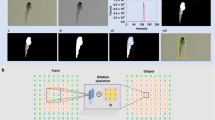
Abstract
The automation methods and technologies of the single cell micro-injection reported in the literature have the common assumption that both the cell and the microtools has already been positioned within the microscopic field of view and well-focused. However, moving the microtools and biological cells from the macro field of view (macro-FOV) into the micro field of view (micro-FOV), and then further moving down into the culture medium and focusing were conducted manually and proved to be time consuming. In this work, we present algorithms and methods to automate this process. An electrothermal microgripper is used for picking and holding a zebrafish embryo instead of traditional micropipette. In order to position the microgripper into the micro-FOV, an extra macro camera is employed such that the microgripper jaws are under the macro-FOV. The micro-FOV is searched by moving the microgripper jaws in a serpentine path and zigzag path, respectively, and the grid-line identification algorithm is proposed to recognize the microgripper jaws that appear in the micro-FOV. Then, a contact detection algorithm is used to determine whether the gripper jaws are in the culture medium or not. Finally, eight algorisms are evaluated and compared to select the algorism with the best performance for auto-focusing the microgripper jaws in the culture medium. Up to 100 experiments are conducted to validate the proposed method for the macro-to-micro positioning and auto focusing of the microgripper jaws with the success rate 100% and 90%, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson K, Sheridan E, Grierson AJ (2018) Use of zebrafish models to investigate rare human disease. J Med Genet 55:641–649
Argenton F, Bitzur S, Yarden A (2007) An inexpensive and easy microinjection embryo-tray. Zebrafish Book 5th Edition
Benhal P, Chase JG, Gaynor P, Obackc B, Wang W (2014) AC electric field induced dipole-based on-chip 3D cell rotation. Lab Chip 14:2717
Chen SY, Qian H, Wu Z (2007) Fast normalized cross-correlation for template matching. Chin J Sens Actuators
Chen D, Sun M, Zhao X (2016) Oocytes polar body detection for automatic enucleation. J Micromach 7:27
Chen T, Wang Y, Yang Z, Liu H, Liu J, Sun L (2017) A PZT actuated triple-finger gripper for multi-target micromanipulation. Micromachines 8(2):33
Chung SE, Dong X, Sitti M (2015) Three-dimensional heterogeneous assembly of coded microgels using an untethered mobile microgripper. Lap Chip 15(7):1667–1676
Desai JP et al (2007) Engineering approaches to biomanipulation. Ann Rev Biomed Eng 9:35–53
Geusebroek J et al (2000) Robust autofocusing in microscopy. Cytometry 36(1):1–9
Ghanbari A, Nock V, Johari S, Blaikie R, Chen XQ, Wang W (2012) A micropillar-based on-chip system for continuous force measurement of C. elegans. J Micromech Microeng 22(9):095009
Gianaroli L (2011) Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: Polar body and embryo biopsy. Hum Reprod 15(suppl 4):69–75
Groen F, Young IT, Ligthart G (1985) A comparison of different focus functions for use in autofocus algorithms. Cytometry 12:81–91
Hamm P et al (2010) Content-based Autofocusing in automated microscopy. Image Anal Stereol 29:173–180
Huang HB, Sun D, Mills JK, Cheng SH (2009) Robotic cell injection system with position and force control: toward automatic batch biomanipulation. IEEE Trans Robotics 25(3):727
Liu X, Sun Y, Wang WH, Lansdorp BM (2007) Vision-based cellular force measurement using an elastic microfabricated device. J Micromech Microeng 17:1281–1288
Liu J, Shi C, Wen J, Pyne D, Ru CH, Luo J, Xie S, Sun Y (2015) Automated vitrification of embryos: a robotics approach. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 22(2):33–40
Liu J, Zhang Z, Wang X, Liu H, Zhao Q, Zhou C, Tan M, Pu H, Xie SR, Sun Y (2017) Automated robotic measurement of cell morphologies. IEEE Robotics Autom Lett 2(2):499
