Abstract
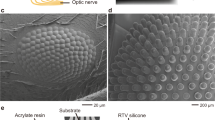
Eyes are one of the most important organs for natural creatures to perceive external information. The curved compound eyes of insects endowing with merits of a wide field of view (FOV), high sensitivity and detecting quick moving targets have aroused extensive concern. There are mainly two categories of compound eyes in nature. One is apposition eyes which can avoid light crosstalk and the other is superposition ones with higher sensitivity. With the rapid development of micron and nano machining technologies, the fabrication techniques of compound eyes have experienced changes from waveguide self-writing initially to advanced femtosecond laser method through thermal reflow and other processes. The diameters of compound eyes varies from the original several hundreds micrometers to the smallest 5 µm currently, which is much closer to the natural ones. Therefore, a critical review is presented to systematically summary and compare the micromachining processes of curved artificial compound eyes in recent years from the perspective of microfabrication technology. Finally, we describe a broad applications including navigation and location, digital camera and rapid detection of moving objects as well as existing challenges and future perspective of curved artificial compound eyes. It is hoped that this review can help researchers to gain a better overall understanding of microfabrication in this field and push forward it to a new stage.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen KW, Farahi N, Li Y, Limberopoulos NI, Walker DE, Urbas AM, Liberman V, Astratov VN (2015) Super-resolution microscopy by movable thin-films with embedded microspheres: resolution analysis. Ann Phys 527(7–8):513–522
Bbk R (1992) A bat-like sonar system for obstacle localization. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 22:636–646
Bidlingmayer WL (1994) How mosquitoes see traps: role of visual responses. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 10:272–279
Boseman A, Nowlin K, Ashraf S, Yang J, Lajeunesse D (2013) Ultrastructural analysis of wild type and mutant Drosophila melanogaster using helium ion microscopy. Micron 51:26–35
Bruckner A, Duparre J, Dannberg P, Brauer A, Tunnermann A (2007) Artificial neural superposition eye. Opt Express 15:11922–11933
Brückner A (2011) Multi-aperture optics for wafer-level cameras. J. Micro-nanolith Mem 10(4):043010
Cao A, Wang J, Pang H, Zhang M, Shi L, Deng Q, Hu S (2018) Design and fabrication of a multifocal bionic compound eye for imaging. Bioinspir Biomim 13(2):026012
Cao A, Pang H, Zhang M, Shi L, Deng Q, Hu S (2019) Design and fabrication of an artificial compound eye for multi-spectral imaging. Micromachines (Basel) 10(3):208
Cao JJ, Hou ZS, Tian ZN, Hua JG, Zhang YL, Chen QD (2020) Bioinspired zoom compound eyes enable variable-focus imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(9):10107–10117
Chang Y, Wei J, Lee C (2020) Metamaterials—from fundamentals and MEMS tuning mechanisms to applications. Nanophotonics 9(10):3049–3070
Chen F, Liu H, Yang Q, Wang X, Hou C, Bian H, Liang W, Si J, Hou X (2010) Maskless fabrication of concave microlens arrays on silica glasses by a femtosecond-laser-enhanced local wet etching method. Opt Express 18:20334–20443
Chen F, Deng Z, Yang Q, Bian H, Du G, Si J, Hou X (2014) Rapid fabrication of a large-area close-packed quasi-periodic microlens array on BK7 glass. Opt Lett 39(3):606–609
