Abstract
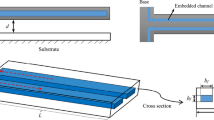
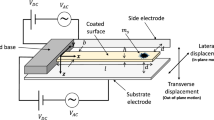
In this paper, dynamics of a suspended microchannel resonator (SMR) will be derived using the strain gradient theory. Accordingly, the size dependent governing equation and corresponding boundary conditions will be obtained using the extended Hamilton’s principle for open systems. The proposed strain gradient theory has three length scale parameters which can be reduced to the modified couple stress theory and the classical theory when two of three length scale parameters or all of them are set to zero, respectively. Also, the size effect of micro-flow associated with the flow velocity profile will be considered in the governing equation of motion. The stability analysis is then carried out to obtain complex frequencies and critical flutter speeds. Finally, the effects of flowing particle in the microchannel and the associated frequency shifts induced by the added mass will be studied.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atcı D, Bağdatlı SM (2017) Vibrations of fluid conveying microbeams under non-ideal boundary conditions. Microsyst Technol 23(10):4741–4752
Belardinelli P, Ghatkesar M, Staufer U, Alijani F (2017) Linear and non-linear vibrations of fluid-filled hollow microcantilevers interacting with small particles. Int J Non-Linear Mech 93:30–40
Benjamin TB (1962) Dynamics of a system of articulated pipes conveying fluid-I. Theory. In: Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A
Burg TP, Godin M, Knudsen SM, Shen W, Carlson G, Foster JS, Manalis SR (2007) Weighing of biomolecules, single cells and single nanoparticles in fluid. Nature 446(7139):1066–1069
de Boer MP, Luck DL, Ashurst WR, Maboudian R, Corwin AD, Walraven JA, Redmond JM (2004) High-performance surface-micromachined inchworm actuator. J Microelectromech Syst 13(1):63–74
Fleck N, Hutchinson J (2001) A reformulation of strain gradient plasticity. J Mech Phys Solids 49(10):2245–2271
Fleck N, Muller G, Ashby M, Hutchinson J (1994) Strain gradient plasticity: theory and experiment. Acta Metall Mater 42(2):475–487
Gao Y, Bando Y (2002) Nanotechnology: carbon nanothermometer containing gallium. Nature 415(6872):599
Godin M, Bryan AK, Burg TP, Babcock K, Manalis SR (2007) Measuring the mass, density, and size of particles and cells using a suspended microchannel resonator. Appl Phys Lett 91(12):123121
Hosseini M, Bahaadini R (2016) Size dependent stability analysis of cantilever micro-pipes conveying fluid based on modified strain gradient theory. Int J Eng Sci 101:1–13
Hu K, Wang Y, Dai H, Wang L, Qian Q (2016) Nonlinear and chaotic vibrations of cantilevered micropipes conveying fluid based on modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 105:93–107
Kazemi A, Vatankhah R, Farid M (2017) Nonlinear pull-in instability of microplates with piezoelectric layers using modified couple stress theory. Int J Mech Sci 130:90–98
Kong S, Zhou S, Nie Z, Wang K (2009) Static and dynamic analysis of micro beams based on strain gradient elasticity theory. Int J Eng Sci 47(4):487–498
Lam DC, Yang F, Chong A, Wang J, Tong P (2003) Experiments and theory in strain gradient elasticity. J Mech Phys Solids 51(8):1477–1508
Lassagne B, Garcia-Sanchez D, Aguasca A, Bachtold A (2008) Ultrasensitive mass sensing with a nanotube electromechanical resonator. Nano Lett 8(11):3735–3738
Lee I, Park K, Lee J (2012) Note: Precision viscosity measurement using suspended microchannel resonators. Rev Sci Instrum 83(11):116106
Miandoab EM, Pishkenari HN, Yousefi-Koma A (2015) Dynamic analysis of electrostatically actuated nanobeam based on strain gradient theory. Int J Struct Stab Dyn 15(04):1450059
Mindlin R, Tiersten H (1962) Effects of couple-stresses in linear elasticity. Arch Ration Mech Anal 11(1):415–448
Moser Y, Gijs MA (2007) Miniaturized flexible temperature sensor. J Microelectromech Syst 16(6):1349–1354
Paidoussis MP (1998) Fluid–structure interactions: slender structures and axial flow, vol 1. Academic Press, New York
Rao SS (2007) Vibration of continuous systems. Wiley, New York
Rinaldi S, Prabhakar S, Vengallatore S, Païdoussis MP (2010) Dynamics of microscale pipes containing internal fluid flow: damping, frequency shift, and stability. J Sound Vib 329(8):1081–1088
Vatankhah R, Kahrobaiyan MH (2016) Investigation of size-dependency in free-vibration of micro-resonators based on the strain gradient theory. Latin Am J Solids Struct 13(3):498–515
Wang L (2010) Size-dependent vibration characteristics of fluid-conveying microtubes. J Fluids Struct 26(4):675–684
Wang L, Liu H, Ni Q, Wu Y (2013) Flexural vibrations of microscale pipes conveying fluid by considering the size effects of micro-flow and micro-structure. Int J Eng Sci 71:92–101
Yan H, Zhang W-M, Jiang H-M, Hu K-M, Hong F-J, Peng Z-K, Meng G (2017) A measurement criterion for accurate mass detection using vibrating suspended microchannel resonators. J Sound Vib 403:1–20
Yang F, Chong A, Lam DC, Tong P (2002) Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int J Solids Struct 39(10):2731–2743
Yin L, Qian Q, Wang L (2011) Strain gradient beam model for dynamics of microscale pipes conveying fluid. Appl Math Model 35(6):2864–2873
Yun M, Lee I, Jeon S, Lee J (2014) Facile phase transition measurements for nanogram level liquid samples using suspended microchannel resonators. IEEE Sens J 14(3):781–785
Zhang W-M, Yan H, Jiang H-M, Hu K-M, Peng Z-K, Meng G (2016) Dynamics of suspended microchannel resonators conveying opposite internal fluid flow: stability, frequency shift and energy dissipation. J Sound Vib 368:103–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vakilzadeh, M., Vatankhah, R. & Eghtesad, M. Dynamics and vibration analysis of suspended microchannel resonators based on strain gradient theory. Microsyst Technol 24, 1995–2005 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3596-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3596-1