Lu Z, Zhang XP, Leung C, Esfandiari N, Casper RF, Sun Y (2011) Robotic ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection). IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(7):2102–2108
Luca G (2011) Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: polar body and embryo biopsy. Human Reprod 15(suppl 4):69–75
Mattos LS, Grant E, Thresher R, Kluckman K (2009) Blastocyst microinjection automation. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine a Publication of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society 13(5):822–831
Murphey RD, Zon LI (2006) Small molecule screening in the zebrafish. Methods 39(3):255–261
Nakajima M, Ayamura Y, Takeuchi M, Hisamoto N, Pastuhov S, Hasegawa Y, Fukuda T, Huang Q (2017) High-Precision Microinjection of Microbeads into C. elegans Trapped in a Suction Microchannel. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore
Nayar SK (1994) Shape from focus. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 16:824–831
Permana S, Grant E, Glenn MW, Yoder Jeffrey A (2016) A review of automated microinjection systems for single cells in the embryogenesis Stage. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 21(5):2391
Pitchar A, Rajaretinam RK, Freeman JL (2019) Zebrafish as an emerging model for bioassay-guided natural product drug discovery for neurological disorders. Medicines (Basel) 6(2):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6020061
Saleem S, Kannan RR (2018) Zebrafish: an emerging real-time model system to study Alzheimer’s disease and neurospecific drug discovery. Cell Death Discov 4:45
Subbarao M, Choi TS (1993) Focusing techniques. J Opt Eng 32:2824–2836
Sun Y, Duthaler S, Nelson BJ (2004) Autofocusing in computer microscopy: selecting the optimal focus algorithm. Microsc Res Tech 65(3):139–149
Wang G, Xu Q (2017) Design and precision position/force control of a piezo-driven microinjection system. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 22(4):1744
Wang WH, Liu XY, Sun Y (2007a) Contact detection in microrobotic manipulation. Int J Robot Res 26(8):821–828
Wang WH, Liu XY, Gelinas D, Ciruna B, Sun Y (2007b) A fully automated robotic system for microinjection of Zebrafish embryos. PLoS ONE 2(9):e8621–8627
Wang Z, Feng C, Ang WT, Tan SYM, Latt WT (2017) Autofocusing and polar body detection in automated cell manipulation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(5):1099
Xie Y, Sun D, Liu C, and Cheng SH (2008) An adaptive impedance force control approach for robotic cell microinjection. In: 2008 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, acropolis convention Center Nice, France, Sept, 22–26
Xie M, Mills JK, Wang Y, Mahmoodi M, Sun D (2016) Automated translational and rotational control of biological cells with a robot-aided optical tweezers manipulation system. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 13(2):543–551
Zhang XP, Leung C, Lu Z, Esfandiari N, Casper RF, Sun Y (2012) Controlled aspiration and positioning of biological cells in a micropipette. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(4):1032
Zhang Z, Yu Y, Song P et al (2019) Automated manipulation of zebrafish embryos using an electrothermal microgripper. Microsystem Technol 26:1823
Zhao QL, Sun M, Cui M, Yu J, Qin Y, Zhao X (2015) Robotic cell rotation based on the minimum rotation force. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 12(4):1504
Zhao YL, Sun H, Sha X, Gu L, Zhan Z, Li WJ (2019) A review of automated microinjection of zebrafish embryos. Micromachines 10(1):7
Zhuang S, Lin W, Gao H, Shang X, Li L (2017) Visual servoed Zebrafish larva heart microinjection system. IEEE Trans. Ind Electron 64(5):3727
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by 2018 Innovative Methodology Project (2018IM010400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, L., Zhang, H., Wei, H. et al. Macro-to-micro positioning and auto focusing for fully automated single cell microinjection. Microsyst Technol 27, 11–21 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-04891-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-04891-w