Cheng Y, Cao J, Zhang Y, Hao Q (2019) Review of state-of-the-art artificial compound eye imaging systems. Bioinspir Biomim 14(3):031002
Davis JD, Barrett SF, Wright CH, Wilcox M (2009) A bio-inspired apposition compound eye machine vision sensor system. Bioinspir Biomim 4(4):046002
De Jesus Maciel M, Rocha RP, Carmo JP, Correia JH (2014) Measurement and statistical analysis toward reproducibility validation of AZ4562 cylindrical microlenses obtained by reflow. Measurement 49:60–67
Deng Z, Chen F, Yang Q, Bian H, Du G, Yong J, Shan C, Hou X (2016) Dragonfly-eye-inspired artificial compound eyes with sophisticated imaging. Adv Func Mater 26(12):1995–2001
Dimitrov AS, Nagayama K (1996) Continuous convective assembling of fine particles into two-dimensional arrays on solid surfaces. Langmuir 12:1303–1311
Duparre JW, Wippermann FC (2006) Micro-optical artificial compound eyes. Bioinspir Biomim 1(1):R1-16
Duparre J, Dannberg P, Schreiber P, Uer AB, Nnermann AT (2004) Artificial apposition compound eye fabricated by micro-optics technology. Appl Opt 43:4303–4310
Duparre J, Schreiber P, Matthes AE, Pshenay-Severin E, Brauer A, Tunnermann A (2005) Microoptical telescope compound eye. Opt Express 13:889–903
Envisioned L-EX-rT (1979) Lobster-eye X-ray telescope envisioned. Science 184:84–85
Eom S-H, Wrzesniewski E, Xue J (2011) Close-packed hemispherical microlens arrays for light extraction enhancement in organic light-emitting devices. Org Electro 12(3):472–476
Fallah HR, Karimzadeh A (2007) Design and simulation of a high-resolution superposition compound eye. J Mod Opt 54(1):67–76
Fallah HR, Karimzadeh A (2010) MTF of compound eye. Opt Express 18:12304
Feng L et al (2011) Design and fabrication of polymer microlens array with self-written waveguide. Chin J Lasers 38:202–207
Fitzgerald RJ (2006) Artificial compound eyes. Phys Today 59(6):21–21
Floreano D, Pericet-Camara R, Viollet S, Ruffier F, Bruckner A, Leitel R, Buss W, Menouni M, Expert F, Juston R, Dobrzynski MK, L’Eplattenier G, Recktenwald F, Mallot HA, Franceschini N (2013) Miniature curved artificial compound eyes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(23):9267–9272
Gao X, Yan X, Yao X, Xu L, Zhang K, Zhang J, Yang B, Jiang L (2007) The dry-style antifogging properties of mosquito compound eyes and artificial analogues prepared by soft lithography. Adv Mater 19(17):2213–2217
Garza-Rivera A, Renero-Carrillo FJ (2011) Design of artificial apposition compound eye. Opt Rev 18:184–186
Grigaliūnas V, Lazauskas A, Jucius D, Viržonis D, Abakevičienė B, Smetona S, Tamulevičius S (2016) Microlens fabrication by 3D electron beam lithography combined with thermal reflow technique. Microelectron Eng 164:23–29
Gu Z-Z, Fujishima A, Sato O (2002) Fabrication of high-quality opal films with controllable thickness. Chem Mater 14:760–765
Gu L, Poddar S, Lin Y, Long Z, Zhang D, Zhang Q, Shu L, Qiu X, Kam M, Javey A, Fan Z (2020) A biomimetic eye with a hemispherical perovskite nanowire array retina. Nature 581(7808):278–282
Hamanaka K, Koshi H (1996) An artificial compound eye using a microlens array and its application to scale-invariant processing. Opt Rev 3:264–268
Hao B, Liu H, Chen F, Yang Q, Qu P, Du G, Si J, Wang X, Hou X (2012) Versatile route to gapless microlens arrays using laser-tunable wet-etched curved surfaces. Opt Express 20:12939
