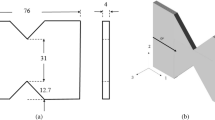
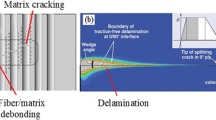
Abstract
The smart materials are capable to integrate the remarkabale active functions into a traditional structure of the composites. There is a wide research possibility towards the embedded patches into a composite primary structure. This particular study aims to investigate the effect of the embedded smart materials in a conventional composite laminate. Carbon fiber reinforced composite (CFRC) specimens with and without PZT piezo elements embedded in the structure are studied for Tensile, In-plane Shear and three point bending properties. Previously researched mechanical behaviour and the operational influence of the piezo sensors are sequentially analysed, particularly for the electric capacitance during all the categories of testing. The limitations have also been studied into the comparison of the structure with and without the piezoelectric material patches. The extended finite element (XFEM) modelling approach has been applied to study the sensorized damage model for the numerical and experimental study. This study also presents simplified and understandable techniques and offers a new direction for the experimental and computational modelling design for the progressive damage, based on the principles of extended finite element method (XFEM). The extensive experimentation and numerical modelling for interlaminar and intralaminar crack of CFRCs materials are studied, with and without piezoelectric patches. The experiments and simulations are designed and grouped into categories of load, boundary conditions and types arranged accordingly for fracture, delamination, fiber breakage and matrix crack towards the damage evolution. The dimensions of the specimens and the effects are also studied regarding lengths, thickness and width in multiple categories. The loading cases of tension and the inplane shear are studied for multiple cases for numerical as well as experimental investigation having different orientations and dimensions. The delaminated and fractured mode I and mode II specimen were analysed for the expected and the real time values of strength to figure out the precise values of trends to predict the composite properties.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergara A, Dorado JI, Martin-Meizoso A, Martínez-Esnaola JM (2017) Fatigue crack propagation in complex stress fields: experiments and numerical simulations using the Extended Finite Element Method (XFEM). Int J Fatigue 103:112–121
Butt Z et al (2016) Generation of electrical energy using lead zirconate titanate (PZT-5A) piezoelectric material: analytical, numerical and experimental verifications. J Mech Sci Technol 30(8):3553–3558
Butt Z, Rahman SU, Pasha RA, Elahi H, Mehmood S, Abbas S (2017) Characterizing barium titanate piezoelectric material using the finite element method. Trans Electr Electron Mater 18(3):163–168
Crawley EF, De Luis J (1987) Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures. AIAA J 25(10):1373–1385
Creighton SL, Regueiro RA, Garikipati K, Klein PA, Marin EB, Bammann DJ (2004) A variational multiscale method to incorporate strain gradients in a phenomenological plasticity model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(48–51):5453–5475
Duarte APC, Díaz Sáez A, Silvestre N (2017) Comparative study between XFEM and Hashin damage criterion applied to failure of composites. Thin-Walled Struct
Elahi H, Pasha RA, Khan MZ (2014) Experimental determination of mechanical quality factor of lead zirconate titanate (PZT-5A4E) by equivalent circuit method under various thermal and resistance conditions. Univ Eng Tech Taxila Tech J 19(2):1
Elahi H et al (2017a) Effects of variable resistance on smart structures of cubic reconnaissance satellites in various thermal and frequency shocking conditions. J Mech Sci Technol 31(9):4151–4157
Elahi H et al (2017b) Stability of piezoelectric material for suspension applications. In: Aerospace science & engineering (ICASE), 2017 fifth international conference on IEEE
Elahi H, Eugeni M, Gaudenzi P (2018a) Electromechanical degradation of piezoelectric patches. In: Analysis and modelling of advanced structures and smart systems. Springer, Singapore, pp 35–44
Elahi H, Eugeni M, Gaudenzi P, Gul M, Swati RF (2018b) Piezoelectric thermo electromechanical energy harvester for reconnaissance satellite structure. Microsyst Technol 1–8
Elahi H et al (2018c) A review on mechanisms for piezoelectric-based energy harvesters. Energies 11(7):1–35
García IG, Paggi M, Mantic V (2014) Fiber-size effects on the onset of fiber-matrix debonding under transverse tension: a comparison between cohesive zone and finite fracture mechanics models. Eng Fract Mech
Geandier G, Gélébart L, Castelnau O, Le Bourhis E, Renault PO, Goudeau P, Thiaudière D (2009) Micromechanical modeling of the elastic behavior of multilayer thin films; comparison with in situ data from X-ray diffraction. In: IUTAM symposium on modelling nanomaterials and nanosystems. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 99–108
