Abstract.
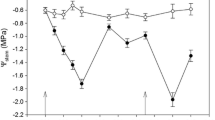
Linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) sensors were used to detect continuous diameter growth responses of Pinus pinea (stone pine) seedlings inoculated with the ectomycorrhizal fungus Rhizopogon roseolus. Colonised and non-colonised seedlings provided with sensors were submitted to different water regimes in two consecutive experiments established in a controlled-temperature greenhouse module (cycle 1), and in an adjacent module without temperature control (cycle 2). Under regular irrigation, colonised seedlings showed significantly higher growth than non-colonised seedlings. Water-stressed seedlings showed no benefit from inoculation in terms of growth. Also, seedlings with a high colonisation level recovered more slowly from water stress than control seedlings. A significant positive relationship between maximum daily shrinkage (amplitude of the daily stem contraction) and global radiation was observed only in the first water-stress period in cycle 1 and in regularly irrigated seedlings in both cycles. However, no differential responses due to inoculation were observed. The mycorrhizal colonisation of the seedlings at the end of the experiment was related with the initial colonisation level. Mycorrhizal colonisation by R. roseolus in old roots was maintained at significantly higher levels in seedlings which had an initial colonisation level >50% than in seedlings with <50% initial colonisation. Also, more newly formed roots became colonised in seedlings which had an initial colonisation level >50% than in seedlings with an initial colonisation <50%, which had almost no new root colonisation. From the results obtained, it can be concluded that LVDT sensors can be used to detect a differential response of plants according to water supply, mycorrhizal status and, in some cases, to their colonisation level. The results are discussed in relation to the predictive possibilities of the method for the selection of efficient mycorrhizal fungi for the promotion of plant growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parladé, J., Cohen, M., Doltra, J. et al. Continuous measurement of stem-diameter growth response of Pinus pinea seedlings mycorrhizal with Rhizopogon roseolus and submitted to two water regimes. Mycorrhiza 11, 129–136 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720100118
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720100118