Abstract
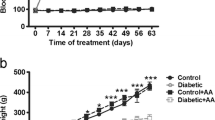
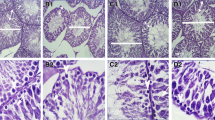
This investigation was conducted to evaluate the effects of maternal diabetes on foetal testicular structure and function and reproductive hormone levels. Sixteen adult female rats were divided in two groups. Diabetes was induced in one group by alloxan. Both groups became pregnant by natural mating. Blood was collected from 60-day-old male offspring from both groups and the level of testosterone, FSH and LH measured in their serum. At the same time, the weight and volume of testes and various histological parameters from testicular histological sections were determined. Results showed significant decrease in LH, FSH and testosterone in sera of offspring from diabetic mothers (ODM) compared with the control group. Body weight and weight and volume of testes from ODM were about 25.5%, 51.6% and 50.8% higher respectively than those of the control group (P < 0.05). Number of seminiferous tubules increased (+15%) significantly (P < 0.05), whilst thickness of testicular capsule (−16%), number of Leydig cells (−14%), number of Sertoli cells (−10%), number of spermatogonia (−38%) and diameter of seminiferous tubules (−17%) showed significantly reduced values in the ODM compared to controls (P < 0.05). In conclusion, maternal hyperglycaemia has deleterious effects on testicular parameters during foetal life which will affect reproductive endocrinology during puberty and may impact on fertility.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts L, Van Assche FA (1977) Rat fetal endocrine pancreas in experimental diabetes. J Endocrinol 73:339–346. doi:10.1677/joe.0.0730339
Ballester J, Munoz C, Dominguez J, Rigau T, Joan J, Guinovart Rodriguez-Gi JE (2004) Insulin-dependent diabetes affects testicular functions by FSH and LH-linked mechanisms. J Androl 25:706–719
Benítez A, Pérez Díaz J (1985) Effect of streptozotocin-diabetes and insulin treatment on regulation of Leydig cell function in the rat. Horm Metab Res 17:5–7. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1013433
Borland K, Mita M, Oppenheimer CL, Blinderman LA, Massague J, Hall PF, Czech MP (1984) The actions of insulin-like growth factor-I and -II on cultured Sertoli cells. Endocrinology 114:240–246
Cameron DF, Rountree J, Schultz RE, Repetta D, Murray FT (1990) Sustained hyperglycemia results in testicular dysfunction and reduced fertility potential in BBWOR diabetic rats. Am J Physiol 259:881–889
Chung CS, Myrianthopoulos NC (1975) Factors affecting risks of congenital malformations. II. Effect of maternal diabetes on congenital malformations. Birth Defects 11:23–38
Devaskar S, McMenamy K, Holtzclaw L, Sadiq F (1990) Long-term maternal–fetal exposure to high-low insulin concentrations alter liver but not brain insulin receptors. Am J Obstet Gynecol 163:1350–1356
Drazancic A, Blajic J, Djelmis J (1993) Early spontaneous abortions and congenital malformations in relation to diabetes regulation in very early pregnancy. 24th Annual Meeting of Diabetic Pregnancy Denmark. Abstract 3.
Fairburn CG, McCulloch DK, Wu FC (1982) The effects of diabetes on male sexual function. Clin Endocrinol Metab 11:749–765. doi:10.1016/S0300-595X(82) 80011-X
Foglia VG, Rosner JM, Ramos M, Lema BE (1969) Sexual disturbances in the male diabetic rat. Horm Metab Res 1:72–77. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1095155
Franca LR, Suescun MO, Miranda JR, Giovambattista A, Perello M, Spinedi E et al (2005) Testis structure and function in a non-genetic hyperadipose rat model at prepubertal and adult ages. Endocrinology 147:1556–1563. doi:10.1210/en.2005-0640
Hassan AA, Hassouna MM, Taketo T, Gagnon C, Elhilali MM (1993) The effect of diabetes on sexual behavior and reproductive tract function in male rats. J Urol 149:148–154
Hurtado de Catalfo G, Nelva I, De Go’mez Dumm T (1998) Lipid dismetabolism in Leydig and Sertoli cells isolated from streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 30:1001–1010. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(98) 00055-7
Hutson JC, Stocco DM, Campbell GT, Wagoner J (1983) Sertoli cell function in diabetic, insulin-treated diabetic, and semi-starved rats. Diabetes 32:112–116. doi:10.2337/diabetes.32.2.112
Jelodar GA, Razmi N, Golampour V (2007) Arginase alteration in reproductive system of alloxan diabetic dogs. J Reprod Dev 53:317–321. doi:10.1262/jrd.18049
Khan S, Teerds K, Dorrington J (1992) Growth factor requirements for DNA synthesis by Leydig cells from the immature rat. Biol Reprod 46:335–341. doi:10.1095/biolreprod46.3.335
Knowler W, Pettitt DJ, Kunzelman CL, Everhart J (1985) Genetic and environment determinants of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1:309
Luna LG (1968) Manual of histologic staining methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology 3rd edn. Am Registry Pathol 34–35:76–77
Mita M, Borland K, Price JM, Hall PF (1985) The influence of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I on hexose transport by Sertoli cells. Endocrinology 116:987–992
Murray FT, Cameron DF, Orth JM (1983) Gonadal dysfunction in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. Metabolism 32:141–147. doi:10.1016/S0026-0495(83) 80028-6
Pedersen J (1977) The pregnant diabetic and her newborn: problems and management, 2nd edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 191–197
Persson B, Hanson U (1998) Neonatal morbidities in gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 21:79–84
Seethalakshmi L, Menon M, Diamond D (1987) The effect of streptozotocin induced diabetes on the neuroendocrine–male reproductive tract axis of the adult rat. J Urol 138:190–194
Ute M, Schaefer-Graf TA, Buchanan XA, Songster G et al (2000) Patterns of congenital anomalies and relationship to initial maternal fasting glucose levels in pregnancies complicated by type 2 and gestational diabetes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 182:313–320. doi:10.1016/S0002-9378(00) 70217-1
Van Assche FA, Aerts L, De Prins FA (1983) Degranulation of the insulin-producing B cells in an infant of a diabetic mother. Case report. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 90:182–185
Vignon F, Lefaou A, Montagnon D (1991) Comparative study of semen in diabetic and healthy men. Diabetes Metab 17:350–354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jelodar, G., Khaksar, Z. & Pourahmadi, M. Endocrine profile and testicular histomorphometry at puberty in rat offspring from diabetic mothers. Comp Clin Pathol 19, 135–139 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-009-0842-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-009-0842-7