Abstract
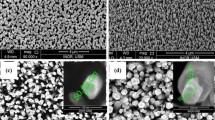
Nanogenerators (NGs) synthesized with sulfur (S) doped zinc oxide (ZnO) nanorods (NRs) by a hydrothermal method were characterized for their performances in this study. The NG formation steps consist of (1) growing the S-doped ZnO NRs on an indium-tin-oxide (ITO) glass substrate, (2) employing an ITO etching paste to create the electrode pattern, and (3) depositing an electrode of aluminum (Al) film on the ITO glass substrate by a radio-frequency magnetron sputtering technique for the final NG assembly. As found, the ZnO NRs doped with 5 at.% S exhibit the best efficiency among all S-doped ZnO NRs, with the optimal operational outputs of 150 mV, 0.16 μA, and 24 nW, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar N, Metkar SK, Girigoswami A, Girigoswami K (2017) ZnO nanoflower based sensitive nano-biosensor for amyloid detection. Mater Sci Eng C 78:960–968
Al-Hadeethi Y, Umar A, Ibrahim AA, Al-Heniti SH, Kumar R, Baskoutas S, Raffah BM (2017) Synthesis, characterization and acetone gas sensing applications of Ag-doped ZnO nanoneedles. Ceram Int 43:6765–6770
Al-Ruqeishi MS, Mohiuddin T, Al-Habsi B, Al-Ruqeishi F, Al-Fahdi A, Al-Khusaibi A (2016) Piezoelectric nanogenerator based on ZnO nanorods. Arab J Chem 12:5173–5179
Arnold MS, Avouris P, Pan ZW, Wang ZL (2003) Field-effect transistors based on single semiconducting oxide nanobelts. J Phys Chem B 107:659–663
Astakhov GV, Yakovlev DR, Kochereshko VP, Ossau W, Faschinger W, Puls J, Henneberger F, Crooker SA, McCulloch Q, Wolverson D, Gippius NA, Waag A (2002) Binding energy of charged excitons in ZnSe-based quantum wells. Phys Rev B 65:165335
Bhatia D, Sharma H, Meena RS, Palkar VR (2016) A novel ZnO piezoelectric microcantilever energy scavenger: fabrication and characterization. Sens Biosens Res 9:45–52
Chand P, Gaur A, Kumar A, Gaur UK (2014) Structural, morphological and optical study of Li doped ZnO thin films on Si (100) substrate deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Ceram Int 40:11915–11923
Chen J, Li J, Li JH, Xiao GQ, Yang XF (2011) Large-scale syntheses of uniform ZnO nanorods and ethanol gas sensors application. J Alloys Compd 509:740–743
Cho J, Lin QB, Yang S, Simmons JG, Cheng YW, Lin E, Yang JQ, Foreman JV, Everitt HO, Yang WT, Kim J, Liu J (2012) Sulfur-doped zinc oxide (ZnO) nanostars: synthesis and simulation of growth mechanism. Nano Res 5:20–26
Dondi D, Bertacchini A, Brunelli D, Larcher L, Benini L (2008) Modeling and optimization of a solar energy harvester system for self-powered wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55:2759–2766
Fang X, Li JH, Zhao DX, Shen DZ, Li BH, Wang XH (2009) Phosphorus-doped p-type ZnO nanorods and ZnO nanorod p–n homojunction LED fabricated by hydrothermal method. J Phys Chem C 113:21208–21212
Fang XS, Zhai TY, Gautam UK, Li L, Wu LM, Bando YS, Golberg D (2011) ZnS nanostructures: from synthesis to applications. Prog Mater Sci 56:175–287
Geng BY, Wang GZ, Jiang Z, Xie T, Sun SH, Meng GW, Zhang LD (2003) Synthesis and optical properties of S-doped ZnO nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 82:4791–4793
Hsu CL, Chen KC (2012) Improving piezoelectric nanogenerator comprises ZnO nanowires by bending the flexible PET substrate at low vibration frequency. J Phys Chem C 116:9351–9355
Hsu CL, Su IL, Hsueh TJ (2017) Tunable schottky contact humidity sensor based on S-doped ZnO nanowires on flexible PET substrate with piezotronic effect. J Alloys Compd 705:722–733
Hu YF, Xu C, Zhang Y, Lin L, Snyder RL, Wang ZL (2011a) A nanogenerator for energy harvesting from a rotating tire and its application as a self-powered pressure/speed sensor. J Adv Mater 23:4068–4071
Hu CJ, Lin YH, Tang CW, Tsai MY, Hsu WK, Kuo HF (2011b) ZnO-coated carbon nanotubes: flexible piezoelectric generators. Adv Mater 23:2941–2945