Hao Bian YW, Yang Q, Chen F, Zhang F, Guangqing Du, Yong J, Hou X (2016) Direct fabrication of compound-eye microlens array on curved surfaces by a facile femtosecond laser enhanced wet etching process. Appl Phys Lett 109:221109
He M, Yuan X, Bu J, Cheong WC (2004) Fabrication of concave refractive microlens arrays in solgel glass by a simple proximity-effect-assisted reflow technique. Opt Lett 29:1007–1009
He Q, Liu J, Yang B, Dong Y, Yang C (2013) Fabrication and characterization of biologically inspired curved-surface artificial compound eyes. J Microelectromech Syst 22(1):4–6
Ho CP, Pitchappa P, Lee C (2016) Digitally reconfigurable binary coded terahertz metamaterial with output analogous to NOR and AND. J Appl Phys 119(15):153104
Hsu YP et al (2005) ICP etching of sapphire substrates Opt. Mater 27:1171–1174
Hu J, Liang Y (2017) A flying-insect-inspired hybrid robot for disaster exploration. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, pp 270–275
Huang CC, Wu X, Liu H, Aldalali B, Rogers JA, Jiang H (2014) Large-field-of-view wide-spectrum artificial reflecting superposition compound eyes. Small 10(15):3050–3057
Huang S, Li M, Shen L, Qiu J, Zhou Y (2017) Flexible fabrication of biomimetic compound eye array via two-step thermal reflow of simply pre-modeled hierarchic microstructures. Opt Commun 393:213–218
Hur J-G (2011) Maskless fabrication of three-dimensional microstructures with high isotropic resolution: practical and theoretical considerations. Appl Opt 50:2383–2390
Jacob F (1977) Evolution and tinkering. Science 196:1161–1166
Jamali M, Gerhardt I, Rezai M, Frenner K, Fedder H, Wrachtrup J (2014) Microscopic diamond solid-immersion-lenses fabricated around single defect centers by focused ion beam milling. Rev Sci Instrum 85(12):123703
Jeong K-H, Kim J, Lee LP (2006) Biologically inspired artificial compound eyes. Science 312:557–561
Jin G-X, Hu X-Y, Ma Z-C, Li C-H, Zhang Y-L, Sun H-B (2019) Femtosecond laser fabrication of 3D templates for mass production of artificial compound eyes. Nanotechnol Precis Eng 2(3):110–117
Johnson W (1980) Helicopter theory
Jung H, Jeong K-H (2009) Microfabricated ommatidia using a laser induced self-writing process for high resolution artificial compound eye optical systems. Opt Express 17:14761–14766
Jung G-Y, Li Z, Wu W, Chen Y, Olynick DL, Wang S-Y, Tong WM, Williams RS (2005) Vapor-phase self-assembled monolayer for improved mold release in nanoimprint lithography. Langmuir 21:1158–1161
Jung YH, Park B, Kim JU, Kim TI (2019) Bioinspired electronics for artificial sensory systems. Adv Mater 31(34):e1803637
Kennedy JS (1938) The visual responses of flying mosquitoes. Proc Zool Soc Ser A
Keum D, Jang KW, Jeon DS, Hwang CSH, Buschbeck EK, Kim MH, Jeong KH (2018) Xenos peckii vision inspires an ultrathin digital camera. Light Sci Appl 7:80
Kim MH, Park OO (2012) Hot embossing of polymeric nanostructures using poly(dimethylsiloxane) replica molds based on three-dimensional colloidal crystals. Microelectron Eng 91:121–126
Kim J et al (2005) Artificial ommatidia by self-aligned microlenses and waveguides. Opt Lett 30:5
Kim J, Jeong KH, Lee LP (2005) Artificial ommatidia by self-aligned microlenses and waveguides. Opt Lett 30(1):5–7
Kim S-H, Kim S-H, Yang S-M (2009) Patterned polymeric domes with 3D and 2D embedded colloidal crystals using photocurable emulsion droplets. Adv Mater 21(37):3771–3775
Kim JJ, Liu H, Ousati Ashtiani A, Jiang H (2020) Biologically inspired artificial eyes and photonics. Rep Prog Phys 83(4):047101
