Abstract
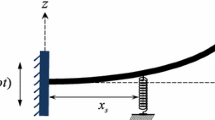
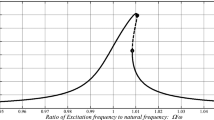
The size-dependent oscillations of a microcantilever with a tip (end) mass and a spring support undergoing a large-amplitude motion is analysed theoretically, taking into account curvature-related nonlinearities. Modelling small-size effects via use of the modified couple stress theory, the size-dependent potential and kinetic energies of the system are obtained. The continuous models for the motion behaviour of the microcantilever are developed via use of an energy method on the basis of Hamilton’s principle. Application of the centreline-inextensibility in oscillation course of the microcantilever results in a continuous model of the system with nonlinear inertial terms, which when coupled with curvature nonlinearities produces a highly nonlinear system. A weighted-residual method is then employed to truncate the continuous model, yielding the reduced-order model of the microcantilever motion with a generalised-coordinate-dependent mass matrix (due to inertial nonlinearities); a coupled continuation-time-integration method is then employed for the numerical simulations. The large-amplitude oscillation behaviour of the system is examined by constructing the frequency–responses and force-responses. The effect of the size of the end-mass on the nonlinear oscillation behaviour of the microcantilever is analysed. The importance of taking into account different nonlinearity sources is discussed. It is shown that the modified couple stress theory results in a stronger softening behaviour when compared to the classical continuum mechanics.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rahman EM, Younis MI, Nayfeh AH (2002) Characterization of the mechanical behavior of an electrically actuated microbeam. J Micromech Microeng 12:759–766
Aboelkassem Y, Nayfeh AH, Ghommem M (2010) Bio-mass sensor using an electrostatically actuated microcantilever in a vacuum microchannel. Microsyst Technol 16:1749–1755
Abouelregal AE, Zenkour AM (2015) Generalized thermoelastic vibration of a microbeam with an axial force. Microsyst Technol 21:1427–1435
Akgöz B, Civalek Ö (2013) A size-dependent shear deformation beam model based on the strain gradient elasticity theory. Int J Eng Sci 70:1–14
Ansari R, Faghih Shojaei M, Gholami R et al (2013) Thermal postbuckling behavior of size-dependent functionally graded Timoshenko microbeams. Int J Non-Linear Mech 50:127–135
Antonello R, Oboe R, Prandi L et al (2009) Automatic mode matching in MEMS vibrating gyroscopes using extremum-seeking control. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56:3880–3891
Baghani M (2012) Analytical study on size-dependent static pull-in voltage of microcantilevers using the modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 54:99–105
Chaterjee S, Pohit G (2009) A large deflection model for the pull-in analysis of electrostatically actuated microcantilever beams. J Sound Vib 322:969–986
Dai HL, Wang YK, Wang L (2015) Nonlinear dynamics of cantilevered microbeams based on modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 94:103–112
Dehrouyeh-Semnani AM (2014) A discussion on different non-classical constitutive models of microbeam. Int J Eng Sci 85:66–73
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2015a) Nonlinear dynamical behaviour of geometrically imperfect microplates based on modified couple stress theory. Int J Mech Sci 90:133–144
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2015b) Thermo-mechanical dynamics of perfect and imperfect Timoshenko microbeams. Int J Eng Sci 91:12–33
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2016) Nonlinear size-dependent dynamics of an imperfect shear deformable microplate. J Sound Vib 361:226–242
Fleck NA, Muller GM, Ashby MF et al (1994) Strain gradient plasticity: theory and experiment. Acta Metall Mater 42:475–487
Ghayesh MH, Amabili M (2013) Steady-state transverse response of an axially moving beam with time-dependent axial speed. Int J Non-Linear Mech 49:40–49
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H (2015) Nonlinear dynamics of microplates. Int J Eng Sci 86:60–73
Ghayesh MH, Kazemirad S, Reid T (2012) Nonlinear vibrations and stability of parametrically exited systems with cubic nonlinearities and internal boundary conditions: a general solution procedure. Appl Math Model 36:3299–3311
Ghayesh M, Farokhi H, Amabili M (2013a) Coupled nonlinear size-dependent behaviour of microbeams. Appl Phys A 112:329–338
Ghayesh MH, Amabili M, Farokhi H (2013b) Coupled global dynamics of an axially moving viscoelastic beam. Int J Non-Linear Mech 51:54–74
