Abstract
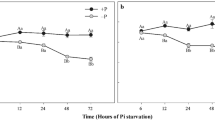
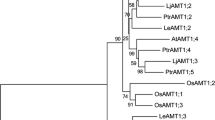
Inorganic phosphorus (Pi) is essential for plant growth, and phosphate (P) deficiency is a primary limiting factor in Pinus tabulaeformis development in northern China. P acquisition in mycorrhizal plants is highly dependent on the activities of phosphate transporters of their root-associated fungi. In the current study, two phosphate transporter genes, RlPT and LbPT, were isolated from Rhizopogon luteolus and Leucocortinarius bulbiger, respectively, two ectomycorrhizal fungi forming symbiotic interactions with the P. tabulaeformis. Phylogenetic analysis suggested that the sequence of the phosphate transporter of L. bulbiger is most closely related to a phosphate transporter of Hebeloma cylindrosporum, whereas the phosphate transporter of R. luteolus is most closely related to that of Piloderma croceum. The subcellular localization indicated that RlPT and LbPT were expressed in the plasma membrane. The complementation assay in yeast indicated that both RlPT and LbPT partially compensated for the absence of phosphate transporter activity in the MB192 yeast strain, with a K m value of 57.90 μmol/L Pi for RlPT and 35.87 μmol/L Pi for LbPT. qPCR analysis revealed that RlPT and LbPT were significantly up-regulated at lower P availability, which may enhance P uptake and transport under Pi starvation. Our results suggest that RlPT and LbPT presumably play a key role in Pi acquisition by P. tabulaeformis via ectomycorrhizal fungi.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai P, Sun S, Zhao J, Fan X, Xin W, Guo Q, Yu L, Shen Q, Wu P, Miller AJ (2009) Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1;2 and OsPht1;6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation. Plant J 57:798–809. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03726.x
Bai S-L, Li G-L, Liu Y, Dumroese RK, Lv R-H (2009) Ostryopsis davidiana seedlings inoculated with ectomycorrhizal fungi facilitate formation of mycorrhizae on Pinus tabulaeformis seedlings. Mycorrhiza 19:425–434. doi:10.1007/s00572-009-0245-2
Benedetto A, Magurno F, Bonfante P, Lanfranco L (2005) Expression profiles of a phosphate transporter gene (GmosPT) from the endomycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae. Mycorrhiza 15:620–627. doi:10.1007/s00572-005-0006-9
Boon N, Goris J, De Vos P, Verstraete W, Top EM (2000) Bioaugmentation of activated sludge by an indigenous 3-chloroaniline-degrading Comamonas testosteroni strain, 12gfp. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2906–2913. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.7.2906-2913.2000
Bucher M (2007) Functional biology of plant phosphate uptake at root and mycorrhiza interfaces. New Phytol 173:11–26. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01935.x
Bun-Ya M, Nishimura M, Harashima S, Oshima Y (1991) The PHO84 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an inorganic phosphate transporter. Mol Cell Biol 11:3229–3238. doi:10.1128/MCB.11.6.3229
Casieri L, Lahmidi NA, Doidy J, Veneault-Fourrey C, Migeon A, Bonneau L, Courty P-E, Garcia K, Charbonnier M, Delteil A (2013) Biotrophic transportome in mutualistic plant–fungal interactions. Mycorrhiza 23:597–625. doi:10.1007/s00572-013-0496-9
Chandra J, Kuhn DM, Mukherjee PK, Hoyer LL, McCormick T, Ghannoum MA (2001) Biofilm formation by the fungal pathogen Candida albicans: development, architecture, and drug resistance. J Bacteriol 183:5385–5394. doi:10.1128/JB.183.18.5385-5394.2001
Chen K, Abbott RJ, Milne RI, Tian XM, Liu J (2008) Phylogeography of Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. (Pinaceae), a dominant species of coniferous forest in northern China. Mol Ecol 17:4276–4288. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03911.x
Classics-Barka T, Anderson P (1962) Histochemical methods for acid phosphatase using hexazonium pararosanalin as coupler. J Histochem Cytochem 10:741–753
Cormack BP, Bertram G, Egerton M, Gow NA, Falkow S, Brown AJ (1997) Yeast-enhanced green fluorescent protein (yEGFP): a reporter of gene expression in Candida albicans. Microbiology 143:303–311. doi:10.1099/00221287-143-2-303
de Campos MC, Pearse SJ, Oliveira RS, Lambers H (2013) Viminaria juncea does not vary its shoot phosphorus concentration and only marginally decreases its mycorrhizal colonization and cluster-root dry weight under a wide range of phosphorus supplies. Ann Bot 111:801–809. doi:10.1093/aob/mct035
