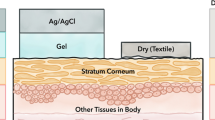
Abstract
In this study we proposed a device composed of dry electrode and dry adhesive medical patch for biopotentials measurement. The behavior of the dry adhesive with mushroom-shaped micropillars is characterized through normal and friction force test. The adhesion strength (~1.2 N/cm2) is comparable to acrylic medical patch, and the repeating cycle testing result demonstrates that the adhesion strength of dry adhesive medical patch is larger than that of acrylic medical patch. Moreover, the dry adhesive medical patch does not cause skin to turn allergic owning to its biocompatibility. The proposed device also is used to record electrocardiogram (ECG) with dry electrode. Compared with conventional wet electrode, the signal quality is outstanding. The QRS-complex and T-wave of ECG are clearly legible.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad J, Zafar F (2012) Review of body area network technology and wireless medical monitoring. Int J Inf 2(2):186–188
Autumn K, Liang YA, Hsieh ST, Zesch W, Chan WP, Kenny TW, Fearing R, Full RJ (2000) Adhesive force of a single gecko foot-hair. Nature 405(6787):681–685
Bae WG, Kim D, Kwak MK, Ha L, Kang SM, Suh KY (2013) Enhanced skin adhesive patch with modulus-tunable composite micropillars. Adv Healthc Mater 2(1):109–113
Barthel E (2008) Adhesive elastic contacts: JKR and more. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(16):163001–163020
Boesel LF, Greiner C, Arzt E, del Campo A (2010) Gecko-inspired surfaces: a path to strong and reversible dry adhesives. Adv Mater 22(19):2125–2137
Chi YM, Jung TP, Cauwenberghs G (2010) Dry-contact and noncontact biopotential electrodes: methodological review. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 3:106–119
Custodio V, Herrera FJ, Lopez G, Moreno JI (2012) A review on architectures and communications technologies for wearable health-monitoring systems. Sensors 12(10):13907–13946
del Campo A, Alvarez I, Filipe S, Wilhelm M (2007a) 3D microstructured surfaces obtained by soft-lithography using fast-crosslinking elastomeric precursors and 2D masters. Adv Funct Mater 17(17):3590–3597
del Campo A, Greiner C, Alvarez I, Arzt E (2007b) Patterned surfaces with pillars with controlled 3D tip geometry mimicking bioattachment devices. Adv Mater 19(15):1973–1977
Gao H, Yao H (2004) Shape insensitive optimal adhesion of nanoscale fibrillar structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(21):7851–7856
Greiner C, del Campo A, Arzt E (2007) Adhesion of bioinspired micropatterned surfaces: effects of pillar radius, aspect ratio, and preload. Langmuir 23(7):3495–3502
Jiao Y, Gorb S, Scherge M (2000) Adhesion measured on the attachment pads of Tettigonia viridissima (Orthoptera, Insecta). J Exp Biol 203(12):1887–1895
Johnson K, Kendall K, Roberts A (1971) Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids. Proc Royal Soc Lond Math Phys Sci 324(1558):301–313
Kadin Y, Kligerman Y, Etsion I (2008) Loading-unloading of an elastic-plastic adhesive spherical microcontact. J Colloid Interface Sci 321(1):242–250
Kang SM, Kim SM, Kim HN, Kwak MK, Tahk DH, Suh KY (2012) Robust superomniphobic surfaces with mushroom-like micropillar arrays. Soft Matter 8(33):8563–8568
Karp JM, Langer R (2011) Dry solution to a sticky problem. Nature 477(7362):42–43
Kim S, Sitti M, Hui CY, Long R, Jagota A (2007) Effect of backing layer thickness on adhesion of single-level elastomer fiber arrays. Appl Phys Lett 91(16):161903–161905
Kwak MK, Jeong HE, Suh KY (2011) Rational design and enhanced biocompatibility of a dry adhesive medical skin patch. Adv Mater 23(34):3949–3953
Kwak MK, Pang C, Jeong HE, Kim HN, Yoon H, Jung HS, Suh KY (2012) Towards the next level of bioinspired dry adhesives: new designs and applications. Adv Funct Mater 21(19):3606–3616
Lin CT, Liao LD, Liu YH, Wang IJ, Lin BS, Chang JY (2011) Novel dry polymer foam electrodes for long-term EEG measurement. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(5):1200–1207
Moon JH, Baek DH, Choi YY, Lee KH, Kim HC, Lee SH (2010) Wearable polyimide-PDMS electrodes for intrabody communication. J Micromech Microeng 20(2):025032
Sameoto D, Menon C (2009) A low-cost, high-yield fabrication method for producing optimized biomimetic dry adhesives. J Micromec Microeng 19(11):115002
Schargott M, Popov V, Gorb S (2006) Spring model of biological attachment pads. J Theor Biol 243(1):48–53
Searle A, Kirkup L (2000) A direct comparison of wet, dry and insulating bioelectric recording electrodes. Physiol Meas 21(2):271–283
Acknowledgments
The authors thank to financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51035005, 61176104), 973 Program (2013CB329401),Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (No. 11JC1405700), WUXI-SJTU project (2011JDZX017), Minhang District Project (2011MH084). The authors are also grateful to the colleagues for their essential contribution to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LF., Liu, JQ., Yang, B. et al. Fabrication and characterization of a dry electrode integrated Gecko-inspired dry adhesive medical patch for long-term ECG measurement. Microsyst Technol 21, 1093–1100 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2279-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2279-4