Kim K, Jang KW, Ryu JK, Jeong KH (2020) Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging. Light Sci Appl 9:28
Kirschfeld K (1974) The absolute sensitivity of lens and compound eyes. Zeitschrift Fur Naturforschung Section C 29:592–596
Ko D-H, Tumbleston JR, Henderson KJ, Euliss LE, DeSimone JM, Lopez R, Samulski ET (2011) Biomimetic microlens array with antireflective “moth-eye” surface. Soft Matter 7(14):6404
Kobayashi H, Kikuchi K, Ochi K, Onogi Y (2003) Navigation strategies referring to insect homing in flying robots. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. IEEE
Kogos LC, Li Y, Liu J, Li Y, Tian L, Paiella R (2020) Plasmonic ommatidia for lensless compound-eye vision. Nat Commun 11(1):1637
Kuo WK, Kuo GF, Lin SY, Yu HH (2015) Fabrication and characterization of artificial miniaturized insect compound eyes for imaging. Bioinspir Biomim 10(5):056010
Kyung CM, Yasuura H, Liu Y, Lin YL (2017) Smart sensors and systems https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-33201-7
Land MF (1980) Compound eyes: old and new optical mechanisms. Nature 287:681–686
Land MF, Nilsson DE (2002) Animal eyes. Q Rev Biol 77:332
Lee LP, Szema R (2005) Inspirations from biological optics for advanced photonic systems. Science 310(5751):1148–1150
Lee CL, Gu E, Dawson MD, Friel I, Scarsbrook GA (2008) Etching and micro-optics fabrication in diamond using chlorine-based inductively-coupled plasma. Diam Relat Mater 17(7–10):1292–1296
Lee CL, Dawson MD, Gu E (2010) Diamond double-sided micro-lenses and reflection gratings. Opt Mater 32(9):1123–1129
Li L, Yi AY (2010) Development of a 3D artificial compound eye. Opt Express 18:18125–18137
Li H, Gong X, Ni Q, Zhao J, Zhang H, Wang T, Yu W (2014) Replication and characterization of the compound eye of a fruit fly for imaging purpose. Appl Phys Lett 105(14)
Li J, Wang W, Mei X, Pan A, Sun X, Liu B, Cui J (2019) Artificial compound eyes prepared by a combination of air-assisted deformation, modified laser swelling, and controlled crystal growth. ACS Nano 13(1):114–124
Li J, Wang W, Mei X, Pan A, Liu B, Cui J (2020) Rapid fabrication of microlens arrays on PMMA substrate using a microlens array by rear-side picosecond laser swelling. Opt Laser Eng 126:105872
Lian Z-J, Hung S-Y, Shen M-H, Yang H (2014) Rapid fabrication of semiellipsoid microlens using thermal reflow with two different photoresists. Microelectron Eng 115:46–50
Liang W-L, Pan J-G, Su G-DJ (2019) One-lens camera using a biologically based artificial compound eye with multiple focal lengths. Optica 6(3):326
Liang Y, Zhu T, Xi M, Song Y, Fu J, Zhao D, Wang Y, Wang J, Wang K, Wang H (2019) Fabrication of biomimetic compound eye on single crystal diamond. Opt Express 27(15):20508
Liu H, Chen F, Yang Q, Qu P, He S, Wang X, Si J, Hou X (2012) Fabrication of bioinspired omnidirectional and gapless microlens array for wide field-ofview detections. Appl Phys Lett 100:133701
Liu H, Reilly S, Herrnsdorf J, Xie E, Savitski VG, Kemp AJ, Gu E, Dawson MD (2016) Large radius of curvature micro-lenses on single crystal diamond for application in monolithic diamond Raman lasers. Diam Relat Mater 65:37–41
Liu X-Q, Chen Q-D, Guan K-M, Ma Z-C, Yu Y-H, Li Q-K, Tian Z-N, Sun H-B (2017) Dry-etching-assisted femtosecond laser machining. Laser Photonics Rev 11(3):1600115
Liu XQ, Yang SN, Yu L, Chen QD, Zhang YL, Sun HB (2019) Rapid engraving of artificial compound eyes from curved sapphire substrate. Adv Funct Mater 29(18):1900037