Gholipour A, Farokhi H, Ghayesh M (2014) In-plane and out-of-plane nonlinear size-dependent dynamics of microplates. Nonlinear Dyn 79:1771–1785
Joglekar MM, Pawaskar DN (2011) Estimation of oscillation period/switching time for electrostatically actuated microbeam type switches. Int J Mech Sci 53:116–125
Kahrobaiyan MH, Rahaeifard M, Tajalli SA et al (2012) A strain gradient functionally graded Euler–Bernoulli beam formulation. Int J Eng Sci 52:65–76
Karparvarfard SMH, Asghari M, Vatankhah R (2015) A geometrically nonlinear beam model based on the second strain gradient theory. Int J Eng Sci 91:63–75
Kong S, Zhou S, Nie Z et al (2008) The size-dependent natural frequency of Bernoulli–Euler micro-beams. Int J Eng Sci 46:427–437
Lam DCC, Yang F, Chong ACM et al (2003) Experiments and theory in strain gradient elasticity. J Mech Phys Solids 51:1477–1508
Li Y, Packirisamy M, Bhat RB (2008) Shape optimizations and static/dynamic characterizations of deformable microplate structures with multiple electrostatic actuators. Microsyst Technol 14:255–266
McFarland AW, Colton JS (2005) Role of material microstructure in plate stiffness with relevance to microcantilever sensors. J Micromech Microeng 15:1060
Mohammadabadi M, Daneshmehr AR, Homayounfard M (2015) Size-dependent thermal buckling analysis of micro composite laminated beams using modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 92:47–62
Nateghi A, Salamat-talab M (2013) Thermal effect on size dependent behavior of functionally graded microbeams based on modified couple stress theory. Compos Struct 96:97–110
Raeisifard H, Zamanian M, Nikkhah Bahrami M et al (2014) On the nonlinear primary resonances of a piezoelectric laminated micro system under electrostatic control voltage. J Sound Vib 333:5494–5510
Rahaeifard M, Kahrobaiyan MH, Asghari M et al (2011) Static pull-in analysis of microcantilevers based on the modified couple stress theory. Sens Actuators A 171:370–374
Rasekh M, Khadem SE (2013) Design and performance analysis of a nanogyroscope based on electrostatic actuation and capacitive sensing. J Sound Vib 332:6155–6168
Rembe C, Muller RS (2002) Measurement system for full three-dimensional motion characterization of MEMS. J Microelectromech Syst 11:479–488
Rezazadeh G, Fathalilou M, Shabani R (2009) Static and dynamic stabilities of a microbeam actuated by a piezoelectric voltage. Microsyst Technol 15:1785–1791
Rhoads JF, Kumar V, Shaw SW et al (2013) The non-linear dynamics of electromagnetically actuated microbeam resonators with purely parametric excitations. Int J Non-Linear Mech 55:79–89
Rokni H, Milani AS, Seethaler RJ (2015) Size-dependent vibration behavior of functionally graded CNT-Reinforced polymer microcantilevers: modeling and optimization. Eur J Mech A Solids 49:26–34
Shooshtari A, Hoseini SM, Mahmoodi SN et al (2012) Analytical solution for nonlinear free vibrations of viscoelastic microcantilevers covered with a piezoelectric layer. Smart Mater Struct 21:075015
Şimşek M, Reddy JN (2013) Bending and vibration of functionally graded microbeams using a new higher order beam theory and the modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 64:37–53
Tang M, Ni Q, Wang L et al (2014) Nonlinear modeling and size-dependent vibration analysis of curved microtubes conveying fluid based on modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 84:1–10
Tavakolian F, Farrokhabadi A, Mirzaei M (2015) Pull-in instability of double clamped microbeams under dispersion forces in the presence of thermal and residual stress effects using nonlocal elasticity theory. Microsyst Technol. doi:10.1007/s00542-015-2785-z
Wang L, Xu YY, Ni Q (2013) Size-dependent vibration analysis of three-dimensional cylindrical microbeams based on modified couple stress theory: a unified treatment. Int J Eng Sci 68:1–10
Yang F, Chong ACM, Lam DCC et al (2002) Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int J Solids Struct 39:2731–2743
Zhang WM, Meng G (2007) Nonlinear dynamic analysis of electrostatically actuated resonant MEMS sensors under parametric excitation. IEEE Sens J 7:370–380
Zheng Q, Dong L, Lee DH et al (2009) Active disturbance rejection control for MEMS gyroscopes. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 17:1432–1438
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghayesh, M.H., Farokhi, H. Size-dependent large-amplitude oscillations of microcantilevers. Microsyst Technol 23, 3477–3488 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3203-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3203-x