Abstract
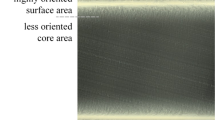
In micro- and thin-wall injection moulding the process conditions affect the developed internal structures and thus the resulting part properties, e.g., wear behaviour. In this paper a dynamic mould tempering was used to affect the local morphology development and the resulting wear. Investigations with a pin on disc measurement on semi crystalline polymers reveal a distinct layer-dependent tribological behaviour of the injection moulded micro parts. Increased mould temperatures during injection moulding favour the morphological structure and the resulting part properties.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelov AK, Coulter JP (2004) Micromolding product manufacture: a progress report. SPE Proceedings ANTEC, Chicago, pp 748–751
Bibber DM (2004) Micro molding challenges. SPE Proceedings ANTEC, Chicago, pp 3703–3711
Dallner CM, Kobes MO, Feulner R, Schmachtenberg E (2007) Proceedings PPS23, Salvador, Brazil
Drummer D, Gruber K, Meister S (2011) Alternating temperature technology controls parts properties. Kunststoffe Int 101:25–27
Drummer D, Kobes MO, Merken D (2012) SPE Proceedings ANTEC, Orlando, pp. 2226–2232
Drummer D, Seefried A, Meister S (2014) Characterization of material stiffness on injection moulded microspecimens using different test methods. Adv Mat Sci Eng 2014:8. doi:10.1155/2014/769206
Drummer D, Meister S, Wildner W (2016) Affecting processing and properties of injection moulded thin-wall parts using dynamic tempered Rapid Tooling moulds. J Plastics Technol 12:1–30
Ehrenstein GW, Riedel G, Trawiel P (2004) Thermal analysis of plastics: theory and practice. Hanser, München
Fischer C, Leisen C, Merken D, Jungmeier A, Drummer D (2014) The influence of processing temperature on morphological and tribological properties of injection-moulded microparts. Adv Eng Mat 6:218761. doi:10.1155/2014/218761
Giessauf J, Pillwein G, Steinbichler G (2008) Variotherm temperature control is fit for production. Kunststoffe Int 98:57–62
Haberstroh E, Brandt M (2002) Determination of mechanical properties of thermoplastics suitable for micro systems. Macromol Mat Eng 287:881–888. doi:10.1002/mame.200290023
Jungmeier A (2010) Struktur und Eigenschaften spritzgegossener, thermoplastischer Mikroformteile: Struktur-Eigenschaftsbeziehungen und Verarbeitung, Dissertation, University Erlangen-Nuernberg
Kohan MI (1995) Nylon plastics handbook. Hanser Gardner Publications, Munich
Künkel R, Ehrenstein GW (2005) SPE Proceedings ANTEC, Boston, pp. 1837–1841
Lurz A, Kühnert I, Schmachtenberg E (2008) Influences on the properties of small and thin-walled in-jection molded parts—Part 2: importance of the thermal conductivity of the mold material. J Plast Technol 4:1–18
Meister S, Drummer D (2013a) Affecting the ageing behaviour of injection moulded micro parts using variothermal mould tempering. Adv Mechan Eng 2013:7. doi:10.1155/2013/407964
Meister S, Drummer D (2013b) Influence of manufacturing conditions on measurement of mechanical material properties on thermoplastic micro tensile bars. Polym Test 32:432–437. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.12.006
Meister S, Jungmeier A, Drummer D (2012) Long term properties of injection moulded micro-parts: influence of part dimensions and cooling conditions on ageing behaviour. Maromol Mat Eng 297:994–1004. doi:10.1002/mame.201100379
Nguyen-Chung T, Loeser C, Juettner G, Obadal M, Pham T, Gehde M (2011) Morphology analysis of injection molded micro parts. J Plast Technol 7:86–114
Pantani R, Balzano L, Peters GWM (2012) Flow-induced morphology of iPP solidified in a shear device. Macromol Mat Eng 297:60–67. doi:10.1002/mame.201100158
Pfirrmann O, Astor M (2006) Trendreport Mikrosystemtechnik. Prognos AG, Basel
Schmiederer D, Schmachtenberg E (2006) Einflüsse auf die Eigenschaften kleiner und dünnwandiger Spritzgussteile. J Polym Technol 2:1–21
Tom AM, Layser GS, Coulter JP (2006) SPE Proceedings ANTEC, Charlotte (USA), pp. 2541–2545
Walter T, Schinkoethe W, Ehrfeld W, Schaumburg C, Weber L (1999) Injection moulding of microstructures with inductive mould heating. 16. Stuttgarter Kunststoff-Kolloquium, Stuttgart: 1–10
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the German Research Foundation (DFG) for funding the work in DR421/16-1. We also extend our gratitude to our industrial partners Hofmann Innovation Group, Single GmbH, Ticona GmbH and BASF SE for providing equipment and material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meister, S., Hertle, S. & Drummer, D. Layer-dependent characterization of wear behaviour on variothermal injection moulded micro parts using pin on disc measurements. Microsyst Technol 23, 2807–2814 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3051-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3051-8