Abstract
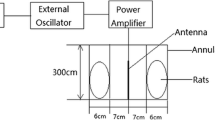
This study was conducted to assess the effect of short-term exposure to RF waves generated by BTS antenna on the viability and motility of stored sperm in different parts of the epididymis. One hundred testes from slaughtered bulls were collected and used for this study. The testes were divided into two groups, test and sham-exposed, each group, according to time of exposure to RF (1 to 5 h), was divided into five subgroups, ten in each group. After a defined time, the motility (tail of the epididymis) and viability of sperms (in three parts of the epididymis) were evaluated in both groups. In the head of the epididymis, the reduction of sperm viability observed in the test group was 13% (after 3 h), 18% (after 4 h) and 21% (after 5 h) compared to the sham-exposed group, which was statistically significant (P < 0.05). In the test group, sperm viability was significantly reduced in the body and tail sections after 4 and 5 h compared to the sham-exposed group (P < 0.05). After 3 h of exposure to RF, the percentage of progressive motility of sperm decreased (8.7%), while the percentage of slow progressive motility increased significantly (6.4%) after 4 h compared to the sham-exposed group (P < 0.05). These results suggested that short-term exposure to RF generated by mobile BTS has a deleterious effect on the quality of epididymal sperm (viability and motility) and that this effect is more severe in the head section and increases with increased exposure time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Deepinder F, Sharma RK, Ranga G, Li J (2008) Effect of cell phone usage on semen analysis in men attending infertility clinic: an observational study. Fertil Steril 89:124–128
Aitken RJ, Bennetts LE, Sawyer D, Wiklendt AM, King BV (2005) Impact of radio frequency electromagnetic radiation on DNA integrity in the male germline. Int J Androl 28:171–179
Aziz DM (2006) Assessment of bovine sperm viability by MTT reduction assay. Anim Reprod Sci 92:1–8
Bearden H, Fuquay J, Willard ST (2003) Applied animal reproduction, 6th edn. Mississippi State University, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Blank M, Goodman R (2004) A biological guide for electromagnetic safety, the stress response. Bioelectromagnetics 25:642–646
Braune S, Wrocklage C, Raczek J, Gailus T, Lucking CH (1998) Resting blood pressure increase during exposure to a radio-frequency electromagnetic field. Lancet 351:1857–1858
Burch JB, Reif JS, Yost MG, Keefe TJ, Pitrat CA (1998) Nocturnal excretion of a urinary melatonin metabolite among electric utility workers. Scand J Work Environ Health 24:183–189
Capkova J, Geussova G, Peknicova J (2000) Monoclonal antibody to human sperm acrosomal protein. Folia Biol (Praha) 46:55–57
Cherry N (2002) Criticism of the health assessment in the ICNIRP guidelines for radiofrequency and microwave radiation (100 kHz–300 GHz). Public Health 2:113–124
Dasdag S, Ketani MA, Akdag Z, Ersay AR, Sari I, Demirtas OC, Celik MS (1999) Whole-body microwave exposure emitted by cellular phones and testicular function of rats. Urol Res 27:219–223
Dasdag S, Zulkuf Akdag M, Aksen F, Yilmaz F, Bashan M, Mutlu Dasdag M, Celik MS (2003) Whole body exposure of rats to microwaves emitted from a cell phone does not affect the testes. Bioelectromagnetics 24:182–188
Fejes I, Zavaczki Z, Szollosi J, Koloszar S, Daru J, Kovacs L (2005) Is there a relationship between cell phone use and semen quality? Arch Androl 51:385–393
Giwercman A, Richthoff J, Hjollund H, Bonde JP, Jepson K, Frohm B (2003) Correlation between sperm motility and sperm chromatin structure assay parameters. Fertil Steril 80:1404–1412
Havas M (2000) Biological effects of non-ionizing electromagnetic energy: a critical review of the reports by the US National Research Council and the US National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences as they relate to the broad realm of EMF bioeffects. Environ Rev 8:173–253
Hjollund NHI, Bonde JP, Skotte J (1997) Semen analysis of personnel operating military radar equipment. Reprod Toxicol 11:897, Letter
Huber R, Graf T, Cote KA, Wittmann L, Gallmann E, Matter D (2000) Exposure to pulsed high-frequency electromagnetic field during waking affects human sleep EEG. Neuroreport 11:3321–3325
Jelodar GA, Nazifi S (2010) Effect of radiation leakage of microwave oven on body weight, cortisol and thyroid hormones of adult female mice. Physio Pharm 13:416–422, in Persian
Jelodar GA, Nazifi S, Nouhravesh M (2010) Effect of electromagnetic field generated by BTS on haematological parameters and cellular composition of bone marrow in rat. Comp Clin Path. doi:10.1007/s00580-010-1031-4
Jung A, Schill WB (2000) Male infertility. Current life style could be responsible for infertility. MMW Fortschr Med 142:31–33, in German
Lai H, Singh NP (1996) Single- and double-strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells after acute exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 69:513–521
Mann K, Roschke J (2004) Sleep under exposure to high-frequency electromagnetic fields. Sleep Med Rev 8:95–107
ESHRE Monograph (2002) Manual of basic semen analysis. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 10–11
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Panagopoulos DJ, Messini N, Karabarbounis A, Filippetis AL, Margaritis LH (2000) A mechanism for action of oscillating electric fields on cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 272:634–640
Pohl HR, Luukinen B, Holler JS (2005) Health effects classification and its role in the derivation of minimal risk levels: reproductive and endocrine effects. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 42:209–217
Schrader SM, Langford RE, Turner TW, Breitenstein MJ, Clark JC, Jenkins BL, Lundy DO, Simon SD, Weyandt TB (1998) Reproductive function in relation to duty assignments among military personnel. Reprod Toxicol 12:465–468
Sharlip ID, Jarow JP, Belker AM, Lipshultz LI, Sigman M, Thomas AJ (2002) Best practice policies for male infertility. Fertil Steril 77:873–882
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jelodar, G., Talebzadeh, M.R. & Lari, M.A. Effect of short-term exposure to radio frequency emitted by base transceiver station (BTS) antenna on epididymal sperms. Comp Clin Pathol 21, 1285–1290 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1282-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1282-8