Giraldo-londoño O, Spring DW, Paulino GH, Buttlar WG (2018) An efficient mixed-mode rate-dependent cohesive fracture model using sigmoidal functions. Eng Fract Mech 192:307–327
Goyal VK, Johnson ER, Dávila CG (2004) Irreversible constitutive law for modeling the delamination process using interfacial surface discontinuities. Compos Struct
Higuchi R, Okabe T, Nagashima T (2017) Numerical simulation of progressive damage and failure in composite laminates using XFEM/CZM coupled approach. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 95:197–207
Hulton AW, Cavallaro PV (2016) Comparing computational and experimental failure of composites using XFEM. In: Volume 9: mechanics of solids, structures and fluids; NDE, diagnosis, and prognosis
I. C. (2013) The U. of T. at A. Inderjit Chopra (University of Maryland). Smart Struct Theory
Jung SN, Nagaraj VT, Chopra I (1999) Assessment of composite rotor blade modeling techniques. J Am Helicopter Soc 44(3):188–205
Jung SN, Nagaraj VT, Chopra I (2002) Refined structural model for thin- and thick-walled composite rotor blades. AIAA J 40(1):105–116
Kirichenko VF, Krys’ko VA, Surova NS (1985) The Bubnov-Galerkin method in the non-linear theory of hollow, flexible multilayer orthotropic shells. J Appl Math Mech
Lancaster IM, Khalid HA, Kougioumtzoglou IA (2013) Extended FEM modelling of crack propagation using the semi-circular bending test. Constr Build Mater 48:270–277
Li X (2012) Application of the meshless Galerkin boundary node method to potential problems with mixed boundary conditions. Eng Anal Bound Elem 36(12):1799–1810
Li X, Chen J (2016) The implementation of the extended cohesive damage model for multicrack evolution in laminated composites. Compos Struct
Li X, Chen J (2017) A highly efficient prediction of delamination migration in laminated composites using the extended cohesive damage model. Compos Struct 160:712–721
Liu SX, Chen C, Chen H, Cheng G (2017) Structural dynamics modeling and experimental study of axially precompressed piezoelectric bimorph. In: Symposium on piezoelectricity, acoustic waves, and device applications (SPAWDA). IEEE, Chengdu, China, pp 240–244
Stier B, Simon JW, Reese S (2015) Comparing experimental results to a numerical meso-scale approach for woven fiber reinforced plastics. Compos Struct 122:553–560
Su X, Yang Z, Liu G (2010) Finite element modelling of complex 3D static and dynamic crack propagation by embedding cohesive elements in abaqus. Acta Mech Solida Sin 23(3):271–282
Swati RF, Hua WL, Elahi H, Khan AA (2018) XFEM damage analysis of carbon fiber reinforced composites and crack propagation in mixed-mode and implementation of the method using ABAQUS. Int J Mater Mech Manuf 6(4):286–290
Swati R et al (2018) Extended finite element method (XFEM) analysis of fiber reinforced composites for prediction of micro-crack propagation and delaminations in progressive damage: a review. Microsyst Technol 1–17
Swati RF, Khan AA, Wen LH (2016) Weight optimized main landing gears for UAV under impact loading for evaluation of explicit dynamics study. In: Advanced materials, structures and mechanical engineering, pp 371–375
Swati RF, Hua WL, Elahi H, Khan AA (2017) Extended finite element method damage analysis of carbon fiber reinforced composites and crack propagation in mixed-mode using multiscale method and implementation of the method using ABAQUS extended finite element method damage analysis of carbon. In: 4th international conference on mechanics and mechatronics research, Xi’an, China
Van Dongen B, Van Oostrum A, Zarouchas D (2018) A blended continuum damage and fracture mechanics method for progressive damage analysis of composite structures using XFEM. Compos Struct 184(September 2017):512–522
Wang Y, Waisman H (2016) From diffuse damage to sharp cohesive cracks: a coupled XFEM framework for failure analysis of quasi-brittle materials. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng
Wang HW, Zhou HW, Ji HW, Zhang XC (2014) Application of extended finite element method in damage progress simulation of fiber reinforced composites. Mater Des
Wu JY, Xu SL (2011) An augmented multicrack elastoplastic damage model for tensile cracking. Int J Solids Struct 48(18):2511–2518
Zhang X, Zhang P, Zhang L (2012) A simple technique to improve computational efficiency of meshless methods. Procedia Eng 31:1102–1107
Zhao L, Zhi J, Zhang J, Liu Z, Hu N (2016) XFEM simulation of delamination in composite laminates. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swati, R.F., Elahi, H., Wen, L.H. et al. Investigation of tensile and in-plane shear properties of carbon fiber reinforced composites with and without piezoelectric patches for micro-crack propagation using extended finite element method. Microsyst Technol 25, 2361–2370 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4120-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4120-y