DiTusa SF, Fontenot EB, Wallace RW, Silvers MA, Steele TN, Elnagar AH, Dearman KM, Smith AP (2015) A member of the phosphate transporter 1 (Pht1) family from the arsenic‐hyperaccumulating fern Pteris vittata is a high‐affinity arsenate transporter. New Phytologist. doi:10.1111/nph.13472
Faber KN, Haima P, Harder W, Veenhuis M, Geert A (1994) Highly-efficient electrotransformation of the yeast Hansenula polymorpha. Curr Genet 25:305–310. doi:10.1007/BF00351482
Facelli E, Duan T, Smith SE, Christophersen HM, Facelli JM, Smith FA (2014) Opening the black box: outcomes of interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) and non‐host genotypes of Medicago depend on fungal identity, interplay between P uptake pathways and external P supply. Plant Cell Environ 37:1382–1392. doi:10.1111/pce.12237
Fan C, Wang X, Hu R, Wang Y, Xiao C, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Zheng C, Fu Y-F (2013) The pattern of phosphate transporter 1 genes evolutionary divergence in Glycine max L. BMC Plant Biol 13:48. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-13-48
Faustino LI, Bulfe NM, Pinazo MA, Monteoliva SE, Graciano C (2013) Dry weight partitioning and hydraulic traits in young Pinus taeda trees fertilized with nitrogen and phosphorus in a subtropical area. Tree Physiol 33:129. doi:10.1093/treephys/tps129
Glassop D, Smith SE, Smith FW (2005) Cereal phosphate transporters associated with the mycorrhizal pathway of phosphate uptake into roots. Planta 222:688–698. doi:10.1007/s00425-005-0015-0
Harrison MJ, van Buuren ML (1995) A phosphate transporter from the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus versiforme. Nature 378:626–629. doi:10.1038/378626a0
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195. doi:10.1023/A:1013351617532
Horton P, Park KJ, Obayashi T, Fujita N, Harada H, Adams-Collier CJ, Nakai K (2007) WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res 35(suppl 2):W585–W587. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm259
Karandashov V, Bucher M (2005) Symbiotic phosphate transport in arbuscular mycorrhizas. Trends Plant Sci 10:22–29. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.003
Kobae Y, Hata S (2010) Dynamics of periarbuscular membranes visualized with a fluorescent phosphate transporter in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots of rice. Plant Cell Physiol 51:341–353. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcq013
Liu J, Versaw WK, Pumplin N, Gomez SK, Blaylock LA, Harrison MJ (2008) Closely related members of the Medicago truncatula PHT1 phosphate transporter gene family encode phosphate transporters with distinct biochemical activities. J Biol Chem 283:24673–24681. doi:10.1074/jbc.M802695200
Liu P, Chen S, Song A, Zhao S, Fang W, Guan Z, Liao Y, Jiang J, Chen F (2014) A putative high affinity phosphate transporter, CmPT1, enhances tolerance to Pi deficiency of chrysanthemum. BMC Plant Biol 14:18. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-14-18
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Loth-Pereda V, Orsini E, Courty P-E, Lota F, Kohler A, Diss L, Blaudez D, Chalot M, Nehls U, Bucher M (2011) Structure and expression profile of the phosphate Pht1 transporter gene family in mycorrhizal Populus trichocarpa. Plant Physiol 156:2141–2154. doi:10.1104/pp.111.180646
Maldonado-Mendoza IE, Dewbre GR, Harrison MJ (2001) A phosphate transporter gene from the extra-radical mycelium of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices is regulated in response to phosphate in the environment. Mol Plant Mic Interact 14:1140–1148. doi:10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.10.1140
Mao X-L (2009) Macromycetes of China. Since Press, Beijing
Marschner H, Rimmington G (1988) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Plant Cell Environ 11:147–148. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.1988.tb01130.x
Martin F, Aerts A, Ahrén D, Brun A, Danchin E, Duchaussoy F, Gibon J, Kohler A, Lindquist E, Pereda V (2008) The genome of Laccaria bicolor provides insights into mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nature 452:88–92. doi:10.1038/nature06556
Martin F, Kohler A, Murat C, Balestrini R, Coutinho PM, Jaillon O, Montanini B, Morin E, Noel B, Percudani R (2010) Périgord black truffle genome uncovers evolutionary origins and mechanisms of symbiosis. Nature 464:1033–1038. doi:10.1038/nature08867
Melikant B, Giuliani C, Halbmayer-Watzina S, Limmongkon A, Heberle-Bors E, Wilson C (2004) The Arabidopsis thaliana MEK AtMKK6 activates the MAP kinase AtMPK13. FEBS Lett 576:5–8. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.08.051
