Abstract
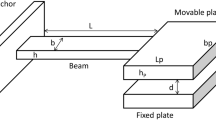
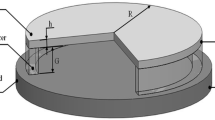
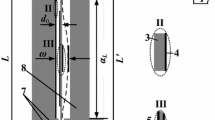
Dynamic performance is one of the most critical factors in many MEMS products, such as micro accelerometers, vibratory gyroscopes, micro deformable mirror, etc. Essentially, the dynamic behavior is totally determined by two factors: the internal factor, the stiffness of structure and the external factor, the damping of environment. In this paper both factors are analyzed accurately and a theoretical dynamic model of parallel-plate actuators is presented. The stiffness of the structure, i.e. the spring constant k of the suspension beam that supports the moving plate of the actuator, is achieved by many accurate experimental tests. The damping of environment, referring to the squeeze film damping coefficient c in parallel-plate actuators, is analyzed by calculation and FEA simulation. Further, we consider c a linear function of the actuator displacement, but not a constant value. This treatment greatly improves the accuracy of the dynamic model and could be applied in parallel-plate actuators with large displacement. Dynamic behaviors of the actuators under squeeze film damping, such as natural frequency, response time and bandwidth, are predicted based on the model. Three kinds of parallel-plate actuators are designed and fabricated using a surface micromachining process to verify the estimation of the presented theoretical model and experimental test results have showed good consistency with the theoretical analysis. The dynamic model proposed in this paper could be broadly applied in the MEMS/NEMS systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews M, Harris I, Turner G (1993) A comparison of squeeze-film theory with measurements on a microstructure. Sens Actuators A-Phys 36:79–87. doi:10.1016/0924-4247(93)80144-6
Bao M, Yang H (2007) Squeeze film air damping in MEMS. Sens Actuators A-Phys 136:3–27. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2007.01.008
Bao M, Yang H, Sun Y, French PJ (2003) Modified Reynolds’ equation and analytical analysis of squeeze-film air damping of perforated structures. J Micromech Microeng 13:780–795. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/13/6/301
Blech JJ (1983) On isothermal squeeze films. J Lubr Technol 105:615–620. doi:10.1115/1.3254692
Cowen A, Hardy B, Mahadevan R, Wilcenski S (2011) PolyMUMPs design handbook, revision 13.0
Feng C, Zhao Y-P, Liu DQ (2007) Squeeze-film effects in MEMS devices with perforated plates for small amplitude vibration. Microsyst Technol 13:625–633. doi:10.1007/s00542-006-0285-x
Gere JM, Timoshenko SP (1997) Mechanics of materials, 4th edn. PWS Publishing Company, Boston
Griffin WS, Richardson HH, Yamanami S (1966) A study of fluid squeeze-film damping. J Basic Eng-T ASME 88:451–456. doi:10.1115/1.3645878
Grigg D, Felkel E, Roth J, Lega XCd, Deck L, Groot Pd (2004) Static and dynamic characterization of MEMS and MOEMS devices using optical interference microscopy. In: MEMS, MOEMS, and micromachining, Strasbourg. Proc. SPIE, vol 5455. SPIE, pp 429–435. doi:10.1117/12.546211
Helmbrecht MA, Juneau T, Hart M, Doble N (2006) Performance of a high-stroke, segmented MEMS deformable-mirror technology. In: Olivier SS, Tadigadapa SA, Henning AK (eds) MEMS/MOEMS components and their applications III, 2006. Proc. SPIE, vol 6113. SPIE, p 61130L. doi:10.1117/12.647884
IntelliSense (2007) IntelliSuite® user guide. IntelliSense. http://www.intellisense.com.cn. Accessed 29 Sept 2015
Kim E-S, Cho Y-H, Kim M-U (1999) Effect of holes and edges on the squeeze film damping of perforated micromechanical structures. In: The 12th IEEE international conference on micro electro mechanical systems. IEEE, pp 296–301. doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.1999.746841
Langlois WE (1962) Isothermal squeeze films. Q Appl Math XX:131–150
Li M, Tang HX, Roukes ML (2007) Ultra-sensitive NEMS-based cantilevers for sensing, scanned probe and very high-frequency applications. Nat Nanotechnol 2:114–120. doi:10.1038/nnano.2006.208
Miller MH, Perrault JA, Parker GG, Bettig BP, Bifano TG (2006) Simple models for piston-type micromirror behavior. J Micromech Microeng 16:303–313. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/16/2/015
Pasquale GD, Veijola T, Somà A (2010) Modelling and validation of air damping in perforated gold and silicon MEMS plates. J Micromech Microeng 20:015010. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/20/1/015010
Perreault JA, Bifano TG, Levine BM, Horenstein MN (2002) Adaptive optic correction using microelectromechanical deformable mirrors. Opt Eng 41:561–566. doi:10.1117/1.1447230
Rahman HU, Babaei J, Ramer R (2008) RF MEMS switches-design and performance in wireless applications. In: Tan HH, Chiao J-C, Faraone L, Jagadish C, Williams J, Wilson AR (eds) Device and process technologies for microelectronics, MEMS, photonics, and nanotechnology IV, vol 6800. SPIE, p 680027. doi:10.1117/12.769359
Rebeiz GM, Muldavin JB (2001) RF MEMS switches and switch circuits. IEEE Microw Mag 2:59–71. doi:10.1109/6668.969936
Sato K, Shikida M (1994) An electrostatically actuated gas valve with an S-shaped film element. J Micromech Microeng 4:205–209. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/4/4/005
Sharipov F (1999) Rarefied gas flow through a long rectangular channel. J Vac Sci Technol, A 17:3062–3066. doi:10.1116/1.582006
Urey H, Kan C, Davis WO (2005) Vibration mode frequency formulae for micromechanical scanners. J Micromech Microeng 15:1713–1721. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/9/013
Yagubizade H, Fathalilou M, Rezazadeh G, Talebian S (2009) Squeeze-film damping effect on dynamic pull-in voltage of an electrostatically-actuated microbeam. Sens Transducers J 103:96–101
Yan D, Lal A (2006) The squeeze film damping effect of perforated microscanners: modeling and characterization. Smart Mater Struct 15:480–484. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/15/2/030
Yang Y-J, Gretillat M-A, Senturia SD (1997) Effect of air damping on the dynamics of nonuniform deformations of microstructures. In: 1997 international conference on solid-state sensors and actuators, Chicago. IEEE, pp 1093–1096. doi:10.1109/SENSOR.1997.635390
Zhang XM, Chau FS, Quan C, Lam YL, Liu AQ (2001) A study of the static characteristics of a torsional micromirror. Sens Actuators A-Phys 90:73–81. doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(01)00453-8
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11403029) and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (Grant No. 2014346). Z. X. Chen’s research is supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61071027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
W. Wang and F. Tao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Tao, F., Wang, Q. et al. Dynamic behavior of perforated parallel-plate actuator under squeeze film damping effect. Microsyst Technol 23, 411–419 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2687-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2687-0