxides boluses to neonatal calves. J Vet Diagn Invest 9:441–443
Haywood S (1985) Copper toxicosis and tolerance in the rat. I. Changes in copper content of the liver and kidney. J Pathol 145:149–158
Haywood S, Comerford B (1980) The effect of excess dietary copper on plasma enzyme activity and on the copper content of the blood of the male rat. J Comp Pathol 90:233–238
Hébert CD, Elwell MR, Travols GS, Fits CJ, Bucher JR (1993) Subchronic toxicity of cupric sulphate administered in drinking water and feed to rats and mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol 21:461–475
Huang YL, Tseng WC, Cheng SY, Lin TH (2000) Trace elements and lipid peroxidation in human seminal plasma. Biol Trace Elem Res 76:207–215
Lyubimov AV, Smith JA, Rousselle SD, Mercieca MD, Tomaszewski JE, Smith AC et al (2004) The effects of tetrathiomolybdate (TTM, NSC-714598) and copper supplementation on fertility and early embryonic development in rats. Reprod Toxicol 19:223–233
Massanyi P, Trandzik J, Nad P, Korenekova B, Skalicka M, Toman R et al (2004) Concentration of copper, iron, zinc, cadmium, lead, and nickel in bull and ram semen and relation to the occurrence of pathological spermatozoa. J Environ Sci Health, Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 39:3005–3014
Meeker JD, Rossano MG, Protas B, Diamond MP, Puscheck E, Daly D, Paneth N, Wirth JJ (2008) Cadmium, lead, and other metals in relation to semen quality: human evidence for molybdenum as a male reproductive toxicant. Environ Health Perspect 116(11):1473–1479
Rana SVS, Kumar A (1978) Simultaneous effects of dietary molybdenum and copper on the accumulation of copper in the liver and kidney of copper poisoned rats. A histochemical study. Ind Health 18:9–17
Raveh O, Pinchuk I, Fainaru M, Lichtenberg D (2001) Kinetics of lipid peroxidation in mixture of HDL and LDL, mutual effects. Free Radic Biol Med 31:1486–1497
Rebrelo L, Guadarrama A, Lopez T, Zegers HF (1996) Effect of Cu ion on the motility, viability, acrosome reaction and fertilizing capacity of human spermatozoa in vitro. Reprod Fertil Dev 8:871–874
Rosmarie AF (1992) Toxicity summary for copper. Prepared for: Oak Ridge Reservation Environmental Restoration Program. Managed by Martin Marietta Energy Systems, Inc., for the US Department of Energy under contract no. DE-AC05-84OR21400
Sakhaee E, Emadi L, Abshenas J, Kheirandish R, Azari O, Amiri E (2012) Evaluation of epididymal sperm quality following experimentally induced copper poisoning in male rats. Andrologia. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0272.2010.01147.x
Salem MH, Kamel KI, Yousef MI, Hassan GA, EL-Nouty FD (2001) Protective role of ascorbic acid to enhance semen quality of rabbits treated with sublethal doses of aflatoxin B1. Toxicology 162:209–218
Salsabili N, Mehrsai AR, Jalaie S (2009) Concentration of blood and seminal plasma elements and their relationships with semen parameters in men with spinal cord injury. Andrologia 41:24–28
Skandhan KP (1992) Review on copper in male reproduction and contraception. Rev Fr Gynecol Obstet 87:594–598
Slivkova J, Popelkova M, Massanyi P, Toporcerova S, Stawarz R, Formicki G et al (2009) Concentration of trace elements in human semen and relation to spermatozoa quality. J Environ Sci Health, Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 44:370–375
Stalker MJ, Hayes MA (2007) Liver and biliary system. In: Maxie MG (ed) Jubb, Kennedy, and Palmer’s pathology of domestic animals, 5th edn. Saunders Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 297–388
Steffen DJ, Carlson MP, Casper HH (1997) Copper toxicosis in suckling beef calves associated with improper administration of copper oxide boluses. J Vet Diagn Invest 9:443–446
Stohs ST, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metals. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–326
Stokinger HE (1981) Copper. In: Clayton GD, Clayton E (eds) Patty’s industrial hygiene and toxicology, vol 2A. Wiley, New York, pp 1620–1630
Sullivan JM, Janovitz EB, Robinson FR (1991) Copper toxicosis in veal calves. J Vet Diagn Investig 3:161–164
Swan SH, Elkin EP, Fenster L (2000) The question of declining sperm density revisited: an analysis of 101 studies published 1934–1996. Environ Health Perspect 108:961–966
Taylor CT (2001) Antioxidants and reactive oxygen species in human fertility. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 10(4):189–198
Venugopal B, Luckey TD (1978) Metal toxicity in mammals. 2. Chemical toxicity of metals and metalloids. Plenum, New York, pp 24–32
Wong WY, Flik G, Groenen PMW, Swinkels DW, Thomas CMG, Copius-Peereboom JHJ et al (2001) The impact of calcium, magnesium, zinc, and copper in blood and seminal plasma on semen parameters in men. Reprod Toxicol 15:131–136
World Health Organization (1999) World Health Organization laboratory manual for examination of human semen and sperm–cervical mucus interaction, 4th edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Yuyan L, Junqing W, Wei Y, Weijin Z, Ersheng G (2007) Are serum zinc and copper levels related to semen quality? Fertil Steril 89:1008–1011
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the research council of Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakhaee, E., Abshenas, J., Emadi, L. et al. Effects of vitamin C on epididymal sperm quality following experimentally induced copper poisoning in mice. Comp Clin Pathol 23, 181–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1592-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1592-5