Miransari M, Mackenzie A (2011) Development of a soil N test for fertilizer requirements for wheat. J Plant Nutr 34:762–777. doi:10.1080/01904167.2011.540922
Murshudov GN, Vagin AA, Dodson EJ (1997) Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Cryst D53:240–255. doi:10.1107/S0907444996012255
Nussaume L, Kanno S, Javot H, Marin E, Pochon N, Ayadi A, Nakanishi TM, Thibaud M-C (2011) Phosphate import in plants: focus on the PHT1 transporters. Front Plant Sci 30:83. doi:10.3389/fpls.2011.00083
Ohta A (1990) A new medium for mycelial growth of mycorrhizal fungi. Trans Mycol Soc Jpn 31:323–334
Pedersen BP, Kumar H, Waight AB, Risenmay AJ, Roe-Zurz Z, Chau BH, Schlessinger A, Bonomi M, Harries W, Sali A (2013) Crystal structure of a eukaryotic phosphate transporter. Nature 496:533–536. doi:10.1038/nature12042
Rausch C, Bucher M (2002) Molecular mechanisms of phosphate transport in plants. Planta 216:23–37. doi:10.1007/s00425-002-0921-3
Ravera S, Virkki LV, Murer H, Forster IC (2007) Deciphering PiT transport kinetics and substrate specificity using electrophysiology and flux measurements. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293:C606–C620. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00064.2007
Roy M, Rochet J, Manzi S, Jargeat P, Gryta H, Moreau PA, Gardes M (2013) What determines Alnus‐associated ectomycorrhizal community diversity and specificity? A comparison of host and habitat effects at a regional scale. New Phytol 198:1228–1238. doi:10.1111/nph.12212
Sezonov G, Joseleau-Petit D, D’Ari R (2007) Escherichia coli physiology in Luria-Bertani broth. J Bacteriol 189:8746–8749. doi:10.1128/JB.01368-07
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic, New York
Smith SE, Smith FA (2012) Fresh perspectives on the roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in plant nutrition and growth. Mycologia 104:1–13. doi:10.3852/11-229
Sokolski S, Dalpé Y, Piché Y (2011) Phosphate transporter genes as reliable gene markers for the identification and discrimination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the genus Glomus. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1888–1891. doi:10.1128/AEM.00919-10
Stonor RN, Smith SE, Manjarrez M, Facelli E, Smith FA (2014) Mycorrhizal responses in wheat: shading decreases growth but does not lower the contribution of the fungal phosphate uptake pathway. Mycorrhiza 1–8 doi:10.1007/s00572-014-0556-9
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tasaki Y, Kamiya Y, Azwan A, Hara T, Joh T (2002) Gene expression during Pi deficiency in Pholiota nameko: accumulation of mRNAs for two transporters. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:790–800. doi:10.1271/bbb.66.790
Tatry MV, El Kassis E, Lambilliotte R, Corratgé C, Van Aarle I, Amenc LK, Alary R, Zimmermann S, Sentenac H, Plassard C (2009) Two differentially regulated phosphate transporters from the symbiotic fungus Hebeloma cylindrosporum and phosphorus acquisition by ectomycorrhizal Pinus pinaster. Plant J 57:1092–1102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03749.x
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25:4876–4882. doi:10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Tusnady GE, Simon I (2001) The HMMTOP transmembrane topology prediction server. Bioinformatics 17:849–850. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/17.9.849
Vance CP, Uhde‐Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
Wang J, Li T, Wu X, Zhao Z (2014) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a H+-dependent phosphate transporter gene from the ectomycorrhizal fungus Boletus edulis in southwest China. Fungal Biol 118:453–461. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2014.03.003
Wu B, Watanabe I, Hayatsu M, Nioh I (1999) Effect of ectomycorrhizae on the growth and uptake and transport of 15N-labeled compounds by Pinus tabulaeformis seedlings under water-stressed conditions. Biol Fert Soils 28:136–138. doi:10.1007/s003740050474
Wu Z, Zhao J, Gao R, Hu G, Gai J, Xu G, Xing H (2011) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of two members of the Pht1 family of phosphate transporters in Glycine max. PLoS One 6:e19752. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019752
Yan X, Wu P, Ling H, Xu G, Xu F, Zhang Q (2006) Plant nutriomics in China: an overview. Ann Bot 98:473–482. doi:10.1093/aob/mcl116