Liu F, Bian H, Zhang F, Yang Q, Shan C, Li M, Hou X, Chen F (2019) IR Artificial Compound Eye. Adv Opt Mater 8(4):1901767
Luo J, Guo Y, Wang X, Fan F (2017) Design and fabrication of a multi-focusing artificial compound eyes with negative meniscus substrate. J Micromech Microeng 27(4):045011
Luo J, Guo Y, Wang X (2018) Enhancing the imaging quality and fabrication efficiency of bionic compound eyes using a sandwich structure. J Mod Opt 65(10):1253–1260
Ma ZC, Hu XY, Zhang YL, Liu XQ, Hou ZS, Niu LG, Zhu L, Han B, Chen QD, Sun HB (2019) Smart compound eyes enable tunable imaging. Adv Func Mater 29(38):1903340
Mao SS, Quéré F, Guizard S, Mao X, Russo RE, Petite G, Martin P (2004) Dynamics of femtosecond laser interactions with dielectrics. Appl Phys A-Mater 79(7):1695–1709
Maquet L, Colinet P, Dorbolo S (2014) Organization of microbeads in Leidenfrost drops. Soft Matter 10(23):4061–4066
Mazuray L, Duparre J, Rogers PJ, Schreiber P, Volkel R, Wartmann R (2004) Theoretical analysis of an artificial superposition compound eye for application in ultra flat digital image acquisition devices. Opt Des Eng
Mendonca CR, Correa DS, Baldacchini T, Tayalia P, Mazur E (2008) Two-photon absorption spectrum of the photoinitiator lucirin tpo-l. Appl Phys A-Mater 90(4):633–636
Nagelberg S, Zarzar LD, Nicolas N, Subramanian K, Kalow JA, Sresht V, Blankschtein D, Barbastathis G, Kreysing M, Swager TM, Kolle M (2017) Reconfigurable and responsive droplet-based compound micro-lenses. Nat Commun 8:14673
Nicholas FB, David LM, Robert HB, Morgan WL (1985) Photolytic technique for producing microlenses in photosensitive glass. Appl Opt 24:2520
Ogawa S, Watanabe H, Wang L, Jinnai H, McCarthy TJ, Takahara A (2014) Liquid marbles supported by monodisperse poly(methylsilsesquioxane) particles. Langmuir 30(30):9071–9075
Overton G (2007) Artificial compound eye applies hyperacuity. Laser Focus World
Pan F, Zhang J, Cai C, Wang T (2006) Rapid fabrication of large-area colloidal crystal monolayers by a vortical surface method. Langmuir 22:7101–7104
Pan CT, Chen YC, Chen MF, Hsu YC (2011) Fabrication and design of various dimensions of multi-step ashperical microlens arrays for OLED package. Opt Commun 284(13):3323–3330
Park M-K, Lee HJ, Park J-S, Kim M, Bae JM, Mahmud I, Kim H-R (2014) Design and fabrication of multi-focusing microlens array with different numerical apertures by using thermal reflow method. J Opt Soc Korea 18(1):71–77
Photolithography RPUMAAiGS (2002) Reduction photolithography using microlens arrays: applications in gray scale photolithography. Anal Chem 74:3267–3273
Pitchappa P, Manjappa M, Ho CP, Singh R, Singh N, Lee C (2016) Active control of electromagnetically induced transparency with dual dark mode excitation pathways using MEMS based tri-atomic metamolecules. Appl Phys Lett 109(21)
Plett J, Bahl A, Buss M, Kuhnlenz K, Borst A (2012) Bio-inspired visual ego-rotation sensor for MAVs. Biol Cybern 106(1):51–63
Pubo Qu FC, Liu H, Yang Q, Jing Lu, Si J, Wang Y, Hou X (2012) A simple route to fabricate artificial compound eye structures. Opt Express 20:5775–5782
Qiu J, Li M, Zhu J, Ji C (2018) Fabrication of microlens array with well-defined shape by spatially constrained thermal reflow. J Micromech Microeng 28(8):085015
Ren Z, Chang Y, Ma Y, Shih K, Dong B, Lee C (2019) Leveraging of MEMS technologies for optical metamaterials applications. Adv Opt Mater 8(3):1900653
Sanders JS, Halford CE (1995) Design and analysis of apposition compound eye optical sensors. Opt Eng 34:222–235