Huang MH, Mao S, Feick H, Yan HQ, Wu YY, Kind H, Weber E, Russo R, Yang PD (2001) Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science 292:1897–1899
Hussain SG, Liu DM, Huang XT, Sulieman KM, Liu JP, Liu HR, Rasool RU (2007) Synthesis and optical properties of heterostructured ZnO:S/ZnO nanosaws. J Phys D 40:7662–7668
Katz E, Buckmann AF, Willner I (2001) Self-powered enzyme-based biosensors. J Am Chem Soc 123:10752–10753
Kim KJ, Park YR (2001) Large and abrupt optical band gap variation in In-doped ZnO. Appl Phys Lett 78:475–477
Ko YH, Nagaraju G, Lee SH, Yu JS (2014) PDMS-based triboelectric and transparent nanogenerators with ZnO nanorod arrays. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:6631–6637
Koike K, Mori Y, Sasa S, Hirofuji Y, Yano M (2016) Glucose sensing by an enzyme-modified ZnO-based FET. Procedia Eng 168:84–88
Li C, Fang GJ, Xu S, Zhao DS, Zhao XZ (2006) Phase-segregation assisted growth of quasi-aligned ZnO nanorods on a Mg0.6Zn0.4O-coated Si substrate by thermal evaporation. Nanotechnology 17:5367–5372
Lin QB, Wu SQ, Zhu ZZ (2016) Formation of star nanowires of sulfur-doped zinc oxide: ab initio calculations. AIP Adv 6:095219
Liu CW, Chang SJ, Hsiao CH, Lo KY, Kao TH, Wang BC, Young SJ, Tsai KS, Wu SL (2014) Noise properties of low-temperature-grown Co-doped ZnO nanorods as ultraviolet photodetectors. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 20:3800707
Lu MP, Song J, Lu MY, Chen MT, Gao Y, Chen LJ, Wang ZL (2009) Piezoelectric nanogenerator using p-type ZnO nanowire arrays. Nano Lett 9:1223–1227
Orton JW (1995) Acceptor binding energy in GaN and related alloys. Semicond Sci Technol 10:101–104
Pietruszka R, Witkowski BS, Gieraltowska S, Caban R, Wachnicki L, Zielony E, Gwozdz K, Bieganski P, Placzek-Popko E, Godlewski M (2015) New efficient solar cell structures based on zinc oxide nanorods. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 143:99–104
Sarma D, Das TM, Baruah S (2016) Bandgap engineering of ZnO nanostructures through hydrothermal growth. ADBU J Eng Technol 4:216–218
Shen GZ, Cho JH, Yoo JK, Yi GC, Lee CJ (2005) Synthesis and optical properties of S-Doped ZnO nanostructures: nanonails and nanowires. J Phys Chem B 109:5491–5496
Wang ZL, Song JH (2006) Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312:242–246
Wang X, Song J, Liu J, Wang ZL (2007a) Direct-current nanogenerator driven by ultrasonic waves. Science 316:102–105
Wang XH, Liu S, Chang P, Tang Y (2007b) Synthesis of sulfur-doped ZnO nanowires by electrochemical deposition. Mater Sci Semicond Process 10:241–245
Wang XD, Gao YF, Wei YG, Wang ZL (2009) Output of an ultrasonic wave-driven nanogenerator in a confined tube. Nano Res 2:177–182
Yang Y, Guo WX, Pradel KC, Zhu G, Zhou YS, Zhang Y, Hu YF, Lin L, Wang ZL (2012) Pyroelectric nanogenerators for harvesting thermoelectric energy. Nano Lett 12:2833–2838
Yoo YZ, Jin ZW, Chikyow T, Fukumura T, Kawasaki M, Koinuma H (2002) S doping in ZnO film by supplying ZnS species with pulsed-laser-deposition method. Appl Phys Lett 81:3798–3800
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan with Project Number: MOST 107-2221-E-150-032, MOST 108-2221-E-024-006, and MOST 108-2221-E-150-013-MY2. The authors would also like to thank the assistance of the Common Laboratory for Micro/Nano Science and Technology of the National Formosa University for some of the measurement equipment used in this work, the Center for Micro/Nano Science and Technology of National Cheng Kung University for device characterization, and B. W. Huang for device fabrication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lam, KT., Chu, YL., Ji, LW. et al. Characterization of nanogenerators based on S-doped zinc oxide nanorod arrays. Microsyst Technol 28, 395–401 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-04863-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-04863-0