Zhang H-H, Tang M, Chen H, Zheng C-L (2010) Effects of inoculation with ectomycorrhizal fungi on microbial biomass and bacterial functional diversity in the rhizosphere of Pinus tabulaeformis seedlings. Eur J Soil Biol 46:55–61. doi:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2009.10.005
Zheng R, Wang J-G, L-h T, Bai S-L, Niu Y-F (2014) Cloning and expression analysis of γ-actin gene from Rhizopogon luteolus. Sci Silvae Sinicae 50:80–85
Zinser E, Sperka-Gottlieb C, Fasch E-V, Kohlwein SD, Paltauf F, Daum G (1991) Phospholipid synthesis and lipid composition of subcellular membranes in the unicellular eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 173:2026–2034
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31060110 and 31360125). We would like to express our appreciation to Prof. J. Hegemann (Institut fur Mikrobiologie, Heinrich-Heine-Universitat Dusseldorf, Germany) for generously providing the yeast mutants (MB192) and two types of vectors (pUG23 and pUG23+GFP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rong Zheng and Jugang Wang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
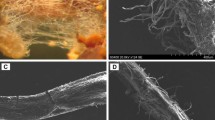
Sporocarps and ectomycorrhizal (ECM) characteristics of the fungi used in the present study. (a) Rhizopogon luteolus; (b) Leucocortinarius bulbiger; (c) mycorrhizal characteristics of Rhizopogon luteolus–Pinus tabulaeformis; (d) mycorrhizal characteristics of Leucocortinarius bulbiger–Pinus tabulaeformis. (GIF 81 kb)
Fig. S2
The ExPASy online hydrophobic prediction of RlPT (a) and LbPT (b). (GIF 123 kb)
Fig. S3
The DNA structures of RlPT and LbPT. The lavender boxes represent the exons, the white boxes represent the introns, and the characters in the box indicate the number of bases. (GIF 28 kb)
Fig. S4
The transmembrane-spanning domains predication of RlPT (a) and LbPT (b) by using TMHMM software. (GIF 182 kb)
Fig. S5
Functional expression of RlPT and LbPT in the MB192 strains and YPD medium. A staining test was performed to determine PT activity in the MB192 mutant yeast transformed with the expression vector pUG23 harboring no insert (MB192+eV) and pUG23+PT (MB192+RlPT/LbPT), and a WT yeast strain transformed with empty expression vector pUG23 (WT+eV) was cultured as a positive control. All aliquots (a and b are the experiment for the RlPT, c and d are the experiment for the LbPT) were cultivated in dishes containing 60 μmol/L (a and c) and 200 μmol/L (b and d) phosphate in a YPD medium at 30 °C for 3 days. The green arrows indicate that all aliquot concentrations decreased along the arrow directions (10-fold dilution each time). (GIF 361 kb)
Fig. S6
The growth (OD 600 nm) curves of MB192+eV, MB192+RlPT, MB192+LbPT, and WT+eV at optimal pH (pH = 6). All of the yeast strains were cultured in YNB medium that contained 80 μmol/L of phosphate at 30 °C and at 180 rpm, and the OD (600) values were determined every 5 h. (GIF 23 kb)
Fig. S7
The functional expression of RlPT and LbPT in yeast. A staining test was applied to determine the acid phosphatase enzyme activities in the MB192 mutant yeast transformed with the empty vector pUG23 (MB192+eV), pUG23+RlPT (MB192+RlPT), and pUG23+LbPT (MB192+LbPT), and a WT yeast strain transformed with empty pUG23 vector (WT+eV) was cultured as a positive control. All aliquots were cultivated in tubes containing 20, 60, 100, and 200 μmol/L of phosphatase YNB medium (pH = 4.8) at 30 °C and at 180 rpm for 24 h. Bromocresol purple was added to the culture medium as a color indicator, and a color shift reflected medium acidification, which correlates with the growth of the yeast cells. (GIF 104 kb)
Table S1
Primers used in this study. In the primers for functional verification and subcellular localization, the cDNA complementary sequences are the underlined bases and the homologous sequences of vectors are the bases without underlining. (XLS 17 kb)
Table S2
The main properties, including ORF length, predicted molecular weight, predicted isoelectric point, hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity, transmembrane regions, optimal pH, and K m values of functionally characterized PTs from ECM fungi. “–” means no data at present time. (XLS 33 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, R., Wang, J., Liu, M. et al. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of two phosphate transporter genes from Rhizopogon luteolus and Leucocortinarius bulbiger, two ectomycorrhizal fungi of Pinus tabulaeformis . Mycorrhiza 26, 633–644 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-016-0702-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-016-0702-7