Schoenemann B, Parnaste H, Clarkson ENK (2017) Structure and function of a compound eye, more than half a billion years old. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(51):13489–13494
Serra F, Gharbi MA, Luo Y, Liu IB, Bade ND, Kamien RD, Yang S, Stebe KJ (2015) Curvature-driven, one-step assembly of reconfigurable smectic liquid crystal “compound eye” lenses. Adv Opt Mater 3(9):1287–1292
Shao J, Ding Y, Wang W, Mei X, Zhai H, Tian H, Li X, Liu B (2014) Generation of fully-covering hierarchical micro-/nano- structures by nanoimprinting and modified laser swelling. Small 10(13):2595–2601
Sherk TE (1978) Development of the compound eyes of dragonflies (Odonata). J Exp Zool 203:183–200
Shieh JY, Kuo JY, Weng HP, Yu HH (2013) Preparation and evaluation of the bioinspired PS/PDMS photochromic films by the self-assembly dip-drawing method. Langmuir 29(2):667–672
Shin D, Huang T, Neibloom D, Bevan MA, Frechette J (2019) Multifunctional liquid marble compound lenses. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(37):34478–34486
Sihai C (2009) Bionic ommatidia based on microlens array. Opt Eng 48(6):063401
Song YM, Xie Y, Malyarchuk V, Xiao J, Jung I, Choi K-J, Liu Z, Park H, Lu C, Kim R-H, Li R, Crozier KB, Huang Y, Rogers JA (2013) Digital cameras with designs inspired by the arthropod eye. Nature 497(7447):95–99
Stavenga DG, Kinoshita M, Yang EC, Arikawa K (2001) Retinal regionalization and heterogeneity of butterfly eyes. Naturwissenschaften 88(11):477–481
Straw AD, Warrant EJ, O’Carroll DC (2006) A “bright zone” in male hoverfly (Eristalis tenax) eyes and associated faster motion detection and increased contrast sensitivity. J Exp Biol 209(Pt 21):4339–4354
Straw AD, Rainsford T, O’Carroll DC (2008) Contrast sensitivity of insect motion detectors to natural images. J Vis 8(3):31–39
Stumm-Tegethoff ABF, Dicke AW (1974) Surface structure of the compound eye of various drosophila species and eye mutants of drosophila melanogaster. Theor Appl Genet 44:262–265
Su Y-SCG-DJ (2013) Fabrication of polydimethylsiloxane microlens array on spherical surface using multi-replication process. J Microelectromech Syst 24
Sun H, Deng S, Cui X, Lu M (2014) Fabrication of microlens arrays with varied focal lengths on curved surfaces using an electrostatic deformed template. J Micromech Microeng 24(6):065008
Tanida J, Kumagai T, Yamada K, Miyatake S, Ishida K, Morimoto T, Kondou N, Miyazaki D, Ichioka Y (2001) Thin observation module by bound optics (TOMBO): concept and experimental verification. Appl Opt 40:1806–1813
Tearney GJ, Yoshimoto K, Wang TD, Yamada K, Sasaki N, Takeda M, Shimizu S, Nagakura T, Takahashi H, Ohno Y (2013) Evaluation of a compound eye type tactile endoscope. Proc of SPIE 8575:85750Z
Thienpont H, Moens E, Van Daele P, Meuret Y, Ottevaere H, Mohr J, Zappe H, Sarkar M, San Segundo Bello D, Merken P, Thienpont H (2010) An insect eye-based image sensor with very large field of view. Micro-Optics
Thinès G (1982) Handbook of sensory physiology volume vii, 6a: invertebrate photoreceptors (edited by h. autrum); volume vii, 6b: invertebrate visual centers and behavior (i) (edited by h. autrum); volume viii: perception (edited by richard held, h.w. leibowitz and h.l. teuber). Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York. 1979, 729 pp. 344 figures; 1981, 629 pp. 319 figures; 1978, 993 pp. 254 figures and 7 anaglyphs, respectively. Behav Processes, 7(4), 387–390.
Tian A, Hou X, Bian H, Yang Q, Li M, Chen F (2019) Fabrication of close-packed microlens array with superhydrophobicity and high imaging performance. In: The Third International Conference on Photonics and Optical Engineering,
Vinna H-TH, Hsieh J-L, Su G-DJ (2011) Design and fabrication of long focal length microlens arrays. Opt Commun 284:5225–5230
Vukusic P, Sambles JR (2003) Photonic structures in biology. Nature 424:852–855
Waldbaur A, Waterkotte B, Schmitz K, Rapp BE (2012) Maskless projection lithography for the fast and flexible generation of grayscale protein patterns. Small 8(10):1570–1578
Wang et al (2012) Biomimetic compound eye with a high numerical aperture and anti-reflective nanostructures on curved surfaces. Opt Lett 37:2397
Wang L, Liu H, Jiang W, Li R, Li F, Yang Z, Yin L, Shi Y, Chen B (2015) Capillary number encouraged the construction of smart biomimetic eyes. J Mater Chem C 3(23):5896–5902
Wang M, Wang T, Shen H, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Du J, Yu W (2016) Subtle control on hierarchic reflow for the simple and massive fabrication of biomimetic compound eye arrays in polymers for imaging at a large field of view. J Mater Chem C 4(1):108–112
Wang Y, Shi C, Liu C, Yu X, Xu H, Wang T, Qiao Y, Yu W (2019) Fabrication and characterization of a polymeric curved compound eye. J Micromech Microeng 29(5):055008
Wang W, Li J, Li R, Li B, Mei X, Sun X (2019) Fabrication of hierarchical micro/nano compound eyes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(37):34507–34516
Wu M-H, Park C, Whitesides GM (2002) Fabrication of arrays of microlenses with controlled profiles using gray-scale microlens projection photolithography. Langmuir 18:9312–9318
Wu H, Odom TW, Chiu DT, Whitesides GM (2003) Fabrication of complex three-dimensional microchannel systems in PDMS. J Am Chem Soc 125:554–559
Wu D, Wang J-N, Niu L-G, Zhang XL, Wu SZ, Chen Q-D, Lee LP, Sun HB (2014) Bioinspired fabrication of high-quality 3D artificial compound eyes by voxel-modulation femtosecond laser writing for distortion-free wide-field-of-view imaging. Adv Opt Mater 2(8):751–758
Wu S, Jiang T, Zhang G, Schoenemann B, Neri F, Zhu M, Bu C, Han J, Kuhnert K-D (2016) Artificial compound eye: a survey of the state-of-the-art. Artif Intell Rev 48(4):573–603
Xiong G-R, Han G-Z, Sun C, Xu H, Wei H-m, Gu Z-Z (2009) Phototunable microlens array based on polymer dispersed liquid crystals. Adv Funct Mater 19(7):1082–1086
Xu H, Lu N, Shi G, Qi D, Yang B, Li H, Xu W, Chi L (2011) Biomimetic antireflective hierarchical arrays. Langmuir 27(8):4963–4967
Yang SM, Hn M, Ozin GA (2002) Opal circuits of lightðplanarized microphotonic crystal chi. Adv Funct Mater 12:425–431
Yao J, Yan X, Lu G, Zhang K, Chen X, Jiang L, Yang B (2004) Patterning colloidal crystals by lift-up soft lithography. Adv Mater 16(1):81–84
Zhang Z, Gao Y, Luo N, Zhong K (2016) Fast fabrication of curved microlens array using DMD-based lithography. AIP Adv. 6(1):015319
Zhang K, Jung YH, Mikael S, Seo JH, Kim M, Mi H, Zhou H, Xia Z, Zhou W, Gong S, Ma Z (2017) Origami silicon optoelectronics for hemispherical electronic eye systems. Nat Commun 8(1):1782
Zhang T, Li P, Yu H, Wang F, Wang X, Yang T, Yang W, Li WJ, Wang Y, Liu L (2020) Fabrication of flexible microlens arrays for parallel super-resolution imaging. Appl Surf Sci 504:144375
Zhu T-F, Fu J, Lin F, Zhang M, Wang W, Wen F, Zhang X, Bu R, Zhang J, Zhu J, Wang J, Wang H-X, Hou X (2017) Fabrication of diamond microlens arrays for monolithic imaging homogenizer. Diam Relat Mater 80:54–58
Zhu TF, Liu Z, Liu Z, Li F, Zhang M, Wang W, Wen F, Wang J, Bu R, Zhang J, Wang HX (2017) Fabrication of monolithic diamond photodetector with microlenses. Opt Express 25(25):31586–31594
Zhu T-F, Fu J, Liu Z, Liang Y, Wang W, Wen F, Zhang J, Wang H-X (2018) Investigation of the occupancy ratio dependence for microlens arrays on diamond. RSC Adv 8(52):29544–29547
Acknowledgements
The authors grateful to the Center for Advanced Electronic Materials and Devices (AEMD). This work was supported by Joint Foundation of Pre-research of Equipment and Ministry of Education (6141A02022637).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Y., Han, Q., Niu, J. et al. Microfabrication of bioinspired curved artificial compound eyes: a review. Microsyst Technol 27, 3241–3262 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05090-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05090-3